Gibberellic acid
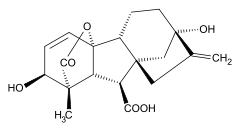 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3S,3aS,4S,4aS,7S,9aR,9bR,12S)-7,12-dihydroxy-3-methyl-6-methylene-2-oxoperhydro-4a,7-methano-9b,3-propenoazuleno[1,2-b]furan-4-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 77-06-5 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28833 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL566653 |
| ChemSpider | 7995349 |
| EC number | 201-001-0 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| KEGG | C01699 |
| PubChem | 522636 |
| |
| UNII | BU0A7MWB6L |
| Properties | |
| C19H22O6 | |
| Molar mass | 346.37 g/mol |
| Melting point | 233 to 235 °C (451 to 455 °F; 506 to 508 K) (decomposition) |
| 5 g/l (20 °C) | |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification | Irritant (Xi) |
| R-phrases | R36 |
| S-phrases | R26, S36 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Gibberellic acid (also called Gibberellin A3, GA, and GA3) is a hormone found in plants and fungi. Its chemical formula is C19H22O6. When purified, it is a white to pale-yellow solid.
However, plants produce low amount of GA3, therefore this hormone can be produced industrially by microorganisms. Nowadays, it is produced by submerse fermentation, but this process presented low yield with high production costs and hence higher sale value. One alternative process to reduce costs of the GA3 production is Solid-State Fermentation (SSF) that allows the use of agro-industrial residues.[1]
Gibberellic acid is a simple gibberellin, a pentacyclic diterpene acid promoting growth and elongation of cells. It affects decomposition of plants and helps plants grow if used in small amounts, but eventually plants develop tolerance to it. GA stimulates the cells of germinating seeds to produce mRNA molecules that code for hydrolytic enzymes. Gibberellic acid is a very potent hormone whose natural occurrence in plants controls their development. Since GA regulates growth, applications of very low concentrations can have a profound effect while too much will have the opposite effect.[2] It is usually used in concentrations between 0.01 and 10 mg/L.
GA was first identified in Japan in 1935, as a metabolic byproduct of the plant pathogen Gibberella fujikuroi (thus the name), which afflicts rice plants; fujikuroi-infected plants develop bakanae ("foolish seedling"), which causes them to grow so much taller than normal that they die from no longer being sturdy enough to support their own weight.
Gibberellins have a number of effects on plant development. They can stimulate rapid stem and root growth, induce mitotic division in the leaves of some plants, and increase seed germination rate.
Gibberellic acid is sometimes used in laboratory and greenhouse settings to trigger germination in seeds that would otherwise remain dormant.[2] It is also widely used in the grape-growing industry as a hormone to induce the production of larger bundles and bigger grapes, especially Thompson seedless grapes. In the Okanagan and Creston valleys, it is also used as a growth replicator in the cherry industry. It is used on Clementine Mandarin oranges, which may otherwise cross-pollinate with other citrus and grow undesirable seeds. Applied directly on the blossoms as a spray, it allows for Clementines to produce a full crop of fruit without seeds.
See also
References
- ↑ Silva ALL, Rodrigues C, Costa JL, Machado MP, Penha RO, Biasi LA, Vandenberghe, LPS, Soccol, CR. (2013). "Gibberellic acid fermented extract obtained by solid-state fermentation using citric pulp by Fusarium moniliforme: Influence on Lavandula angustifolia Mill. cultivated in vitro" (PDF). Pakistan Journal of Botany 45 (6): 2057-2064. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Riley, John M. "Gibberellic Acid for Fruit Set and Seed Germination". Retrieved 26 Oct 2012.