Germany
| Federal Republic of Germany Bundesrepublik Deutschland
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: Deutschlandlied[1] (English: "Song of Germany")[lower-alpha 1] |
||||||
![Location of Germany (dark green)– in Europe (green & dark grey)– in the European Union (green) – [Legend]](../I/m/EU-Germany.svg.png) Location of Germany (dark green) – in Europe (green & dark grey) |
||||||
| Capital and largest city | Berlin 52°31′N 13°23′E / 52.517°N 13.383°E | |||||
| Official languages | German[lower-alpha 2] | |||||
| Demonym | German | |||||
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional republic | |||||
| - | President | Joachim Gauck | ||||
| - | President/Bundestag | Norbert Lammert | ||||
| - | Chancellor | Angela Merkel | ||||
| - | President/Bundesrat | Volker Bouffier | ||||
| Legislature | ||||||
| - | Upper house | Bundesrat | ||||
| - | Lower house | Bundestag | ||||
| Formation | ||||||
| - | Holy Roman Empire | 2 February 962 | ||||
| - | German Confederation | 8 June 1815 | ||||
| - | German Empire | 18 January 1871 | ||||
| - | Federal Republic | 23 May 1949 | ||||
| - | EEC Foundation[lower-alpha 3] | 1 January 1958 | ||||
| - | Reunification | 3 October 1990 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 357,168 km2 (63rd) 137,847 sq mi |
||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2014 estimate | 80,716,000[2] (16th) | ||||
| - | Density | 226/km2 (58th) 583/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2015 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $3.815 trillion[3] (5th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $46,896[3] (20th) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2015 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $3.413 trillion[3] (4th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $41,955[3] (20th) | ||||
| Gini (2011) | 29.0[4] low |
|||||
| HDI (2013) | very high · 6th |
|||||
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) | |||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Calling code | 49 | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | DE | |||||
| Internet TLD | .de and .eu | |||||
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (German: Bundesrepublik Deutschland, pronounced [ˈbʊndəsʁepuˌbliːk ˈdɔʏtʃlant]),[6] is a federal parliamentary republic in western-central Europe. It consists of 16 constituent states, which retain some sovereignty, and covers an area of 357,021 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi) with a largely temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Berlin. With 80.7 million inhabitants, Germany is the most populous member state in the European Union. After the United States, it is the second most popular migration destination in the world.[7]
Various Germanic tribes have occupied what is now northern Germany and southern Scandinavia since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented by the Romans before AD 100. During the Migration Period that coincided with the decline of the Roman Empire, the Germanic tribes expanded southward and established kingdoms throughout much of Europe. Beginning in the 10th century, German territories formed a central part of the Holy Roman Empire.[8] During the 16th century, northern German regions became the centre of the Protestant Reformation. The rise of Pan-Germanism inside the German Confederation, which had been occupied by France during the Napoleonic Wars, resulted in the unification of most of the German states in 1871 into the Prussian-dominated German Empire.
After World War I and the German Revolution of 1918–1919, the Empire was replaced by the parliamentary Weimar Republic. The establishment of the Third Reich in 1933 eventually led to World War II and the Holocaust. In 1945 the regime surrendered to the Allied Powers. Germany lost some of its territory and was divided by the victors into Allied occupation zones, and evolved into two states, East Germany and West Germany. On 3 October 1990, the country was reunified, regaining full sovereignty about six months later.
Germany is a great power and has the world's fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial and technological sectors, it is both the world's third-largest exporter and third-largest importer of goods. It is a developed country with a very high standard of living maintaining a comprehensive social security that includes the world's oldest universal health care system. Known for its rich cultural history Germany has been the home of many influential philosophers, artists, musicians, entrepreneurs, scientists and inventors. Germany was a founding member of the European Communities in 1957, which became the European Union in 1993. It is part of the Schengen Area, and has been a member of the Eurozone since 1999. Germany is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the G8, the G20, and the OECD.
Etymology
The English word Germany derives from the Latin Germania, which came into use after Julius Caesar adopted it for the peoples east of the Rhine.[9] The German term Deutschland (originally diutisciu land, "the German lands") is derived from deutsch, descended from Old High German diutisc "popular" (i.e. belonging to the diot or diota "people"), originally used to distinguish the language of the common people from Latin and its Romance descendants. This in turn descends from Proto-Germanic *þiudiskaz "popular" (see also the Latinised form Theodiscus), derived from *þeudō, descended from Proto-Indo-European *tewtéh₂- "people".[10]
History

The discovery of the Mauer 1 mandible in 1907 shows that ancient humans were present in Germany at least 600,000 years ago.[11] The oldest complete hunting weapons found anywhere in the world were discovered in a coal mine in Schöningen in 1995 where three 380,000 year old wooden javelins 6–7.5 feet long were unearthed.[12] The Neander Valley (German "Neanderthal") was the location where the first ever non-modern human fossil was discovered and recognised in 1856, the new species of human was named Neanderthal man. The Neanderthal 1 fossils are now known to be 40,000 years old. Evidence of modern humans, similarly dated, has been found in caves in the Swabian Jura near Ulm. The finds include 42,000 year old bird bone and mammoth ivory flutes which are the oldest musical instruments ever found,[13] the 40,000 year old Ice Age Lion Man which is the oldest uncontested figurative art ever discovered,[14] and the 35,000 year old Venus of Hohle Fels which is the oldest uncontested human figurative art ever discovered.[15] The Nebra sky disk is a bronze disk attributed to a site near Nebra, Saxony-Anhalt. UNESCO's Memory of the World Register calls it "one of the most important archaeological finds of the 20th century."[16]
Germanic tribes and Frankish Empire
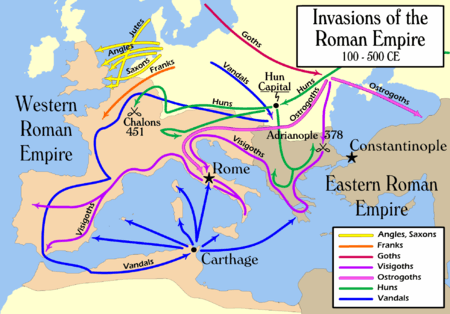
The Germanic tribes are thought to date from the Nordic Bronze Age or the Pre-Roman Iron Age. From southern Scandinavia and north Germany, they expanded south, east and west from the 1st century BC, coming into contact with the Celtic tribes of Gaul as well as Iranian, Baltic, and Slavic tribes in Central and Eastern Europe.[17] Under Augustus, Rome began to invade Germania (an area extending roughly from the Rhine to the Ural Mountains). In AD 9, three Roman legions led by Varus were defeated by the Cheruscan leader Arminius. By AD 100, when Tacitus wrote Germania, Germanic tribes had settled along the Rhine and the Danube (the Limes Germanicus), occupying most of the area of modern Germany; Austria, southern Bavaria and the western Rhineland, however, were Roman provinces.[18]
In the 3rd century a number of large West Germanic tribes emerged: Alemanni, Franks, Chatti, Saxons, Frisii, Sicambri, and Thuringii. Around 260, the Germanic peoples broke into Roman-controlled lands.[19] After the invasion of the Huns in 375, and with the decline of Rome from 395, Germanic tribes moved further south-west. Simultaneously several large tribes formed in what is now Germany and displaced the smaller Germanic tribes. Large areas (known since the Merovingian period as Austrasia) were occupied by the Franks, and Northern Germany was ruled by the Saxons and Slavs.[18]
Holy Roman Empire
On 25 December 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor and founded the Carolingian Empire, which was divided in 843.[20] The Holy Roman Empire comprised the eastern portion of Charlemagne's original kingdom and emerged as the strongest. Its territory stretched from the Eider River in the north to the Mediterranean coast in the south.[20] Under the reign of the Ottonian emperors (919–1024), several major duchies were consolidated, and the German king Otto I was crowned Holy Roman Emperor of these regions in 962. In 996 Gregory V became the first German Pope, appointed by his cousin Otto III, whom he shortly after crowned Holy Roman Emperor.[21] The Holy Roman Empire absorbed northern Italy and Burgundy under the reign of the Salian emperors (1024–1125), although the emperors lost power through the Investiture Controversy.[22]
_workshop_-_Martin_Luther_(Uffizi).jpg)
Under the Hohenstaufen emperors (1138–1254), the German princes increased their influence further south and east into territories inhabited by Slavs, preceding German settlement in these areas and further east (Ostsiedlung). Northern German towns grew prosperous as members of the Hanseatic League.[23] Starting with the Great Famine in 1315, then the Black Death of 1348–50, the population of Germany declined.[24] The edict of the Golden Bull in 1356 provided the basic constitution of the empire and codified the election of the emperor by seven prince-electors who ruled some of the most powerful principalities and archbishoprics.[25]
Martin Luther publicised The Ninety-Five Theses in 1517 in Wittenberg, challenging the Roman Catholic Church and initiating the Protestant Reformation. Lutheranism and the Reformed faith became the official religions in many German states after 1530 and 1648, respectively. Religious conflict led to the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), which devastated German lands.[26] The population of the German states was reduced by about 30%.[27] The Peace of Westphalia (1648) ended religious warfare among the German states. Throughout its entire history, the empire was de facto divided into numerous independent principalities. In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 such territories.[28]
From 1740 onwards, dualism between the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy and the Kingdom of Prussia dominated German history. In 1806 the Imperium was overrun and dissolved as a result of the Napoleonic Wars.[29]
German Confederation and Empire

Following the fall of Napoleon, the Congress of Vienna convened in 1814 and founded the German Confederation (Deutscher Bund), a loose league of 39 sovereign states. Disagreement with restoration politics partly led to the rise of liberal movements, followed by new measures of repression by Austrian statesman Metternich. The Zollverein, a tariff union, furthered economic unity in the German states.[30] National and liberal ideals of the French Revolution gained increasing support among many, especially young, Germans. The Hambach Festival in May 1832 was a main event in support of German unity, freedom and democracy. In the light of a series of revolutionary movements in Europe, which established a republic in France, intellectuals and commoners started the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states. King Frederick William IV of Prussia was offered the title of Emperor, but with a loss of power; he rejected the crown and the proposed constitution, leading to a temporary setback for the movement.[31]
King William I appointed Otto von Bismarck the new Minister President of Prussia in 1862. Bismarck successfully waged war on Denmark in 1864. Prussian victory in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 enabled him to create the North German Confederation (Norddeutscher Bund) and to exclude Austria from the federation's affairs. After the French defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, the German Empire was proclaimed in 1871 in Versailles, uniting all scattered parts of Germany except Austria. Prussia was the dominating constituent of the new state; the Hohenzollern King of Prussia ruled as its concurrent Emperor, and Berlin became its capital.[31]

In the Gründerzeit period following the unification of Germany, Bismarck's foreign policy as Chancellor of Germany under Emperor William I secured Germany's position as a great nation by forging alliances, isolating France by diplomatic means, and avoiding war. As a result of the Berlin Conference in 1884 Germany claimed several colonies including German East Africa, German South-West Africa, Togo, and Cameroon.[32] Under Wilhelm II, however, Germany, like other European powers, took an imperialistic course leading to friction with neighbouring countries. Most alliances in which Germany had previously been involved were not renewed, and new alliances excluded the country.[33]
The assassination of Austria's crown prince on 28 June 1914 triggered World War I. Germany, as part of the Central Powers, suffered defeat against the Allies in one of the bloodiest conflicts of all time. In total, approximately two million German soldiers were killed in World War I.[34] The German Revolution broke out in November 1918, and Emperor Wilhelm II and all German ruling princes abdicated. An armistice ended the war on 11 November, and Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles in June 1919. Germans perceived the treaty as humiliating and unjust and it was later seen by historians as influential in the rise of Adolf Hitler.[35][36][37]
Weimar Republic and the Third Reich
At the beginning of the German Revolution in November 1918, Germany was declared a republic. However, the struggle for power continued, with radical-left Communists seizing power in Bavaria. The revolution came to an end on 11 August 1919, when the democratic Weimar Constitution was signed by President Friedrich Ebert.[38] After a tumultuous period seeing the occupation of the Ruhr by Belgian and French troops and the rise of inflation culminating in the hyperinflation of 1922–23, a debt restructuring plan (the Dawes Plan) and the creation of a new currency in 1924 ushered in the Golden Twenties, an era of increasing national confidence, artistic innovation, liberal cultural life and economic prosperity. However, the economic situation was still quite volatile and Germany remained politically tempestuous. Historians connote the period between 1924 and 1929 in Germany as one of "Partial Stabilization."[39]

