Glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating)
| Glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | GLDC ; GCE; GCSP; HYGN1 | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 238300 MGI: 1341155 HomoloGene: 141 GeneCards: GLDC Gene | ||||||||||||
| EC number | 1.4.4.2 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
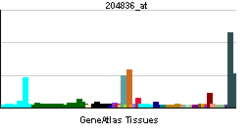 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 2731 | 104174 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000178445 | ENSMUSG00000024827 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | P23378 | Q91W43 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_000170 | NM_138595 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_000161 | NP_613061 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 9: 6.53 – 6.65 Mb | Chr 19: 30.1 – 30.18 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
| glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.4.4.2 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 37259-67-9 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Glycine dehydrogenase [decarboxylating], mitochondrial also known as glycine cleavage system P protein or glycine decarboxylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GLDC gene.[1][2][3]
Reaction
Glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (EC 1.4.4.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
- glycine + H-protein-lipoyllysine
 H-protein-S-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO2
H-protein-S-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO2
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are glycine and H-protein-lipoyllysine, whereas its two products are H-protein-S-aminomethyldihydrolipoyllysine and CO2.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-NH2 group of donors with a disulfide as acceptor. This enzyme participates in glycine, serine and threonine metabolism. It employs one cofactor, pyridoxal phosphate.
Function
Glycine decarboxylase is a P-protein of the glycine cleavage system in eukaryotes. The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine. The P protein binds the alpha-amino group of glycine through its pyridoxal phosphate cofactor. Carbon dioxide is released and the remaining methylamine moiety is then transferred to the lipoamide cofactor of the H protein.
Degradation of glycine is brought about by the glycine cleavage system, which is composed of four mitochondrial protein components: P protein (a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent glycine decarboxylase), H protein (a lipoic acid-containing protein), T protein (a tetrahydrofolate-requiring enzyme), and L protein (a lipoamide dehydrogenase).[3]
Clinical significance
Glycine encephalopathy may be due to a defect in any one of these enzymes.[3]
References
- ↑ Kume A, Koyata H, Sakakibara T, Ishiguro Y, Kure S, Hiraga K (Mar 1991). "The glycine cleavage system. Molecular cloning of the chicken and human glycine decarboxylase cDNAs and some characteristics involved in the deduced protein structures". J Biol Chem 266 (5): 3323–9. PMID 1993704.
- ↑ Kure S, Narisawa K, Tada K (Mar 1991). "Structural and expression analyses of normal and mutant mRNA encoding glycine decarboxylase: three-base deletion in mRNA causes nonketotic hyperglycinemia". Biochem Biophys Res Commun 174 (3): 1176–82. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(91)91545-N. PMID 1996985.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Entrez Gene: GLDC glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating)".
Further reading
- Hiraga K, Kikuchi G (1980). "The mitochondrial glycine cleavage system. Functional association of glycine decarboxylase and aminomethyl carrier protein". J. Biol. Chem. 255 (24): 11671–6. PMID 7440563.
- Perham RN (2000). "Swinging arms and swinging domains in multifunctional enzymes: catalytic machines for multistep reactions". Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69: 961–1004. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.961. PMID 10966480.
- Broadwater JA, Haas JA, Fox BG, Booker SJ (2005). "Expression, purification, and physical characterization of Escherichia coli lipoyl(octanoyl)transferase". Protein. Expr. Purif. 39 (2): 269–82. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2004.10.021. PMID 15642479.*Applegarth DA, Toone JR (2001). "Nonketotic hyperglycinemia (glycine encephalopathy): laboratory diagnosis". Mol. Genet. Metab. 74 (1–2): 139–46. doi:10.1006/mgme.2001.3224. PMID 11592811.
- Kure S, Takayanagi M, Narisawa K et al. (1992). "Identification of a common mutation in Finnish patients with nonketotic hyperglycinemia". J. Clin. Invest. 90 (1): 160–4. doi:10.1172/JCI115831. PMC 443076. PMID 1634607.
