German war crimes

The government of Germany ordered, organized and condoned a substantial number of war crimes in both World War I and World War II. The most notable of these is the Holocaust in which millions of people were murdered or died from abuse and neglect, 60% of them (approximately 6 million out of 10 million) Jews. However, millions also died as a result of other German actions in those two conflicts. The true number of victims may never be known, since much of the evidence was destroyed by the perpetrators, by burning of bodies, murder of witnesses and destruction of documentation in an attempt to conceal the crimes.
Pre-World War I
The Herero and Namaqua Genocide is considered to have been the first genocide of the 20th century.[2][3][4][5][6] It took place between 1904 and 1907 in German South-West Africa (modern day Namibia), during the scramble for Africa.
On January 12, 1904, the Herero people, led by Samuel Maharero, rebelled against German colonialism. In August, General Lothar von Trotha of the Imperial German Army defeated the Herero in the Battle of Waterberg and drove them into the desert of Omaheke, where most of them died of thirst. In October, the Nama people also rebelled against the Germans only to suffer a similar fate.
In total, from 24,000 up to 100,000 Herero and 10,000 Nama died.[7][8][9][10][11] The genocide was characterized by widespread death by starvation and thirst because the Herero who fled the violence were prevented from returning from the Namib Desert. Some sources also claim that the German colonial army systematically poisoned desert wells.[12][13]
World War I
Chemical weapons in warfare
Poison gas was introduced by Imperial Germany, and was subsequently used by all major belligerents in the war against enemy soldiers, in violation of the 1899 Hague Declaration Concerning Asphyxiating Gases and the 1907 Hague Convention on Land Warfare, which explicitly forbade the use of "poison or poisoned weapons" in warfare.[14][15]
Belgium
In August 1914, as part of the Schlieffen Plan, the German Army invaded and occupied the neutral nation of Belgium without explicit warning, which violated a treaty of 1839 that the German chancellor dismissed as a "scrap of paper" and the 1907 Hague Convention on Opening of Hostilities.[16] Within the first two months of the war, the German occupiers terrorized the Belgians, killing thousands of civilians and looting and burning scores of towns, including Leuven, which housed the country's preeminent university, mainly in fear of Belgian resistance fighters, or francs-tireurs. This action was in violation of the 1907 Hague Convention on Land Warfare provisions that prohibited collective punishment on civilians and looting and destruction of civilian property in occupied territories.[17]
Bombardment of English coastal towns
The raid on Scarborough, Hartlepool and Whitby, which took place on December 16, 1914, was an attack by the Imperial German Navy on the British seaport towns of Scarborough, Hartlepool, West Hartlepool, and Whitby. The attack resulted in 137 fatalities and 592 casualties. The raid was in violation of the ninth section of the 1907 Hague Convention which prohibited naval bombardments of undefended towns without warning,[18] because only Hartlepool was protected by shore batteries.[19] Germany was a signatory of the 1907 Hague Convention.[20] Another attack followed on 26 April 1916 on the coastal towns of Yarmouth and Lowestoft but both were important naval bases and defended by shore batteries.
Unrestricted submarine warfare
Unrestricted submarine warfare was instituted in 1915 in response to the British blockade of Germany in the North Sea. Prize rules, which were codified under the 1907 Hague Convention—such as those that required commerce raiders to warn their targets and allow time for the crew to board lifeboats—were disregarded and commercial vessels were sunk regardless of nationality, cargo, or destination. Following the sinking of the RMS Lusitania on 7 May 1915 and subsequent public outcry in various neutral countries, including the United States, the practice was withdrawn. However, Germany resumed the practice on 1 February 1917 and declared that all merchant ships regardless of nationalities would be sunk without warning. This outraged the U.S. public, prompting the U.S. to break diplomatic relations with Germany two days later, and, along with the Zimmermann Telegram, led the U.S. entry into the war two months later on the side of the Allied Powers.
Attempts to destroy evidence of German crimes
During World War II, after occupying France, Nazis seized Allied documentation regarding German war crimes in World War I and destroyed monuments commemorating them.[21]
World War II
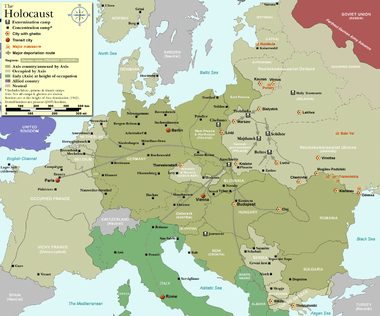


.jpg)
.jpg)