The Great Depression hit Germany in 1929. After the federal election of 1930, forming a coalition government proved impossible and Chancellor Heinrich Brüning's government asked President Paul von Hindenburg to grant him Article 48 powers so that he could enact emergency policies without parliamentary approval. Hindenburg approved the request and Brüning's government pursued a policy of fiscal austerity and deflation which caused high unemployment of nearly 30% by 1932.[40] In the special federal election of 1932 the Nazi Party won 37% of the vote but could not form a coalition government. After a series of unsuccessful cabinets, Hindenburg appointed Hitler as Chancellor of Germany in 1933.[41] After the Reichstag Fire Decree was passed abrogating basic civil rights and within weeks the first Nazi concentration camp, Dachau, was opened.[42] The Enabling Act of 1933 gave Hitler unrestricted legislative power, his government established a centralised totalitarian state, withdraw from the League of Nations, and began military rearmament.[43]
In 1935 the regime withdrew from the Treaty of Versailles and introduced the Nuremberg Laws which targeted Jews and other minorities. Germany reacquired control of the Saar in 1935.[44] Austria was annexed in 1938 and Czechoslovakia occupied in early 1939. Hitler's government then signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop pact with Stalin and in late 1939 the German Wehrmacht invaded Poland along with the Soviet Red Army. The United Kingdom and France then declared war on Germany, marking the beginning of World War II.[45] In 1940, Germany attacked France forcing the French government to sign an armistice after German troops occupied most of the country. The British repelled German air attacks in the same year. In 1941, German troops invaded the Soviet Union. At that point, Germany and the other Axis powers controlled most of continental Europe and North Africa. In early 1943, the German troops begun to retreat from the Soviet Union after their defeat in the Battle of Stalingrad.[45]

In what later became known as The Holocaust, the Nazi regime enacted policies which targeted minorities as well as political and religious opposition. Over 10 million civilians were executed during the Holocaust, including 6 million Jews, between 220,000 and 1,500,000 Romani people, 275,000 persons with mental and/or physical disabilities, thousands of Jehovah's Witnesses, thousands of homosexuals, and hundreds of thousands of members of the political and religious opposition.[46] Further, 2.7 million Poles[47] and 1.3 million Ukrainians,[48] along with an estimated 2.8 million Soviet war prisoners died from Nazi policies of forced labour, expulsion, internment and mass executions in the German occupied countries.
After the D-Day invasion Allied forces had entered Germany by 1945. Following Hitler's suicide and the Battle of Berlin, the German armed forces surrendered on 8 May 1945.[49] The war caused the deaths of around 40 million people in Europe.[50] German army war casualties were between 3.25 million and 5.3 million soldiers,[51] and approximately 2 million German civilians were killed.[52] Losing the war resulted in territorial losses for Germany and the expulsion of millions of ethnic Germans from the former eastern territories of Germany. Germany suffered the destruction of numerous cities and cultural heritage due to bombing and fighting. After World War II, former members of the regime were tried for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.[53]
East and West Germany
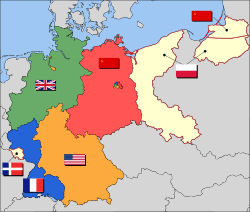
After the surrender of Germany, the remaining German territory and Berlin were partitioned by the Allies into four military occupation zones. Together these zones accepted more than 6.5 million of the ethnic Germans expelled from eastern areas.[54] The western sectors, controlled by France, the United Kingdom, and the United States, were merged on 23 May 1949 to form the Federal Republic of Germany (Bundesrepublik Deutschland); on 7 October 1949, the Soviet Zone became the German Democratic Republic (Deutsche Demokratische Republik). They were informally known as "West Germany" and "East Germany". East Germany selected East Berlin as its capital, while West Germany chose Bonn as a provisional capital, to emphasise its stance that the two-state solution was an artificial and temporary status quo.[55]
West Germany was established as a federal parliamentary republic with a "social market economy". Starting in 1948 West Germany became a major recipient of reconstruction aid under the Marshall Plan and used this to rebuild its industry.[56] Konrad Adenauer was elected the first Federal Chancellor (Bundeskanzler) of Germany in 1949 and remained in office until 1963. Under his and Ludwig Erhard's leadership, the country enjoyed prolonged economic growth beginning in the early 1950s, that became known as an "economic miracle" (Wirtschaftswunder).[57] West Germany joined NATO in 1955 and was a founding member of the European Economic Community in 1957.
East Germany was an Eastern Bloc state under political and military control by the USSR via occupation forces and the Warsaw Pact. Though East Germany claimed to be a democracy, political power was exercised solely by leading members (Politbüro) of the communist-controlled Socialist Unity Party of Germany, supported by the Stasi, an immense secret service controlling many aspects of the society.[58] A Soviet-style command economy was set up and the GDR later became a Comecon state.[59] While East German propaganda was based on the benefits of the GDR's social programmes and the alleged constant threat of a West German invasion, many of its citizens looked to the West for freedom and prosperity.[60] The Berlin Wall, built in 1961 to stop East Germans from escaping to West Germany, became a symbol of the Cold War,[31] hence its fall in 1989 became a symbol of the Fall of Communism, German Reunification and Die Wende.
Tensions between East and West Germany were reduced in the early 1970s by Chancellor Willy Brandt's Ostpolitik. In summer 1989, Hungary decided to dismantle the Iron Curtain and open the borders, causing the emigration of thousands of East Germans to West Germany via Hungary. This had devastating effects on the GDR, where regular mass demonstrations received increasing support. The East German authorities eased the border restrictions, allowing East German citizens to travel to the West; originally intended to help retain East Germany as a state, the opening of the border actually led to an acceleration of the Wende reform process. This culminated in the Two Plus Four Treaty a year later on 12 September 1990, under which the four occupying powers renounced their rights under the Instrument of Surrender, and Germany regained full sovereignty. This permitted German reunification on 3 October 1990, with the accession of the five re-established states of the former GDR.[31]
German reunification and the EU

The modernisation and integration of the eastern German economy is a long-term process scheduled to last until the year 2019, with annual transfers from west to east amounting to roughly $80 billion.[61]
Based on the Berlin/Bonn Act, adopted on 10 March 1994, Berlin once again became the capital of the reunified Germany, while Bonn obtained the unique status of a Bundesstadt (federal city) retaining some federal ministries.[62] The relocation of the government was completed in 1999.[63] Following the 1998 elections, SPD politician Gerhard Schröder became the first Chancellor of a red–green coalition with the Alliance '90/The Greens party, lasting until the 2005 elections.
Since reunification, Germany has taken a more active role in the European Union. Together with its European partners Germany signed the Maastricht Treaty in 1992, established the Eurozone in 1999, and signed the Lisbon Treaty in 2007.
Germany sent a peacekeeping force to secure stability in the Balkans and sent a force of German troops to Afghanistan as part of a NATO effort to provide security in that country after the ousting of the Taliban.[64] These deployments were controversial since Germany was bound by domestic law only to deploy troops for defence roles.[65]
In 2005, Angela Merkel became the first female Chancellor of Germany as the leader of a grand coalition.[31] In 2009 the German government approved a €50 billion economic stimulus plan to protect several sectors from a downturn and a subsequent rise in unemployment rates.[66]
In 2009, a liberal-conservative coalition under Merkel assumed leadership of the country. In 2013, a grand coalition was established in a Third Merkel cabinet. Among the major German political projects of the early 21st century are the energy transition (Energiewende) for a sustainable energy supply, the "Debt Brake" (Schuldenbremse) for balanced budgets, the reform of German immigration laws, the legislation for a general minimum wage, and high-tech strategies for the informatization and future transition of the German economy, summarized as Industry 4.0.[67]
Geography
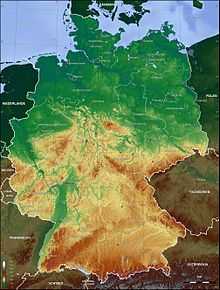
Germany is in Western and Central Europe, with Denmark bordering to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France and Luxembourg to the southwest, and Belgium and the Netherlands to the northwest. It lies mostly between latitudes 47° and 55° N (the tip of Sylt is just north of 55°), and longitudes 5° and 16° E. The territory covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of water. It is the seventh largest country by area in Europe and the 62nd largest in the world.[1]
Elevation ranges from the mountains of the Alps (highest point: the Zugspitze at 2,962 metres or 9,718 feet) in the south to the shores of the North Sea (Nordsee) in the northwest and the Baltic Sea (Ostsee) in the northeast. The forested uplands of central Germany and the lowlands of northern Germany (lowest point: Wilstermarsch at 3.54 metres or 11.6 feet below sea level) are traversed by such major rivers as the Rhine, Danube and Elbe. Glaciers are found in the Alpine region, but are experiencing deglaciation. Significant natural resources are iron ore, coal, potash, timber, lignite, uranium, copper, natural gas, salt, nickel, arable land and water.[1]
Climate

Most of Germany has a temperate seasonal climate in which humid westerly winds predominate. The country is situated in between the oceanic Western European and the continental Eastern European climate. The climate is moderated by the North Atlantic Drift, the northern extension of the Gulf Stream. This warmer water affects the areas bordering the North Sea; consequently in the northwest and the north the climate is oceanic. Germany gets an average of 789 mm (31 in) precipitation per year. Rainfall occurs year-round, with no consistent dry season. Winters are mild and summers tend to be warm: temperatures can exceed 30 °C (86 °F).[68]
The east has a more continental climate: winters can be very cold and summers very warm, and longer dry periods can occur. Central and southern Germany are transition regions which vary from moderately oceanic to continental. In addition to the maritime and continental climates that predominate over most of the country, the Alpine regions in the extreme south and, to a lesser degree, some areas of the Central German Uplands have a mountain climate, with lower temperatures and greater precipitation.[68]
Biodiversity

The territory of Germany can be subdivided into two ecoregions: European-Mediterranean montane mixed forests and Northeast-Atlantic shelf marine.[69] As of 2008 the majority of Germany is covered by either arable land (34%) or forest and woodland (30.1%); only 13.4% of the area consists of permanent pastures, 11.8% is covered by settlements and streets.[70]
Plants and animals are those generally common to Central Europe. Beeches, oaks, and other deciduous trees constitute one-third of the forests; conifers are increasing as a result of reforestation. Spruce and fir trees predominate in the upper mountains, while pine and larch are found in sandy soil. There are many species of ferns, flowers, fungi, and mosses. Wild animals include deer, wild boar, mouflon, fox, badger, hare, and small numbers of beavers.[71] The blue cornflower was once a German national symbol.[72]
The 14 national parks in Germany include the Jasmund National Park, the Vorpommern Lagoon Area National Park, the Müritz National Park, the Wadden Sea National Parks, the Harz National Park, the Hainich National Park, the Black Forest National Park, the Saxon Switzerland National Park, the Bavarian Forest National Park and the Berchtesgaden National Park. In addition, there are 14 Biosphere Reserves, as well as 98 nature parks. More than 400 registered zoos and animal parks operate in Germany, which is believed to be the largest number in any country.[73] The Berlin Zoo, opened in 1844, is the oldest zoo in Germany, and presents the most comprehensive collection of species in the world.[74]
Politics
 | _cropped.jpg) |
| Joachim Gauck President since 2012 |
Angela Merkel Chancellor since 2005 |
Germany is a federal, parliamentary, representative democratic republic. The German political system operates under a framework laid out in the 1949 constitutional document known as the Grundgesetz (Basic Law). Amendments generally require a two-thirds majority of both chambers of parliament; the fundamental principles of the constitution, as expressed in the articles guaranteeing human dignity, the separation of powers, the federal structure, and the rule of law are valid in perpetuity.[75]
The president, currently Joachim Gauck, is the head of state and invested primarily with representative responsibilities and powers. He is elected by the Bundesversammlung (federal convention), an institution consisting of the members of the Bundestag and an equal number of state delegates. The second-highest official in the German order of precedence is the Bundestagspräsident (President of the Bundestag), who is elected by the Bundestag and responsible for overseeing the daily sessions of the body. The third-highest official and the head of government is the Chancellor, who is appointed by the Bundespräsident after being elected by the Bundestag.[31]
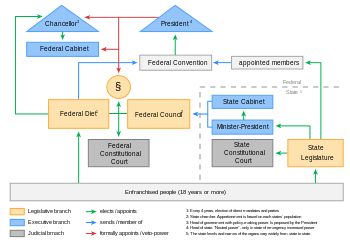
The chancellor, currently Angela Merkel, is the head of government and exercises executive power, similar to the role of a Prime Minister in other parliamentary democracies. Federal legislative power is vested in the parliament consisting of the Bundestag (Federal Diet) and Bundesrat (Federal Council), which together form the legislative body. The Bundestag is elected through direct elections, by proportional representation (mixed-member).[1] The members of the Bundesrat represent the governments of the sixteen federated states and are members of the state cabinets.[31]
Since 1949, the party system has been dominated by the Christian Democratic Union and the Social Democratic Party of Germany. So far every chancellor has been a member of one of these parties. However, the smaller liberal Free Democratic Party (which had members in the Bundestag from 1949 to 2013) and the Alliance '90/The Greens (which has had seats in parliament since 1983) have also played important roles.[76]
Law