- Sakakibara T, Koyata H, Ishiguro Y et al. (1991). "One of the two genomic copies of the glycine decarboxylase cDNA has been deleted at a 5' region in a patient with nonketotic hyperglycinemia". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 173 (3): 801–6. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(05)80858-7. PMID 2268343.
- Burton BK, Pettenati MJ, Block SM et al. (1989). "Nonketotic hyperglycinemia in a patient with the 9p- syndrome". Am. J. Med. Genet. 32 (4): 504–5. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320320416. PMID 2773994.
- Hayasaka K, Kochi H, Hiraga K, Kikuchi G (1981). "Purification and properties of glycine decarboxylase, a component of the glycine cleavage system, from rat liver mitochondria and immunochemical comparison of this enzyme from various sources". J. Biochem. 88 (4): 1193–9. PMID 6778858.
- Hiraga K, Kochi H, Hayasaka K et al. (1981). "Defective glycine cleavage system in nonketotic hyperglycinemia. Occurrence of a less active glycine decarboxylase and an abnormal aminomethyl carrier protein". J. Clin. Invest. 68 (2): 525–34. doi:10.1172/JCI110284. PMC 370827. PMID 6790577.
- Takayanagi M, Kure S, Sakata Y et al. (2000). "Human glycine decarboxylase gene (GLDC) and its highly conserved processed pseudogene (psiGLDC): their structure and expression, and the identification of a large deletion in a family with nonketotic hyperglycinemia". Hum. Genet. 106 (3): 298–305. doi:10.1007/s004390051041. PMID 10798358.
- Toone JR, Applegarth DA, Coulter-Mackie MB, James ER (2000). "Biochemical and molecular investigations of patients with nonketotic hyperglycinemia". Mol. Genet. Metab. 70 (2): 116–21. doi:10.1006/mgme.2000.3000. PMID 10873393.
- Toone JR, Applegarth DA, Coulter-Mackie MB, James ER (2001). "Recurrent mutations in P- and T-proteins of the glycine cleavage complex and a novel T-protein mutation (N145I): a strategy for the molecular investigation of patients with nonketotic hyperglycinemia (NKH)". Mol. Genet. Metab. 72 (4): 322–5. doi:10.1006/mgme.2001.3158. PMID 11286506.
- Kure S, Kojima K, Ichinohe A et al. (2002). "Heterozygous GLDC and GCSH gene mutations in transient neonatal hyperglycinemia". Ann. Neurol. 52 (5): 643–6. doi:10.1002/ana.10367. PMID 12402263.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Toone JR, Applegarth DA, Laliberte G (2003). "Gene Symbol: GLDC. Disease: NKH glycine encephalopathy". Hum. Genet. 113 (5): 465. doi:10.1007/s00439-003-1014-5. PMID 14552331.
- Dinopoulos A, Kure S, Chuck G et al. (2006). "Glycine decarboxylase mutations: a distinctive phenotype of nonketotic hyperglycinemia in adults". Neurology 64 (7): 1255–7. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000156800.23776.40. PMID 15824356.
- Flusser H, Korman SH, Sato K et al. (2006). "Mild glycine encephalopathy (NKH) in a large kindred due to a silent exonic GLDC splice mutation". Neurology 64 (8): 1426–30. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000158475.12907.D6. PMID 15851735.
- Boneh A, Korman SH, Sato K et al. (2005). "A single nucleotide substitution that abolishes the initiator methionine codon of the GLDC gene is prevalent among patients with glycine encephalopathy in Jerusalem". J. Hum. Genet. 50 (5): 230–4. doi:10.1007/s10038-005-0243-y. PMID 15864413.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Korman SH, Wexler ID, Gutman A et al. (2006). "Treatment from birth of nonketotic hyperglycinemia due to a novel GLDC mutation". Ann. Neurol. 59 (2): 411–5. doi:10.1002/ana.20759. PMID 16404748.