Glufosinate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
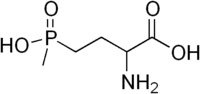
| IUPAC name
(RS)-2-Amino-4-(hydroxy(methyl)phosphonoyl)butanoic acid | |
| Other names
Phosphinothricin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 51276-47-2 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:52136 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL450298 |
| ChemSpider | 4630 |
| EC number | 257-102-5 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| KEGG | C05042 |
| PubChem | 4794 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C5H12NO4P |
| Molar mass | 181.13 g·mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Glufosinate or its ammonium salt DL-phosphinothricin is an active ingredient in several nonselective herbicides such as Basta, Rely, Finale, Ignite, Challenge, and Liberty. It interferes with the biosynthetic pathway of the amino acid glutamine and with ammonia detoxification. It has been used in pre-harvest crop desiccation.[1]
Some plants have been genetically modified for resistance to glufosinate. The gene which gives resistance to glufosinate is a bar or pat gene which was first isolated from two species of Streptomyces bacteria. There are glufosinate-resistant transgenic varieties of several crops, including cotton, canola, corn, soybean, sugarbeet, and rice. Of these, canola, cotton, soybean and maize are currently on the market. This includes Bayer's LibertyLink genes, used in over 100 hybrids.
Glufosinate was found to be toxic to reproduction[2] and was included in a biocide ban proposed by the Swedish Chemicals Agency[3] and approved by the European Parliament on January 13, 2009.[4]
Liberty Link crops
In response to Monsanto's hugely successful Roundup Ready crops, Bayer Crop Science released its own herbicide tolerant crops. The range of crops tolerant to the herbicide glufosinate include cotton, soybean, canola and corn. These crops are also known as Liberty Link crops.
One advantage to producing Liberty Link crops is that any glyphosate resistance encountered in problematic weeds, such as rye grass, is overcome due to glufosinate having a completely different mode of action.
Mode of action
Phosphinothricin is an glutamine synthetase inhibitor that binds to the glutamate site. Glufosinate-treated plants die due to a buildup of ammonia and corresponding decrease in pH in the thylakoid lumen, leading to the uncoupling of photophosphorylation. The uncoupling of photophosphorylation causes the production of reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation, and membrane destruction.[5]
References
- ↑ "The agronomic benefits of glyphosate in Europe" (PDF). Monsanto Europe SA. February 2010. Retrieved 06/02/2013. Check date values in:
|accessdate=(help) - ↑ "Neue rechtliche Regelungen für Pflanzenschutzmittel auf EU-Ebene" (PDF). Bundesministerium für Ernährung, Landwirtschaft und Verbraucherschutz (BMELV). January 2000. Retrieved 2013-03-22.
- ↑ "Interpretation of criteria for approval of active substances in the proposed EU plant protection regulation" (PDF). Swedish Chemicals Agency (KemI). 2008-09-23. Retrieved 2013-03-20.
- ↑ "MEPs approve pesticides legislation". 2009-01-13. Retrieved 2013-02-22.
- ↑ Summary of Herbicide Mechanism of Action, HRAC and WSSA
External links
- Bayer's site of LibertyLink crops
- Basta technical guide
- Glufosinate in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
- Glufosinate-ammonium in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
- Glufosinate-P in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||