Germany has a civil law system based on Roman law with some references to Germanic law. The Bundesverfassungsgericht (Federal Constitutional Court) is the German Supreme Court responsible for constitutional matters, with power of judicial review.[31][77] Germany's supreme court system, called Oberste Gerichtshöfe des Bundes, is specialised: for civil and criminal cases, the highest court of appeal is the inquisitorial Federal Court of Justice, and for other affairs the courts are the Federal Labour Court, the Federal Social Court, the Federal Finance Court and the Federal Administrative Court.
Criminal and private laws are codified on the national level in the Strafgesetzbuch and the Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch respectively. The German penal system is aimed towards rehabilitation of the criminal and the protection of the general public.[78] Except for petty crimes, which are tried before a single professional judge, and serious political crimes, all charges are tried before mixed tribunals on which lay judges (Schöffen) sit side by side with professional judges.[79][80] Many of the fundamental matters of administrative law remain in the jurisdiction of the states.
Constituent states
Germany comprises sixteen federal states which are collectively referred to as Bundesländer.[81] Each state has its own state constitution[82] and is largely autonomous in regard to its internal organisation. Because of differences in size and population the subdivisions of these states vary, especially as between city states (Stadtstaaten) and states with larger territories (Flächenländer). For regional administrative purposes five states, namely Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, Hesse, North Rhine-Westphalia and Saxony, consist of a total of 22 Government Districts (Regierungsbezirke). As of 2013 Germany is divided into 402 districts (Kreise) at a municipal level; these consist of 295 rural districts and 107 urban districts.[83]
|
Foreign relations

Germany has a network of 229 diplomatic missions abroad[85] and maintains relations with more than 190 countries.[86] As of 2011 it is the largest contributor to the budget of the European Union (providing 20%)[87] and the third largest contributor to the UN (providing 8%).[88] Germany is a member of NATO, the OECD, the G8, the G20, the World Bank and the IMF. It has played a leading role in the European Union since its inception and has maintained a strong alliance with France since the end of World War II. Germany promotes the creation of a more unified European political, defence, and security apparatus.[89][90]
The development policy of the Federal Republic of Germany is an independent area of German foreign policy. It is formulated by the Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ) and carried out by the implementing organisations. The German government sees development policy as a joint responsibility of the international community.[91] It is the world's third biggest aid donor after the United States and France.[92][93]
During the Cold War, Germany's partition by the Iron Curtain made it a symbol of East–West tensions and a political battleground in Europe. However, Willy Brandt's Ostpolitik was a key factor in the détente of the 1970s.[94] In 1999, Chancellor Gerhard Schröder's government defined a new basis for German foreign policy by taking part in the NATO decisions surrounding the Kosovo War and by sending German troops into combat for the first time since World War II.[95] The governments of Germany and the United States are close political allies.[31] The 1948 Marshall Plan and strong cultural ties have crafted a strong bond between the two countries, although Schröder's vocal opposition to the Iraq War suggested the end of Atlanticism and a relative cooling of German-American relations.[96] The two countries are also economically interdependent: 8.8% of German exports are US-bound and 6.6% of German imports originate from the US.[97]
Military

Germany's military, the Bundeswehr, is organised into Heer (Army and special forces KSK), Marine (Navy), Luftwaffe (Air Force), Bundeswehr Joint Medical Service and Streitkräftebasis (Joint Support Service) branches. In 2011, military spending was an estimated 1.3% of the country's GDP, which is low in comparison with allied NATO members. In absolute terms, German military expenditure is the 9th highest in the world.[98] In peacetime, the Bundeswehr is commanded by the Minister of Defence. In state of defence, the Chancellor would become commander-in-chief of the Bundeswehr.[99]
As of March 2012 the Bundeswehr employs 183,000 professional soldiers and 17,000 volunteers.[100] The German government plans to reduce the number of soldiers to 170,000 professionals and up to 15,000 short-term volunteers.[101] Reservists are available to the Armed Forces and participate in defence exercises and deployments abroad.[101] According to SIPRI, Germany was the fourth largest exporter of major arms in the world in 2014. In the same year the German Government announced a more restrictive arms export policy.[102]

The role of the Bundeswehr is described in the Constitution of Germany as defensive only. But after a ruling of the Federal Constitutional Court in 1994 the term "defense" has been defined to not only include protection of the borders of Germany, but also crisis reaction and conflict prevention, or more broadly as guarding the security of Germany anywhere in the world. As of January 2015, the German military has about 2,370 troops stationed in foreign countries as part of international peacekeeping forces, including about 850 Bundeswehr troops in the NATO-led ISAF force in Afghanistan and Uzbekistan, 670 German soldiers in Kosovo, and 120 troops with UNIFIL in Lebanon.[103]
Until 2011, military service was compulsory for men at age 18, and conscripts served six-month tours of duty; conscientious objectors could instead opt for an equal length of Zivildienst (civilian service), or a six-year commitment to (voluntary) emergency services like a fire department or the Red Cross. On 1 July 2011 conscription was officially suspended and replaced with a voluntary service.[104][105] Since 2001 women may serve in all functions of service without restriction, but they have not been subject to conscription. There are presently some 17,500 women on active duty and a number of female reservists.[106]
Economy

Germany has a social market economy with a highly skilled labour force, a large capital stock, a low level of corruption,[108] and a high level of innovation.[109] It has the largest and most powerful national economy in Europe, the fourth largest by nominal GDP in the world,[110] and the fifth largest by PPP.[111] The service sector contributes approximately 71% of the total GDP (including information technology), industry 28%, and agriculture 1%.[1] The official average national unemployment rate in April 2014 was 6.8%.[112] The unemployment rate published by Eurostat amounts to 4.7% in January 2015. which is the lowest rate of all 28 EU member states.[113] Germany also has with 7.1% the lowest youth unemployment rate of all EU member states.[113] According to the OECD Germany has one of the highest labour productivity levels in the world.[114]
Germany is an advocate of closer European economic and political integration. Its commercial policies are increasingly determined by agreements among European Union (EU) members and by EU legislation. Germany introduced the common European currency, the Euro, on 1 January 2002.[115][116] Its monetary policy is set by the European Central Bank, which is headquartered in Frankfurt. Two decades after German reunification, standards of living and per capita incomes remain significantly higher in the states of the former West Germany than in the former East.[117]
Being home to the modern car, the automotive industry in Germany is regarded as the most competitive and innovative in the world,[118] and is the fourth largest by production in the world, after Japan, the United States and China.[119]
Of the world's 500 largest stock-market-listed companies measured by revenue in 2010, the Fortune Global 500, 37 are headquartered in Germany. 30 Germany-based companies are included in the DAX, the German stock market index. As of 2014 well-known global brands include Mercedes-Benz, BMW, SAP, Volkswagen, Audi, Siemens, Allianz, Adidas, Porsche, and DHL.[120] Germany is recognised for its large portion of specialised small and medium enterprises, globally known and followed as the Mittelstand model. Around 1,000 of these companies are global market leaders in their segment and are labelled hidden champions.[121]

The list includes the largest German companies by revenue in 2011:[122]
| Rank | Name | Headquarters | Revenue (mil. €) | Profit (mil. €) | Employees (world) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Volkswagen AG | Wolfsburg | 159,000 | 15,800 | 502,000 |
| 2. | E.ON SE | Düsseldorf | 113,000 | −1,900 | 79,000 |
| 3. | Daimler AG | Stuttgart | 107,000 | 6,000 | 271,000 |
| 4. | Siemens AG | Berlin, München | 74,000 | 6,300 | 360,000 |
| 5. | BASF SE | Ludwigshafen am Rhein | 73,000 | 6,600 | 111,000 |
| 6. | BMW AG | München | 69,000 | 4,900 | 100,000 |
| 7. | Metro AG | Düsseldorf | 67,000 | 740 | 288,000 |
| 8. | Schwarz Gruppe | Neckarsulm | 63,000 | N/A | 315,000 |
| 9. | Deutsche Telekom AG | Bonn | 59,000 | 670 | 235,000 |
| 10. | Deutsche Post AG | Bonn | 53,000 | 1,300 | 471,000 |
| — | Allianz SE | München | 104,000 | 2,800 | 141,000 |
| — | Deutsche Bank AG | Frankfurt am Main | 21,600 | 4,300 | 101,000 |
Infrastructure

With its central position in Europe, Germany is a transport hub for the continent.[123] Like its neighbours in Western Europe, Germany's road network is amongst the densest in the world.[124] The motorway (Autobahn) network ranks as the third-largest worldwide in length and is known for its lack of a general speed limit.[125] Germany has established a polycentric network of high-speed trains. The InterCityExpress or ICE network of the Deutsche Bahn serves major German cities as well as destinations in neighbouring countries with speeds up to 300 kph (186 mph).[126] The largest German airports are Frankfurt Airport and Munich Airport, both hubs of Lufthansa, while Air Berlin has hubs at Berlin Tegel and Düsseldorf. Other major airports include Berlin Schönefeld, Hamburg, Cologne/Bonn and Leipzig/Halle. Both airports in Berlin will be consolidated at a site adjacent to Berlin Schönefeld, which will become Berlin Brandenburg Airport.[127] The Port of Hamburg is one of the top twenty largest container ports in the world.[128]
In 2008, Germany was the world's sixth-largest consumer of energy,[129] and 60% of its primary energy was imported.[130] Government policy promotes energy conservation and renewable energy commercialisation. Energy efficiency has been improving since the early 1970s; the government aims to meet the country's electricity demands using 40% renewable sources by 2020 and 100% by 2050.[131] In 2014, energy sources were: oil (35.0%); coal, including lignite (24.6%); natural gas (20.5%); nuclear (8.1%); hydro-electric and renewable sources (11.1%).[132] In 2000, the government and the nuclear power industry agreed to phase out all nuclear power plants by 2021.[133] Germany is committed to the Kyoto protocol and several other treaties promoting biodiversity, low emission standards, recycling, and the use of renewable energy, and supports sustainable development at a global level.[134] The German government has initiated wide-ranging emission reduction activities and the country's overall emissions are falling.[135] Nevertheless the country's greenhouse gas emissions were the highest in the EU in 2010, while it is also the largest country by population and economical output.[136] The German energy transition (German: Energiewende) is the globally recognised move to a sustainable economy by means of renewable energy, energy efficiency and sustainable development. The final goal is the abolition of coal and other non-renewable energy sources.[137]
Science and technology
Germany's achievements in the sciences have been significant, and research and development efforts form an integral part of the economy.[138] The Nobel Prize has been awarded to 104 German laureates.[139] For most of the 20th century, German laureates had more awards than those of any other nation, especially in the sciences (physics, chemistry, and physiology or medicine).[140][141]
Notable German physicists before the 20th century include Hermann von Helmholtz, Joseph von Fraunhofer and Gabriel Daniel Fahrenheit, among others. Albert Einstein introduced the relativity theories for light and gravity in 1905 and 1915 respectively. Along with Max Planck, he was instrumental in the introduction of quantum mechanics, in which Werner Heisenberg and Max Born later made major contributions.[142] Wilhelm Röntgen discovered X-rays.[143] Otto Hahn was a pioneer in the fields of radiochemistry and discovered nuclear fission,[144] while Ferdinand Cohn and Robert Koch were founders of microbiology. Numerous mathematicians were born in Germany, including Carl Friedrich Gauss, David Hilbert, Bernhard Riemann, Gottfried Leibniz, Karl Weierstrass, Hermann Weyl and Felix Klein. Research institutions in Germany include the Max Planck Society, the Helmholtz Association and the Fraunhofer Society. The Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize is granted to ten scientists and academics every year. With a maximum of €2.5 million per award it is one of highest endowed research prizes in the world.[145]
Germany has been the home of many famous inventors and engineers, such as Johannes Gutenberg, credited with the invention of movable type printing in Europe; Hans Geiger, the creator of the Geiger counter; and Konrad Zuse, who built the first fully automatic digital computer.[146] German inventors, engineers and industrialists such as Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin, Otto Lilienthal, Gottlieb Daimler, Rudolf Diesel, Hugo Junkers and Karl Benz helped shape modern automotive and air transportation technology.[147] German institutions like the German Aerospace Center (DLR) are the largest contributor to ESA. Aerospace engineer Wernher von Braun developed the first space rocket and later on was a prominent member of NASA and developed the Saturn V Moon rocket, which paved the way for the success of the US Apollo programme. Heinrich Rudolf Hertz's work in the domain of electromagnetic radiation was pivotal to the development of modern telecommunication.[148]
Germany is one of the leading countries in developing and using green technologies. Companies specialising in this branch have an estimated turnover of €200 billion. Key sectors of Germany's green technology industry are power generation, sustainable mobility, material efficiency, energy efficiency, waste management and recycling, and sustainable water management.[149] With Wendelstein 7-X in Greifswald, Germany also hosts a leading facility in the research of fusion power.[150]
Tourism
.jpg)
Germany is the seventh most visited country in the world,[151][152] with a total of 407.26 million overnights during 2012.[153] This number includes 68.83 million nights by foreign visitors. In 2012, over 30.4 million international tourists arrived in Germany, bringing over US$38 billion in international tourism receipts to the country.[154] Additionally, more than 30% of Germans spend their holiday in their own country, with the biggest share going to Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. According to Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Reports, Germany is rated as one of the safest travel destinations worldwide. Domestic and international travel and tourism combined directly contribute over EUR43.2 billion to German GDP. Including indirect and induced impacts, the industry contributes 4.5% of German GDP and supports 2 million jobs (4.8% of total employment).[155]
Germany is well known for its diverse tourist routes, such as the Romantic Road, the Wine Route, the Castle Road, the Timber-Frame Road and the Avenue Road. There are 39 UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Germany, including the old town cores of Regensburg, Bamberg, Lübeck, Quedlinburg, Weimar, Stralsund and Wismar. Germany's most-visited landmarks include i. e. Neuschwanstein Castle, Cologne Cathedral, Berlin Bundestag, Hofbräuhaus Munich, Heidelberg Castle, Dresden Zwinger, Fernsehturm Berlin and Aachen Cathedral. The Europa-Park near Freiburg is Europe's second most popular theme park resort.[156]
Demographics
With a population of 80.2 million according to the May 2011 census,[157] Germany is the most populous country in the European Union, the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and ranks as the 16th most populous country in the world.[158] Its population density stands at 225 inhabitants per square kilometre. The overall life expectancy in Germany at birth is 80.19 years (77.93 years for males and 82.58 years for females).[1] The fertility rate of 1.41 children born per woman (2011 estimates), or 8.33 births per 1000 inhabitants, is one of the lowest in the world.[1] Since the 1970s, Germany's death rate has continuously exceeded its birth rate.[159]
However, Germany is witnessing increased birth rates and migration rates since the beginning of the 2010s.[160] It is experiencing a rise in the number of well-educated migrants.[161][162]Most immigrants coming from countries of southern and eastern Europe and settling in urban areas.[163]
Four sizable groups of people are referred to as "national minorities" because they have lived in their respective regions for centuries: Danes, Frisians, Roma and Sinti, and Sorbs.[164] There is a Danish minority (about 50,000) in the northernmost state of Schleswig-Holstein.[164] Eastern and Northern Frisians live on Schleswig-Holstein's western coast, and in the north-western part of Lower Saxony. The Sorbs, a Slavic population of about 60,000, are in the Lusatia region of Saxony and Brandenburg.[164]
Immigrant population
Germans by nationality make up 92.3% of the population of Germany as of 9 May 2011.[157] As of 2011, about six million foreign citizens (7.7% of the population) were registered in Germany.[157] Regarding ethnic background, 20%[166] of the country's residents, or more than 16 million people, were of foreign or partially foreign descent in 2009 (including persons descending or partially descending from ethnic German repatriates), 96% of whom lived in the former West Germany or Berlin.[167] In 2010, 2.3 million families with children under 18 years were living in Germany, in which at least one parent had foreign roots. They represented 29% of the total of 8.1 million families with minor children. Compared with 2005 the proportion of migrant families has risen by 2 percentage points.[168]
Most of the population with a migrant background live in the western part of Germany. In 2010, the proportion of migrant families in all families was 32% in the pre-unification territory of the Federal Republic. This figure was more than double that in the new Länder (including Berlin) where it stood at 15%.[168]
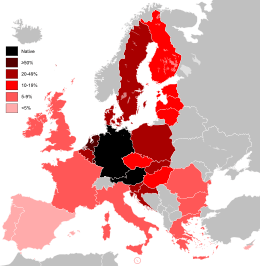
The United Nations Population Fund lists Germany as host to the third-highest number of international migrants worldwide, about 5% or 10 million of all 191 million migrants.[169] In 2009, 20% of the population had immigrant roots, the highest since 1945.[170] As of 2008, the largest national group was from Turkey (2.5 million), followed by Italy (776,000) and Poland (687,000).[171] Since 1987, around 3 million ethnic Germans, mostly from the former eastern bloc, have taken advantage of their right of return and emigrated to Germany.[172]
Urbanization
Germany has a number of large cities. There are 11 officially recognised metropolitan regions in Germany – and since 2006, 34 cities have been identified which can be called a regiopolis (metropolitan area).
The largest conurbation is the Rhine-Ruhr region (11.7 million in 2008), including Düsseldorf (the capital of North Rhine-Westphalia), Cologne, Bonn, Dortmund, Essen, Duisburg, and Bochum.[173]
| | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | State | Pop. | Rank | Name | State | Pop. | ||
 Berlin  Hamburg |
1 | Berlin | Berlin | 3,471,756 | 11 | Dresden | Saxony | 523,058 |  Munich  Cologne |
| 2 | Hamburg | Hamburg | 1,786,448 | 12 | Leipzig | Saxony | 522,883 | ||
| 3 | Munich | Bavaria | 1,353,186 | 13 | Hannover | Lower Saxony | 522,686 | ||
| 4 | Cologne | North Rhine-Westphalia | 1,007,119 | 14 | Nuremberg | Bavaria | 505,664 | ||
| 5 | Frankfurt | Hesse | 688,664 | 15 | Duisburg | North Rhine-Westphalia | 489,599 | ||
| 6 | Stuttgart | Baden-Württemberg | 606,588 | 16 | Bochum | North Rhine-Westphalia | 374,737 | ||
| 7 | Düsseldorf | North Rhine-Westphalia | 598,786 | 17 | Wuppertal | North Rhine-Westphalia | 349,721 | ||
| 8 | Dortmund | North Rhine-Westphalia | 580,444 | 18 | Bonn | North Rhine-Westphalia | 324,899 | ||
| 9 | Essen | North Rhine-Westphalia | 574,635 | 19 | Bielefeld | North Rhine-Westphalia | 323,270 | ||
| 10 | Bremen | Bremen (state) | 547,340 | 20 | Mannheim | Baden-Württemberg | 313,174 | ||
Religion
According to the latest official nationwide census of 2011, Christianity is the largest religion in Germany, claiming 66.8% of the total population.[174] The census provided detailed statistics on religion in the Federal Republic. Results for the total population of Germany were as follows: 30.8% declared themselves as Roman Catholics; 30.3% as Protestants as represented by the Evangelical Church in Germany (EKD); 5.7% were reported to be other Christians (including Protestants outside the EKD).[175]


Geographically, Protestantism is concentrated in the northern, central and eastern parts of the country, mostly within the Evangelical Church, while Roman Catholicism is concentrated in the south and west. People with no or other religions are concentrated in the former East Germany and major metropolitan areas.[176]
Islam is the second largest religion in the country. In the 2011 census only 1.9% declared themselves to be Muslims,[175] however other sources estimate 3.8 to 4.3 million adherents (4.6% to 5.2%).[177] Most of the Muslims are Sunnis and Alevites from Turkey, but there are a small number of Shi'ites, Ahmadiyyas and other denominations.[177] German Muslims, a large portion of whom are of Turkish origin, lack full official state recognition of their religious community.[176]
Other religions comprising less than 1% of Germany's population[175] are Buddhism with 250,000 and Judaism with around 200,000 adherents (both roughly 0.3%). Hinduism has some 100,000 adherents (0.1%). All other religious communities in Germany have fewer than 50,000 adherents each.[178] Germany has Europe's third largest Jewish population (after France and the United Kingdom).[179] Approximately 50% of the Buddhists in Germany are Asian immigrants.[180]
The remaining 32%–35% are not members of any religious body-a proportion that has grown steadily over recent decades. German reunification in 1990 greatly increased the country's non-religious population, a legacy of the state atheism of the previously Soviet-controlled East. The Christian population has decreased in recent decades, particularly among Protestants.[176]
Languages
German is the official and predominant spoken language in Germany.[181] It is one of 24 official and working languages of the European Union,[182] and one of the three working languages of the European Commission. German is the most widely spoken first language in the European Union, with around 100 million native speakers.[183]
Recognized native minority languages in Germany are Danish, Low German, Sorbian, Romany, and Frisian; they are officially protected by the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. The most used immigrant languages are Turkish, Kurdish, Polish, the Balkan languages, and Russian. 67% of German citizens claim to be able to communicate in at least one foreign language and 27% in at least two languages other than their own.[181]
Standard German is a West Germanic language and is closely related to and classified alongside English, Low German, Dutch, and the Frisian languages. To a lesser extent, it is also related to the East (extinct) and North Germanic languages. Most German vocabulary is derived from the Germanic branch of the Indo-European language family.[184] Significant minorities of words are derived from Latin and Greek, with a smaller amount from French and most recently English (known as Denglisch). German is written using the Latin alphabet. German dialects, traditional local varieties traced back to the Germanic tribes, are distinguished from varieties of standard German by their lexicon, phonology, and syntax.[185]
Education

Over 99% of Germans aged 15 and above are estimated to be able to read and write.[1] Responsibility for educational supervision in Germany is primarily organised within the individual federal states. A system of apprenticeship called Duale Ausbildung ("dual education") allows students in vocational training to learn in a company as well as in a state-run vocational school.[187] This successful model is highly regarded and reproduced all around the world.[188]
Optional kindergarten education is provided for all children between three and six years old, after which school attendance is compulsory for at least nine years. Primary education usually lasts for four to six years and public schools are not stratified by academic ability at this stage.[187] In contrast, secondary education includes three traditional types of schools focused on different academic levels: the Gymnasium enrols the most gifted children and prepares students for university studies; the Realschule for intermediate students lasts six years; the Hauptschule prepares pupils for vocational education.[189] Since the 1960s, a reform movement has attempted to unify secondary education in a Gesamtschule (comprehensive school).
The general entrance requirement for university is the Abitur, a qualification normally based on continuous assessment during the last few years at school and final examinations; however there are a number of exceptions, and precise requirements vary, depending on the state, the university and the subject. Germany's universities are recognised internationally: in the Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) for 2008, six of the top 100 universities in the world are in Germany, and 18 of the top 200.[190]
Most of the German universities are public institutions, funded by the Länder governments, and students have traditionally studied without fee payment.[191] Academic education is open to most citizens and is increasingly common in Germany.[192] The dual education system that combines practical and theoretical learning, but does not lead to an academic degree, is typical for Germany and is recognised as a model for other countries.[193]
The established universities in Germany include some of the oldest in the world, with Heidelberg University being the oldest in Germany (established in 1386). Heidelberg is followed by Leipzig University (1409), Rostock University (1419), Greifswald University (1456), Freiburg University (1457), LMU Munich (1472) and the University of Tübingen (1477).
Health
Germany has the world's oldest universal health care system, dating back to Bismarck's social legislation in 1883.[195] Since then there have been many reforms and provisions to ensure a balanced health care system. Currently the population is covered by a health insurance plan provided by statute, with criteria allowing some groups to opt for a private health insurance contract instead. According to the World Health Organization, Germany's health care system was 77% government-funded and 23% privately funded as of 2005.[196] In 2005, Germany spent 11% of its GDP on health care. Germany ranked 20th in the world in life expectancy with 77 years for men and 82 years for women, and it had a very low infant mortality rate (4 per 1,000 live births).[196]
In 2010, the principal cause of death was cardiovascular disease, at 41%, followed by malignant tumours, at 26%.[197] In 2008, about 82,000 Germans had been infected with HIV/AIDS and 26,000 had died from the disease (cumulatively, since 1982).[198] According to a 2005 survey, 27% of German adults are smokers.[198]
Culture

From its roots, culture in German states has been shaped by major intellectual and popular currents in Europe, both religious and secular. Historically Germany has been called Das Land der Dichter und Denker ("the land of poets and thinkers"),[199] because of the major role its writers and philosophers have played in the development of Western thought and culture.
There are 240 subsidised theatres, hundreds of symphonic orchestras, thousands of museums and over 25,000 libraries spread in Germany.[200] As of 2013 the UNESCO inscribed 38 properties in Germany on the World Heritage List.[201]
Germany has established a high level of gender equality,[202] promotes disability rights, and is socially tolerant towards homosexuals, who can legally adopt their partner's biological children, and can engage in civil unions.[203] Since the mid-1990s, the Germans acknowledged that controlled immigration should be allowed based on qualification standards.[204]
Germany has been named the world's second most respected nation among 50 countries in 2013.[205] A global opinion poll for the BBC revealed that Germany is recognised for having the most positive influence in the world in 2011, 2013 and 2014.[206][207][208]
There are a number of public holidays in Germany. The country is particularly associated with its traditional Oktoberfest celebrations, its carnival culture and globally influential Christmas customs known as Weihnachten.[209][210] 3 October has been the national day of Germany since 1990, celebrated as the German Unity Day (Tag der Deutschen Einheit).
Music

German classical music includes works by some of the world's most well-known composers. Johann Sebastian Bach and Georg Friedrich Händel were influential composers of the Baroque period. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical era. Ludwig van Beethoven was a crucial figure in the transition between the Classical and Romantic eras. Franz Schubert was an important figure in the late Classical era and early Romantic era. Carl Maria von Weber and Felix Mendelssohn were important in the early Romantic period. Robert Schumann and Johannes Brahms composed in the Romantic idiom. Richard Wagner was known for his operas. Richard Strauss was a leading composer of the late Romantic and early modern eras. Karlheinz Stockhausen is one of the most important composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries.
Germany is the second largest music market in Europe, and fourth largest in the world.[211] German popular music of the 20th and 21st century includes the movements of Neue Deutsche Welle (Nena, Trio), Pop (Boney M., Alphaville, Modern Talking), Ostrock (City, Keimzeit), Metal/Rock (Rammstein, Scorpions), Punk (Die Ärzte, Die Toten Hosen), Pop rock (Beatsteaks, Tokio Hotel), Indie (Tocotronic, Blumfeld) and Schlager pop (Katja Ebstein, Hildegard Knef, Helene Fischer). German Electronic music gained global influence, with Kraftwerk and Tangerine Dream pioneering in this genre.[212] DJs and artists of the Techno and House music scenes of Germany have become well known (e.g. Paul van Dyk, Paul Kalkbrenner, and Scooter).[213]
Art

German painters have been influential on western art throughout history. Albrecht Dürer, Hans Holbein the Younger, Matthias Grünewald and Lucas Cranach the Elder were important German artists of the Renaissance, Peter Paul Rubens and Johann Baptist Zimmermann of Baroque, Caspar David Friedrich and Carl Spitzweg of Romanticism, Max Liebermann of Impressionism and Max Ernst of Surrealism.
Several German artist groups formed in the 20th century, such as the November Group or Die Brücke (The Bridge) and Der Blaue Reiter (The Blue Rider) in Expressionism. The New Objectivity arose as a counter-style to it during the Weimar Republic. After World War II, Neo-expressionism, performance art and Conceptual art evolved, with notable artists such as Joseph Beuys, Gerhard Richter, Jörg Immendorff, HA Schult, Aris Kalaizis, Neo Rauch (New Leipzig School) and Andreas Gursky (photography). Major art exhibitions and festivals in Germany are the documenta, transmediale and Art Cologne.
Architecture
Vernacular architecture in Germany is often identified by its timber framing traditions, while it offers a great variety of styles and techniques due to its scattered regional history. Architectural contributions from Germany include the Carolingian and Ottonian styles, which were precursors of Romanesque. Brick Gothic is a distinctive medieval style that evolved in Germany. Also in Renaissance and Baroque art, regional and typically German elements evolved (e.g. Weser Renaissance and Dresden Baroque). Among many renowned Baroque masters were Pöppelmann, Balthasar Neumann, Knobelsdorff and the Asam brothers.
When industrialisation spread across Europe, Classicism and a distinctive style of historism developed in Germany, sometimes referred to as Gründerzeit style, due to the economical boom years at the end of the 19th century. Regional historicist styles include the Hanover School, Nuremberg Style and Dresden's Semper-Nicolai School. Resort architecture and Spa architecture are sub-styles that evolved since the 18th century in Germany, with the first modern spas and seaside resorts of Europe. German artists and gallerists also contributed to the development of Art Nouveau at the turn of the 20th century, known as Jugendstil in German.[214]
Expressionist architecture developed in the 1910s in Germany and influenced Art Deco and other modern styles, with e.g. Fritz Höger, Erich Mendelsohn, Dominikus Böhm and Fritz Schumacher being influential architects. Germany was particularly important in the early modernist movement: it is the home of Werkbund initiated by Hermann Muthesius (New Objectivity), and of the Bauhaus movement founded by Walter Gropius. Thus Germany is often considered the cradle of modern architecture and design. Ludwig Mies van der Rohe became one of the world's most renowned architects in the second half of the 20th century. He conceived of the glass façade skyscraper.[215]
Renowned contemporary architects and offices include Hans Kollhoff, Sergei Tchoban, Helmut Jahn, Graft, Behnisch, GMP, Ingenhoven, Sauerbruch Hutton, AWA, Hadi Teherani, Oswald Mathias Ungers, Stephan Braunfels, Anna Heringer, Gottfried Böhm and Frei Otto (the last two being Pritzker Prize winners).[216]




Literature and philosophy

German literature can be traced back to the Middle Ages and the works of writers such as Walther von der Vogelweide and Wolfram von Eschenbach. Well-known German authors include Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Friedrich Schiller, Gotthold Ephraim Lessing and Theodor Fontane. The collections of folk tales published by the Brothers Grimm popularised German folklore on an international level. Influential authors of the 20th century include Gerhart Hauptmann, Thomas Mann, Hermann Hesse, Heinrich Böll and Günter Grass.[217] German-speaking book publishers produce some 700 million books every year, with about 80,000 titles, nearly 60,000 of them new. Germany comes third in quantity of books published, after the English-speaking book market and the People's Republic of China.[218] The Frankfurt Book Fair is the most important in the world for international deals and trading, with a tradition spanning over 500 years,[219] also the Leipzig Book Fair retains a major position in Europe.[220]
German philosophy is historically significant. Gottfried Leibniz's contributions to rationalism; the enlightenment philosophy by Immanuel Kant; the establishment of classical German idealism by Johann Gottlieb Fichte, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel and Friedrich Wilhelm Joseph Schelling; Arthur Schopenhauer's composition of metaphysical pessimism; the formulation of communist theory by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels; Friedrich Nietzsche's development of perspectivism; Gottlob Frege's contributions to the dawn of analytic philosophy; Martin Heidegger's works on Being; and the development of the Frankfurt school by Max Horkheimer, Theodor Adorno, Herbert Marcuse and Jürgen Habermas have been particularly influential. In the 21st century, Germany has contributed to the development of contemporary analytic philosophy in continental Europe.[221]
Cinema

German cinema dates back to the earliest years of the medium, it has made major technical and artistic contributions to film, as with the work of the Skladanowsky Brothers, who showed the first film sequences ever to an audience, in 1895. The renowned Babelsberg Studio in Berlin's suburb Potsdam was established in 1912, and thus was the first large-scale film studio in the world; today it is Europe's largest studio.[222] Early German cinema was particularly influential with German expressionists such as Robert Wiene and Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau. Director Fritz Lang's Metropolis (1927) is referred to as the first major science-fiction film, only predated by the Homunculus series (1916) of Otto Rippert.[223] In 1930 Josef von Sternberg directed The Blue Angel, the first major German sound film.[224] Propaganda films of Leni Riefenstahl came to international fame and were stylistically copied in several productions, especially in post-war advertisements.[225]
During the 1970s and 1980s, New German Cinema directors such as Volker Schlöndorff, Werner Herzog, Wim Wenders, and Rainer Werner Fassbinder put West German auteur cinema on the international stage. Some German movies have had international success, such as Das Boot (1981), The Never Ending Story (1984), Good Bye, Lenin! (2003), Head On (2004), The White Ribbon (2009), Animals United (2010), and Cloud Atlas (2012). The Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film ("Oscar" trophy) went to the German production Die Blechtrommel (The Tin Drum) in 1979, to Nirgendwo in Afrika (Nowhere in Africa) in 2002, and to Das Leben der Anderen (The Lives of Others) in 2007.[226]
The annual European Film Awards ceremony awarding the "Felix" trophy is held every other year in Berlin, home of the European Film Academy (EFA). The Berlin Film Festival, known as "Berlinale", awarding the "Golden Bear" and held annually since 1951, is one of the world's leading film festivals.[227] The "Lolas" are annually awarded also in Berlin, at the German Film Awards, that have been presented since 1951.
Media

The largest internationally operating media companies in Germany are the Bertelsmann enterprise, Axel Springer SE and ProSiebenSat.1 Media. The German Press Agency DPA is also significant.
Germany's television market is the largest in Europe, with some 38 million TV households.[228] Around 90% of German households have cable or satellite TV, with a variety of free-to-view public and commercial channels.[229] The top ten most watched television broadcasts of all-time in Germany all feature the German national football team.[230] Foreign TV shows and other formats are usually dubbed into German.[231] There are more than 500 public and private radio stations in Germany, with the public Deutsche Welle being the main German radio (and television) broadcaster in foreign languages.
Many of Europe's best-selling newspapers and magazines are produced in Germany. The papers with the highest circulation are Die Zeit, Süddeutsche Zeitung, Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung and Die Welt, the largest magazines include Der Spiegel, Stern and Focus. The Bild is a tabloid and has the largest circulation of all German papers.[232]
The German video gaming market is one of the largest in the world.[233] The Gamescom in Cologne is the world's leading gaming convention.[234] Popular game series from Germany include Turrican, the Anno series, The Settlers series, the Gothic series, SpellForce, the FIFA Manager series, Far Cry and Crysis. The most relevant game developers and publishers are Blue Byte, Crytek, Deep Silver, Kalypso Media, Piranha Bytes and Yager Development. Bigpoint, Gameforge, Goodgame and Wooga are leading developers of online and social games.[235]
Cuisine

German cuisine varies from region to region. The southern regions of Bavaria and Swabia, for instance, share a culinary culture with Switzerland and Austria. Across German regions, meat is often eaten as sausages which are produced in almost 1,500 varieties.[236] Organic food has gained a market share of about 4 percent in 2012, and is expected to increase further.[237]
Although wine is becoming more popular in many parts of Germany, especially from German wine regions,[238] the national alcoholic drink is beer. German beer consumption per person is declining, but at 121.4 litres in 2009 it is still among the highest in the world.[239]
The Michelin Guide of 2015 has awarded eleven restaurants in Germany three stars, the highest designation, while 38 more received two stars and 233 one star.[240] Overall, German restaurants have become the world's second-most decorated after France.[241][242]
Sports

Twenty-seven million Germans are members of a sports club and an additional twelve million pursue sports individually.[243] Association football is the most popular sport. With more than 6.3 million official members, the German Football Association (Deutscher Fußball-Bund) is the largest sports organisation of its kind worldwide, and the German top league, the Bundesliga, attracts the second highest average attendance of all professional sports leagues in the world.[243] The German men's national football team won the FIFA World Cup in 1954, 1974, 1990, and 2014 and the UEFA European Championship in 1972, 1980 and 1996. Germany hosted the FIFA World Cup in 1974 and 2006 and the UEFA European Championship in 1988.
Other popular spectator sports include winter sports, boxing, handball, volleyball, basketball, ice hockey, tennis, horse riding and golf. Water sports like sailing, rowing, and swimming are popular in Germany as well.[243]
Germany is one of the leading motor sports countries in the world. Constructors like BMW and Mercedes are prominent manufacturers in motor sport. Porsche has won the 24 Hours of Le Mans race 16 times, and Audi 11 times. The Formula One driver Michael Schumacher has set many motor sport records during his career, having won more Formula One World Drivers' Championships with seven titles, and more Formula One races than any other driver; he is one of the highest paid sportsmen in history.[244] With four championship titles, Sebastian Vettel is also among the top three most successful Formula One drivers of all time.[245]
Historically, German athletes have been successful contenders in the Olympic Games, ranking third in an all-time Olympic Games medal count, combining East and West German medals. In the 2012 Summer Olympics, Germany finished fifth in the medal count, while in the 2006 Winter Olympics they finished first.[246] Germany has hosted the Summer Olympic Games twice, in Berlin in 1936 and in Munich in 1972. The Winter Olympic Games were held in Germany once, in 1936 in Garmisch-Partenkirchen.
Fashion and design

German designers were leaders of modern product design, with the Bauhaus designers like Mies van der Rohe, and Dieter Rams of Braun being essential.[247]
Germany is a leading country in the fashion industry. The German textile industry consisted of about 1,300 companies with more than 130,000 employees in 2010, which generated a revenue of 28 billion Euro. Almost 44 percent of the products are exported. The textile branch thus is the second largest producer of consumer goods after food production in the country.[248] Berlin is the center of young and creative fashion in Germany, prominently displayed at Berlin Fashion Week. It also hosts Europe's largest fashion trade fair called Bread & Butter.
Munich, Hamburg and Düsseldorf are also important design and production hubs of the German fashion industry, among smaller towns.[249] Renowned fashion designers from Germany include Karl Lagerfeld, Jil Sander, Wolfgang Joop, Philipp Plein and Michael Michalsky. Important brands include Hugo Boss, Escada and Triumph, as well as special outfitters like Adidas, PUMA and Jack Wolfskin. The German supermodels Claudia Schiffer, Heidi Klum, Tatjana Patitz and Nadja Auermann came to international fame.[250]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Only the third stanza of the song is used as the national anthem.
- ↑ Danish, Low German, Sorbian, Romany, and Frisian are recognised by the ECRML
- ↑ European Union since 1993.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "Germany". CIA World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ↑ Statistische Ämter des Bundes und der Länder: Bevölkerung Deutschland 2013. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Germany". International Monetary Fund. April 2015. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
- ↑ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income (source: SILC)". Eurostat Data Explorer. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ↑ "2014 Human Development Report Summary" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2014. pp. 21–25. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ↑ Mangold, Max, ed. (1995). Duden, Aussprachewörterbuch (in German) (6th ed.). Dudenverlag. pp. 271, 53f. ISBN 978-3-411-20916-3.
- ↑ "Germany Top Migration Land After U.S. in New OECD Ranking". Bloomberg. 20 May 2014. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
- ↑ The Latin name Sacrum Imperium (Holy Empire) is documented as far back as 1157. The Latin name Sacrum Romanum Imperium (Holy Roman Empire) was first documented in 1254. The full name "Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation" (Heiliges Römisches Reich Deutscher Nation) dates back to the 15th century.
Zippelius, Reinhold (2006) [1994]. Kleine deutsche Verfassungsgeschichte: vom frühen Mittelalter bis zur Gegenwart [Brief German Constitutional History: from the Early Middle Ages to the Present] (in German) (7th ed.). Beck. p. 25. ISBN 978-3-406-47638-9. - ↑ Schulze, Hagen (1998). Germany: A New History. Harvard University Press. p. 4. ISBN 0-674-80688-3.
- ↑ Lloyd, Albert L.; Lühr, Rosemarie; Springer, Otto (1998). Etymologisches Wörterbuch des Althochdeutschen, Band II (in German). Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht. pp. 699–704. ISBN 3-525-20768-9. (for diutisc) Lloyd, Albert L.; Lühr, Rosemarie; Springer, Otto (1998). Etymologisches Wörterbuch des Althochdeutschen, Band II (in German). Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht. pp. 685–686. ISBN 3-525-20768-9. (for diot)
- ↑ "Radiometric dating of the type-site for Homo heidelbergensis at Mauer, Germany". PNAS. 27 August 2010. Retrieved 27 August 2010.
- ↑ "World's Oldest Spears". archive.archaeology.org. 3 May 1997. Retrieved 27 August 2010.
- ↑ "Earliest music instruments found". BBC. 25 May 2012. Retrieved 25 May 2012.
- ↑ "Ice Age Lion Man is world's earliest figurative sculpture". The Art Newspaper. 31 January 2013. Retrieved 31 January 2013.
- ↑ "The Venus of Hohle Fels". donsmaps.com. 14 May 2009. Retrieved 14 May 2009.
- ↑ "Nebra Sky Disc". Unesco memory of the World. 2013.
- ↑ Claster, Jill N. (1982). Medieval Experience: 300–1400. New York University Press. p. 35. ISBN 0-8147-1381-5.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Fulbrook 1991, pp. 9–13.
- ↑ Bowman, Alan K.; Garnsey, Peter; Cameron, Averil (2005). The crisis of empire, A.D. 193–337. The Cambridge Ancient History 12. Cambridge University Press. p. 442. ISBN 0-521-30199-8.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Fulbrook 1991, p. 11.
- ↑ McBrien, Richard (2000). Lives of the Popes: The Pontiffs from St. Peter to Benedict XVI. HarperCollins. p. 138.
- ↑ The lumping of Germanic people into the generic term 'Germans' has its roots in the Investiture Controversy according to historian Herwig Wolfram, who claims it was a defensive move made by the papacy to delineate them as outsiders, partly due to the papacy's insecurity and so as to justify counterattacks upon them. See: Wolfram, Herwig (1997). 'The Roman Empire and its Germanic Peoples. California University Press. pp. 11–13.
- ↑ Fulbrook 1991, pp. 13–24.
- ↑ Nelson, Lynn Harry. The Great Famine (1315–1317) and the Black Death (1346–1351). University of Kansas. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ Fulbrook 1991, p. 27.
- ↑ Philpott, Daniel (January 2000). "The Religious Roots of Modern International Relations". World Politics 52 (2): 206–245. doi:10.1017/S0043887100002604.
- ↑ Macfarlane, Alan (1997). The savage wars of peace: England, Japan and the Malthusian trap. Blackwell. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-631-18117-0.
- ↑ Gagliardo, G (1980). Reich and Nation, The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806. Indiana University Press. pp. 12–13.
- ↑ Fulbrook 1991, p. 97.
- ↑ Henderson, W. O. (January 1934). "The Zollverein". History 19 (73): 1–19. doi:10.1111/j.1468-229X.1934.tb01791.x.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 31.4 31.5 31.6 31.7 31.8 "Germany". U.S. Department of State. 10 November 2010. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ Black, John, ed. (2005). 100 maps. Sterling Publishing. p. 202. ISBN 978-1-4027-2885-3.
- ↑ Fulbrook 1991, pp. 135, 149.
- ↑ Crossland, David (22 January 2008). "Last German World War I Veteran Believed to Have Died". Spiegel Online. Retrieved 25 March 2011.
- ↑ Boemeke, Manfred F.; Feldman, Gerald D.; Glaser, Elisabeth (1998). "Introduction". Versailles: A Reassessment after 75 Years. Publications of the German Historical Institute. Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–20. ISBN 978-0-521-62132-8.
- ↑ Klein, Fritz (1998). "Between Compiègne and Versailles: The Germans on the Way from a Misunderstood Defeat to an Unwanted Peace". In Boemeke, Manfred F.; Feldman, Gerald D.; Glaser, Elisabeth. Versailles: A Reassessment after 75 Years. Publications of the German Historical Institute. Cambridge University Press. pp. 203–220. ISBN 978-0-521-62132-8.
- ↑ Keylor, William R. (1998). "Versailles and International Diplomacy". In Boemeke, Manfred F.; Feldman, Gerald D.; Glaser, Elisabeth. Versailles: A Reassessment after 75 Years. Publications of the German Historical Institute. Cambridge University Press. pp. 469–505. ISBN 978-0-521-62132-8.
- ↑ Fulbrook 1991, pp. 156–160.
- ↑ Williamson (2005). Germany since 1815: A Nation Forged and Renewed. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 186–204.
- ↑ "PROLOGUE: Roots of the Holocaust". The Holocaust Chronicle. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ Fulbrook 1991, pp. 155–158, 172–177.
- ↑ "Ein Konzentrationslager für politische Gefangene In der Nähe von Dachau". Münchner Neueste Nachrichten ("The Munich Latest News") (in German) (The Holocaust History Project). 21 March 1933.
- ↑ "Industrie und Wirtschaft" (in German). Deutsches Historisches Museum. Retrieved 25 March 2011.
- ↑ Fulbrook 1991, pp. 188–189.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 Fulbrook 1991, pp. 190–195.
- ↑ Niewyk, Donald L.; Nicosia, Francis R. (2000). The Columbia Guide to the Holocaust. Columbia University Press. pp. 45–52. ISBN 978-0-231-11200-0.
- ↑ Institute of National Remembrance (Poland), Polska 1939–1945 Straty osobowe i ofiary represji pod dwiema okupacjami. Materski and Szarota. page 9 "Total Polish population losses under German occupation are currently calculated at about 2 770 000".
- ↑ Maksudov, S. (1994). "Soviet Deaths in the Great Patriotic War: A Note". Europe-Asia Studies 46 (4): 671–680.
- ↑ Steinberg, Heinz Günter (1991). Die Bevölkerungsentwicklung in Deutschland im Zweiten Weltkrieg: mit einem Überblick über die Entwicklung von 1945 bis 1990 (in German). Kulturstiftung der dt. Vertriebenen. ISBN 978-3-88557-089-9.
- ↑ "Leaders mourn Soviet wartime dead". BBC News. 9 May 2005. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ↑ Overmans, Rüdiger (2000). Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg. Oldenbourg. ISBN 3-486-56531-1.
- ↑ Winter, JM (2003). "Demography of the war". In Dear, I; Foot, M. The Oxford Companion to World War II (ebook ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780191727603.
- ↑ Overy, Richard (17 February 2011). "Nuremberg: Nazis on Trial". BBC History. Retrieved 25 March 2011.
- ↑ Evans, Richard. "The Other Horror, Review of Orderly and Humane: The Expulsion of the Germans After the Second World War, by R.M. Douglas". New Republic. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ Wise, Michael Z. (1998). Capital dilemma: Germany's search for a new architecture of democracy. Princeton Architectural Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-1-56898-134-5.
- ↑ Carlin, Wendy (1996). "West German growth and institutions (1945–90)". In Crafts, Nicholas; Toniolo, Gianni. Economic Growth in Europe Since 1945. Cambridge University Press. p. 464. ISBN 0-521-49964-X.
- ↑ Werner Bührer (24 December 2002). "Deutschland in den 50er Jahren: Wirtschaft in beiden deutschen Staaten" [Economy in both German states]. Informationen zur Politischen Bildung (256). Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung.
- ↑ maw/dpa (11 March 2008). "New Study Finds More Stasi Spooks". Der Spiegel. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
- ↑ "Germany (East)", Library of Congress Country Study, Appendix B: The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance
- ↑ Protzman, Ferdinand (22 August 1989). "Westward Tide of East Germans Is a Popular No-Confidence Vote". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
- ↑ Kulish, Nicholas (19 June 2009). "In East Germany, a Decline as Stark as a Wall". The New York Times. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ "Gesetz zur Umsetzung des Beschlusses des Deutschen Bundestages vom 20. Juni 1991 zur Vollendung der Einheit Deutschlands" (in German). Bundesministerium der Justiz. 26 April 1994. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ↑ "Brennpunkt: Hauptstadt-Umzug". Focus (in German). 12 April 1999. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ Dempsey, Judy (31 October 2006). "Germany is planning a Bosnia withdrawal". International Herald Tribune. Retrieved 7 May 2011.
- ↑ Merz, Sebastian (November 2007). "Still on the way to Afghanistan? Germany and its forces in the Hindu Kush" (PDF). Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. pp. 2, 3. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ↑ "Germany agrees on 50-billion-euro stimulus plan". France 24. 6 January 2009. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ "Government declaration by Angela Merkel" (in German). ARD Tagesschau. 29 January 2014. Archived from the original on 1 January 2015. Retrieved 15 December 2014.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 "Climate in Germany". GermanCulture. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ "Terrestrial Ecoregions". WWF. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ Strohm, Kathrin (May 2010). "Arable farming in Germany" (PDF). Agri benchmark. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ↑ Bekker, Henk (2005). Adventure Guide Germany. Hunter. p. 14. ISBN 978-1-58843-503-3.
- ↑ Marcel Cleene; Marie Claire Lejeune (2002). Compendium of Symbolic and Ritual Plants in Europe: Herbs. Man & Culture.
The Cornflower was once the floral emblem of Germany (hence the German common name Kaiserblume).
- ↑ "Zoo Facts". Zoos and Aquariums of America. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ↑ "Der Zoologische Garten Berlin" (in German). Zoo Berlin. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ "Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany" (PDF). Deutscher Bundestag. Btg-bestellservice. October 2010. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ↑ "Christian Democratic Union/Christian Social Union". U.S. Library of Congress. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ "Federal Constitutional Court". Bundesverfassungsgericht. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ "§ 2 Strafvollzugsgesetz" (in German). Bundesministerium der Justiz. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ Jehle, Jörg-Martin; German Federal Ministry of Justice (2009). Criminal Justice in Germany. Forum-Verlag. p. 23. ISBN 978-3-936999-51-8.
- ↑ Casper, Gerhard; Zeisel, Hans (January 1972). "Lay Judges in the German Criminal Courts". Journal of Legal Studies 1 (1): 141. doi:10.1086/467481. JSTOR 724014.
- ↑ "The Federal States". Bundesrat of Germany. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ↑ "Example for state constitution: "Constitution of the Land of North Rhine-Westphalia"". Landtag (state assembly) of North Rhine-Westphalia. Archived from the original on 17 January 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ↑ "Kreisfreie Städte und Landkreise nach Fläche und Bevölkerung auf Grundlage des ZENSUS 2011 und Bevölkerungsdichte - Gebietsstand 31.12.2013" (XLS) (in German). Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland. October 2014. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ↑ "Bevölkerungszahlen 2011 und 2012 nach Bundesländern" (in German). Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland. August 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- ↑ "German Missions Abroad". German Federal Foreign Office. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ "The Embassies". German Federal Foreign Office. Retrieved 18 July 2012.
- ↑ "The EU budget 2011 in figures". European Commission. Retrieved 6 May 2011.
- ↑ "United Nations regular budget for the year 2011". UN Committee on Contributions. Retrieved 6 May 2011.
- ↑ "Declaration by the Franco-German Defence and Security Council". French Embassy UK. 13 May 2004. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ Freed, John C. (4 April 2008). "The leader of Europe? Answers an ocean apart". The New York Times. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "Aims of German development policy". Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development. 10 April 2008. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ "Net Official Development Assistance 2009" (PDF). OECD. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ "Speech by Chancellor Angela Merkel to the United Nations General Assembly". Die Bundesregierung. 21 September 2010. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ↑ Harrison, Hope (2004). "American détente and German ostpolitik, 1969–1972" (PDF). Bulletin Supplement (German Historical Institute) 1. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ "Germany's New Face Abroad". Deutsche Welle. 14 October 2005. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ "Ready for a Bush hug?". The Economist. 6 July 2006. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ "U.S.-German Economic Relations Factsheet" (PDF). U.S. Embassy in Berlin. May 2006. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ "The 15 countries with the highest military expenditure in 2011". Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. September 2011. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- ↑ "Grundgesetz für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland, Artikel 65a,87,115b" (PDF) (in German). Bundesministerium der Justiz. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ "Die Stärke der Streitkräfte" (in German). Bundeswehr. 23 March 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2012.
- ↑ 101.0 101.1 "Ausblick: Die Bundeswehr der Zukunft" (in German). Bundeswehr. Retrieved 5 June 2011.
- ↑ "Trends in International Arms Transfer, 2014". www.sipri.org. Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ↑ "Einsatzzahlen – Die Stärke der deutschen Einsatzkontingente" (in German). Bundeswehr. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- ↑ Connolly, Kate (22 November 2010). "Germany to abolish compulsory military service". The Guardian. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
- ↑ Pidd, Helen (16 March 2011). "Marching orders for conscription in Germany, but what will take its place?". The Guardian. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
- ↑ "Frauen in der Bundeswehr" (in German). Bundeswehr. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ↑ "Country Comparison: Exports". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 10 November 2012.
- ↑ "CPI 2009 table". Transparency International. Retrieved 15 May 2012.
- ↑ "The Innovation Imperative in Manufacturing: How the United States Can Restore Its Edge" (PDF). Boston Consulting Group. March 2009. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ "Gross domestic product (2009)" (PDF). The World Bank: World Development Indicators database. World Bank. 27 September 2010. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
Field listing – GDP (official exchange rate) - ↑ "Gross domestic product (2009)" (PDF). The World Bank: World Development Indicators database. World Bank. 27 September 2010. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
Field listing – GDP (PPP exchange rate) - ↑ "Arbeitslosenquote in Deutschland von Mai 2013 bis April 2014".
- ↑ 113.0 113.1 Eurostat: Euro area unemployment rate at 11.2%, Press release of 2 March 2015
- ↑ "Labour productivity levels in the total economy". OECD. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ↑ Andrews, Edmund L. (1 January 2002). "Germans Say Goodbye to the Mark, a Symbol of Strength and Unity". The New York Times. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ↑ Taylor Martin, Susan (28 December 1998). "On Jan. 1, out of many arises one Euro". St. Petersburg Times. p. National, 1.A.
- ↑ Berg, S.; Winter, S.; Wassermann, A. (5 September 2005). "The Price of a Failed Reunification". Spiegel Online. Retrieved 28 November 2006.
- ↑ Germany – The World’s Automotive Hub of Innovation, Germany Trade & Invest, Ernst & Young European Automotive Survey 2013, retrieved 25 April 2015
- ↑ Automotive production statistics of 2013, OICA
- ↑ "Best Global Brands - 2014 Rankings". Interbrand. Archived from the original on 15 March 2015. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ↑ Gavin, Mike (23 September 2010). "Germany Has 1,000 Market-Leading Companies, Manager-Magazin Says". Businessweek. Archived from the original on 30 April 2011. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ "Global 500: Countries – Germany". Forbes. 26 July 2010. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ "Assessment of strategic plans and policy measures on Investment and Maintenance in Transport Infrastructure" (PDF). International Transport Forum. 2012. Retrieved 15 March 2014.
- ↑ "Road density (km of road per 100 sq. km of land area)". World Bank. 2014. Archived from the original on 1 January 2015. Retrieved 7 July 2014.
- ↑ "Autobahn-Temporegelung" (Press release) (in German). ADAC. June 2010. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ "Geschäftsbericht 2006" (in German). Deutsche Bahn. Archived from the original on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ "Airports in Germany". Air Broker Center International. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ↑ "Port of Hamburg authority". The official website of the Port of Hamburg. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ "Overview/Data: Germany". U.S. Energy Information Administration. 30 June 2010. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ↑ "Energy imports, net (% of energy use)". The World Bank Group. Retrieved 18 April 2011.
- ↑ "Renewable energy Germany targets switch to 100% renewables for its electricity by 2050". The Guardian. Reuters Berlin. 7 July 2010. Retrieved 18 April 2011.
- ↑ Ziesing, Hans-Joachim. "Energieverbrauch in Deutschland im Jahr 2014" (PDF) (in German). AG Energiebilanzen. p. 4. Retrieved 10 March 2015.
- ↑ "Germany split over green energy". BBC News. 25 February 2005. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ "Deutschland erfüllte 2008 seine Klimaschutzverpflichtung nach dem Kyoto-Protokoll" (PDF) (Press release) (in German). Umweltbundesamt. 1 February 2010. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ "Germany greenest country in the world". The Times of India. 21 June 2008. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ↑ "Record High 2010 Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Fossil-Fuel Combustion and Cement Manufacture Posted on CDIAC Site". Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center. Retrieved 15 May 2012.
- ↑ Federal Ministry for the Environment (29 March 2012). Langfristszenarien und Strategien für den Ausbau der erneuerbaren Energien in Deutschland bei Berücksichtigung der Entwicklung in Europa und global [Long-term Scenarios and Strategies for the Development of Renewable Energy in Germany Considering Development in Europe and Globally] (PDF). Berlin, Germany: Federal Ministry for the Environment (BMU).
- ↑ "Federal Report on Research and Innovation 2014" (PDF). Federal Ministry of Education and Research. 2014. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize". Nobelprize.org. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ "Swedish academy awards". ScienceNews. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ National Science Nobel Prize shares 1901–2009 by citizenship at the time of the award and by country of birth. From Schmidhuber, J. (2010). "Evolution of National Nobel Prize Shares in the 20th century". Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ Roberts, J. M. (2002). The New Penguin History of the World. Allen Lane. p. 1014. ISBN 978-0-7139-9611-1.
- ↑ "The First Nobel Prize". Deutsche Welle. 8 September 2010. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ "Otto Hahn". FamousScientists.org. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- ↑ "Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize". DFG. Archived from the original on 21 June 2008. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ Bianchi, Luigi. "The Great Electromechanical Computers". York University. Retrieved 17 April 2011.
- ↑ "The Zeppelin". U.S. Centennial of Flight Commission. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ "Historical figures in telecommunications". International Telecommunication Union. 14 January 2004. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- ↑ Roland Berger Strategy Consultants (2010). Green Growth, Green Profit – How Green Transformation Boosts Business. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-28543-9
- ↑ "Preparations for operation of Wendelstein 7-X starting". PhysOrg. 13 May 2014. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) in Greifswald in May started the preparations for operation of this the world's largest fusion device of the stellarator type.
- ↑ "Interim Update" (PDF). UNWTO World Tourism Barometer (UNWTO). April 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "UNWTO Annual Report" (PDF). UNWTO. 2010. Retrieved April 2011.
- ↑ Zahlen Daten Fakten 2012 (in German), German National Tourist Board
- ↑ "Tourism Highlights 2014 edition" (PDF). UNWTO. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ↑ "2013 Travel & Tourism Economic Impact Report Germany" (PDF). WTTC. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ "Top Tourist Attractions of Germany". Germany.Travel, official site. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ↑ 157.0 157.1 157.2 Zensus 2011: Bevölkerung am 9. Mai 2011. Retrieved 1 June 2013.
- ↑ "Country Comparison :: Population". CIA. Retrieved 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "Demographic Transition Model". Barcelona Field Studies Centre. 27 September 2009. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "Birth rate on the rise in Germany". The Local. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ "The New Guest Workers: A German Dream for Crisis Refugees". Spiegel Online. 28 February 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ "More skilled immigrants find work in Germany". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ "German population rises thanks to immigration". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ 164.0 164.1 164.2 "National Minorities in Germany" (PDF). Federal Ministry of the Interior (Germany). May 2010. Article number: BMI10010. Retrieved 23 June 2014.
- ↑ "International Migration 2006" (PDF). UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ↑ Bevölkerung und Erwerbstätigkeit: Bevölkerung mit Migrationshintergrund – Ergebnisse des Mikrozensus 2010, p. 64 statistics
- ↑ "Population and employment: Population with migrant background – Results of the 2010 microcensus" (PDF). 13 March 2012. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ 168.0 168.1 "Publikation — STATmagazin — Population — Families with a migrant background: traditional values count — Federal Statistical Office (Destatis)". Destatis.de. 13 March 2012. Retrieved 4 November 2012.
- ↑ "International Migration 2006" (PDF). UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ↑ "20% of Germans have immigrant roots". Burlington Free Press. 15 July 2010. p. 4A.
- ↑ "Bevölkerung nach Migrationshintergrund" (in German). German Federal Statistical Office. Archived from the original on 29 December 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "Fewer Ethnic Germans Immigrating to Ancestral Homeland". Migration Information Source. February 2004. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ↑ "Regionales Monitoring 2010 – Daten und Karten zu den Europäischen Metropolregionen in Deutschland" (PDF) (in German). Bundesamt für Bauwesen und Raumordnung. 2010. p. 10. Retrieved 11 April 2012.
- ↑ Pressekonferenz „Zensus 2011 – Fakten zur Bevölkerung in Deutschland" am 31. Mai 2013 in Berlin
- ↑ 175.0 175.1 175.2 "Bevölkerung am 9. Mai 2011 Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland Bundesrepublik" (PDF). destatis.de (in German). Federal Statistical Office of Germany. 9 May 2011. p. Zensus 2011 – Page 6. Retrieved 9 May 2011.
- ↑ 176.0 176.1 176.2 "Germany". Berkley Center for Religion, Peace, and World Affairs. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
- ↑ 177.0 177.1 "Chapter 2: Wie viele Muslime leben in Deutschland?". Muslimisches Leben in Deutschland (PDF) (in German). Bundesamt für Migration und Flüchtlinge. June 2009. pp. 80, 97. ISBN 978-3-9812115-1-1. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "Religionen in Deutschland: Mitgliederzahlen" (in German). Religionswissenschaftlicher Medien- und Informationsdienst. 31 October 2009. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ Blake, Mariah (10 November 2006). "In Nazi cradle, Germany marks Jewish renaissance". Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ Schnabel, U. (15 March 2007). "Buddhismus Eine Religion ohne Gott". Die Zeit (in German). Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ 181.0 181.1 European Commission (2006). "Special Eurobarometer 243: Europeans and their Languages (Survey)" (PDF). Europa (web portal). Retrieved 28 March 2011.
European Commission (2006). "Special Eurobarometer 243: Europeans and their Languages (Executive Summary)" (PDF). Europa (web portal). Retrieved 28 March 2011. - ↑ European Commission. "Official Languages". Retrieved 29 July 2014.
- ↑ Marten, Thomas; Sauer, Fritz Joachim, eds. (2005). Länderkunde – Deutschland, Österreich, Schweiz und Liechtenstein im Querschnitt [Regional Geography – An Overview of Germany, Austria, Switzerland and Liechtenstein] (in German). Inform-Verlag. p. 7. ISBN 3-9805843-1-3.
- ↑ European Commission (2004). "Many tongues, one family. Languages in the European Union" (PDF). Europa (web portal). Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "Sprechen Sie Deutsch?". The Economist. 18 March 2010. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ↑ Björn Bertram. "Rankings: Universität Heidelberg in International Comparison". Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ 187.0 187.1 "Country profile: Germany" (PDF). Library of Congress. April 2008. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "A German model goes global". Financial Times. Retrieved 28 September 2014. (registration required (help)).
- ↑ "The Educational System in Germany". Cuesta College. 31 August 2002. Retrieved 16 May 2011.
- ↑ "Top 100 World Universities". Academic Ranking of World Universities. Archived from the original on 22 August 2008. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ Tim Pitman; Hannah Forsyth (18 March 2014). "Should we follow the German way of free higher education?". The Conversation. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ↑ Von Markus Verbeet (18 July 2011). "Mehr Studienanfänger denn je: Jetzt kommt die Flut". Spiegel Online (in German). Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ↑ "Vocational Education and Training — Germany's Dual System as a Role Model?". Deutsche Welle. 2 March 2012. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ↑ "Hospital of the Holy Spirit Lübeck". Lübeck + Travemünde. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ↑ Health Care Systems in Transition: Germany (PDF). European Observatory on Health Care Systems. 2000. p. 8. AMS 5012667 (DEU). Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- ↑ 196.0 196.1 "Core Health Indicators". World Health Organization. Retrieved 6 June 2011.
- ↑ "2010: Herz-/Kreislauferkrankungen verursachen 41 % aller Todesfälle" (in German). Destatis.de. Retrieved 6 April 2012.
- ↑ 198.0 198.1 "Country Profile Germany" (PDF). Library of Congress Federal Research Division. April 2008. Retrieved 7 May 2011.
This article may incorporate text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ Wasser, Jeremy (6 April 2006). "Spätzle Westerns". Spiegel Online International. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "Unbelievable Multitude". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Sites in Germany". UNESCO. Retrieved 3 October 2010.
- ↑ "Human Development Report 2010 Table 4 Gender Inequality Index" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. pp. 156–160. Retrieved 20 April 2011.
- ↑ "Germany extends gay rights". News24. 29 October 2004. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ Heckmann, Friedrich (2003). The Integration of Immigrants in European Societies: national differences and trends of convergence. Lucius & Lucius. pp. 51 ff. ISBN 978-3-8282-0181-1.
- ↑ "Anholt-GfK Nation Brand Index 2013" (Press release). GfK. 14 November 2013. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ↑ "Views of US Continue to Improve in 2011 BBC Country Rating Poll". Worldpublicopinion.org. 7 March 2011. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "BBC poll: Germany most popular country in the world". BBC. 23 May 2013. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "World Service Global Poll: Negative views of Russia on the rise". BBC.co.uk. 4 June 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ↑ MacGregor, Neil (28 September 2014). "The country with one people and 1,200 sausages". BBC. Retrieved 11 December 2014.
- ↑ "Christmas Traditions in Austria, Germany, Switzerland". German Ways. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ↑ "The Recorded Music Industry In Japan" (PDF). Recording Industry Association of Japan. 2013. p. 24. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ↑ "Kraftwerk maintain their legacy as electro-pioneers". Deutsche Welle. 8 April 2011. Retrieved 14 May 2013.
- ↑ Nye, Sean. "Minimal Understandings: The Berlin Decade, The Minimal Continuum, and Debates on the Legacy of German Techno". Journal of Popular Music Studies, Volume 25, Issue 2. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ↑ "Art Nouveau — Art Nouveau Art". Huntfor.com. Retrieved 25 March 2013.
- ↑ A Dictionary of Architecture and Landscape Architecture. Oxford University Press. 2006. p. 880. ISBN 0-19-860678-8.
- ↑ Jodidio, Philip (21 January 2008). 100 Contemporary Architects (1 ed.). Taschen. ISBN 3836500914.
- ↑ Espmark, Kjell (3 December 1999). "The Nobel Prize in Literature". Nobelprize.org. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "Land of ideas". Land-der-ideen.matrix.de. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ Weidhaas, Peter; Gossage, Carolyn; Wright, Wendy A. (2007). A History of the Frankfurt Book Fair. Dundurn Press Ltd. pp. 11 ff. ISBN 978-1-55002-744-0.
- ↑ Chase, Jefferson (13 March 2015). "Leipzig Book Fair: Cultural sideshow with a serious side". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ↑ Searle, John (1987). "Introduction". The Blackwell Companion to Philosophy. Wiley-Blackwell.
- ↑ Studio Babelsberg – Mit der Erschließung des direkt in der Nachbarschaft befindlichen Filmgeländes mit den Studios Neue Film 1 und Neue Film 2 konnte Studio Babelsberg seine Studiokapazitäten verdoppeln und verfügt so über Europas größten zusammenhängenden Studiokomplex., retrieved 3 December 2013 (German)
- ↑ "SciFi Film History – Metropolis (1927)". Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ Bordwell, David; Thompson, Kristin (2003) [1994]. "The Introduction of Sound". Film History: An Introduction (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 204. ISBN 978-0-07-115141-2.
- ↑ Rother, Rainer (1 July 2003). Leni Riefenstahl: The Seduction of Genius. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 1441159010.
- ↑ "Awards:Das Leben der Anderen". IMDb. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "2006 FIAPF accredited Festivals Directory" (PDF). International Federation of Film Producers Associations. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "Distribution of TV in Germany (German)". Astra Sat. 19 February 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- ↑ "Country profile: Germany". BBC News. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ "Allzeitrekord bei TV-Quote mit knapp 35 Millionen".
- ↑ "Hollywood dubbing: The German Bruce Willis and other invisible stars". BBC. 21 February 2013. Retrieved 14 April 2015.
- ↑ "ZDB OPAC - start/text". d-nb.de. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- ↑ Purchese, Robert (17 August 2009). "Germany's video game market". Eurogamer.net. Retrieved 4 March 2012.
- ↑ "Press releases". gamescom Press Center. 2014. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ↑ "Made in Germany: The most important games from Germany (German)". PC Games Hardware. 27 November 2011. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "Guide to German Hams and Sausages". German Foods North America. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ↑ "Numbers, data, facts about the organic food sector (German)". Foodwatch. Retrieved 14 December 2014.
- ↑ "German Wine Statistics". Wines of Germany, Deutsches Weininstitut. Retrieved 14 December 2014.
- ↑ Schneibel, Gerhard (23 April 2010). "Brewers not worried by beer consumption drop". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 6 April 2012.
- ↑ "Michelin Guide restaurants for Germany". Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ↑ "German cuisine beats Italy, Spain in gourmet stars". Reuters. 28 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ "Schnitzel Outcooks Spaghetti in Michelin Guide". Deutsche Welle. 15 November 2007. Retrieved 6 April 2012.
- ↑ 243.0 243.1 243.2 "Germany Info: Culture & Life: Sports". Germany Embassy in Washington, D.C. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ↑ Ornstein, David (23 October 2006). "What we will miss about Michael Schumacher". The Guardian. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ "Vettel makes Formula One history with eighth successive victory". Irish Independent. 17 November 2013.
- ↑ "Turin 2006 Medal Table". International Olympic Committee. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ↑ "Bauhaus: The Single Most Influential School of Design". gizmodo. 13 June 2012. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "BMWI Branchenfokus Textil und Bekleidung". Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ "Die deutsche Mode kommt aus der Provinz". BRIGITTE. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ↑ "German Cultures Today: Fashion Stars - One Germany in Europe". German History Docs GHDI. Retrieved 26 April 2015.
Work cited Fulbrook, Mary (1991). A Concise History of Germany. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-36836-0.
External links
- Official site of the Federal Government
- Official site of the Federal President
- Official site of German Chancellor
- Official Germany Tourism website
- Deutschland.de – Topical website about Germany
- Germany entry at The World Factbook
- Germany at University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Germany at DMOZ
-
 Wikimedia Atlas of Germany
Wikimedia Atlas of Germany -
 Geographic data related to Germany at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Germany at OpenStreetMap



.jpg)


.svg.png)