- The Holocaust of the Jews, the Action T4 killing of the disabled and the Porajmos of the Gypsies. Not all the crimes committed during the Holocaust and similar mass atrocities were war crimes. Telford Taylor (The U.S. prosecutor in the German High Command case at the Nuremberg Trials and Chief Counsel for the twelve trials before the U.S. Nuremberg Military Tribunals) explained in 1982:
it should be noted that, as far as wartime actions against enemy nationals are concerned, the [1948] Genocide Convention added virtually nothing to what was already covered (and had been since the Hague Convention of 1899) by the internationally accepted laws of land warfare, which require an occupying power to respect "family honors and rights, individual lives and private property, as well as religious convictions and liberty" of the enemy nationals. But the laws of war do not cover, in time of either war or peace, a government's actions against its own nationals (such as Nazi Germany's persecution of German Jews). And at the Nuremberg war crimes trials, the tribunals rebuffed several efforts by the prosecution to bring such "domestic" atrocities within the scope of international law as "crimes against humanity."—Telford Taylor[22]
- Le Paradis massacre, May 1940, British soldiers of the Royal Norfolk Regiment, captured by the SS and subsequently murdered. Fritz Knoechlein tried, found guilty and hanged.
- Wormhoudt massacre, May 1940, British and French soldiers captured by the SS and subsequently murdered. No one found guilty of the crime.
- Lidice massacre after assassination of Reinhard Heydrich in 1942, when the Czech village was utterly destroyed, and inhabitants murdered.
- Ardenne Abbey massacre,[23] June 1944 Canadian soldiers captured by the SS and Murdered by 12th SS Panzer Division Hitlerjugend. SS General Kurt Meyer (Panzermeyer) sentenced to be shot 1946; sentence commuted; released 1954
- Malmedy massacre, December 1944, United States POWs captured by Kampfgruppe Peiper were murdered outside of Malmedy, Belgium.
- Wereth massacre. 17 December 1944, soldiers from 3./SS-PzAA1 LSSAH captured eleven African-American soldiers from 333rd Artillery Battalion in the hamlet of Wereth, Belgium. Subsequently the prisoners were shot and had their fingers cut off, legs broken, and at least one was shot while trying to bandage a comrade's wounds.
- Gardelegen (war crime) of April 1945 when Nazi concentration camp prisoners were herded into a barn, which was the set alight, killing all inside
- Oradour-sur-Glane
- Massacre of Kalavryta
- Unrestricted submarine warfare against merchant shipping.
- The intentional destruction of major medieval churches of Novgorod, of monasteries in the Moscow region (e.g., of New Jerusalem Monastery) and of the imperial palaces around St. Petersburg (many of them were left by the post-war authorities in ruins or simply demolished).
- The campaign of extermination of Slavic population in the occupied territories. Several thousand villages were burned with their entire population (e.g., Khatyn massacre in Belarus). A quarter of the inhabitants of Belarus did not survive the German occupation.
- Commando Order, the secret order issued by Hitler in October 1942 stating that Allied combatants encountered during commando operations were to be executed immediately without trial, even if they were properly uniformed, unarmed, or intending to surrender.
- Commissar Order, the order from Hitler to Wehrmacht troops before the invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941 to shoot Commissars immediately on capture
- Nacht und Nebel decree of 1941 for disappearance of prisoners
War criminals
- List of Axis war criminals
- List of Wikipedia Nazi doctors
- Adolf Eichmann
- Heinrich Gross
- Hans Heinze
- Rudolf Hoess
- Karl Linnas
- Josef Mengele
- Otmar Freiherr von Verschuer
- Alfred Trzebinski
Massacres and war crimes of World War II by location
Austria
- Murders of children by Heinrich Gross
Belarus
- The Holocaust in Belarus
- Anti-partisan operations in Belarus
- Operation Bamberg
- Operation Cottbus
1941
- 28 September – 17 October, Pleszczenice-Bischolin-Szack (Šacak)-Bobr-Uzda (White Ruthenia) massacre (1,126 children)
1942
- 26 March – 6 April, Operation Bamberg (Hłusk, Bobrujsk; 4,396 people, including children)
- 9 – 12 May, Kliczów-Bobrujsk massacre (520 people, including children)
- Beginning of June, Słowodka-Bobrujsk massacre (1,000 people, including children)
- 15 June Borki (powiat białostocki) massacre (1,741 people, including children)
- 21 June Zbyszin massacre (1,076 people, including children)
- 25 June Timkowiczi massacre (900 people, including children)
- 26 June Studenka massacre (836 people, including children)
- 18 July, Jelsk massacre (1,000 people, including children)
- 15 July – 7 August, Operation Adler (Bobrujsk, Mohylew, Berezyna; 1,381 people, including children)
- 14 – 20 August, Operation Greif (Orsza, Witebsk; 796 people, including children)
- 22 August – 21 September, Operation Sumpffieber (White Ruthenia; 10,063 people, including children)
- August, Bereźne massacre
- 22 September – 26 September, Małoryta massacre; 4,038 people, including children)
- 23 September – 3 October, Operation Blitz (Połock, Witebsk; 567 people, including children)
- 11 – 23 October, Operation Karlsbad (Orsza, Witebsk; 1,051 people, including children)
- 23 – 29 November, Operation Nürnberg (Dubrowka; 2,974 people, including children)
- 10 – 21 December, Operation Hamburg (Niemen River-Szczara River; 6,172 people, including children)
- 22 – 29 December, Operation Altona (Słonim; 1,032 people, including children)
1943
- 6 – 14 January, Operation Franz (Grodsjanka; 2,025 people, including children)
- 10 – 11 January, Operation Peter (Kliczów, Kolbcza; 1,400 people, including children)
- 18 – 23 January, Słuck-Mińsk-Czerwień massacre (825 people, including children)
- 28 January – 15 February, Operation Schneehase; Połock, Rossony, Krasnopole; 2,283 people, including children); 54; 37
- Until 28 January, Operation Erntefest I (Czerwień, Osipowicze; 1,228 people, including children)
- Jaanuar, Operation Eisbär (between Briańsk and Dmitriev-Lgowski)
- Until 1 February, Operation Waldwinter (Sirotino-Trudy; 1,627 people, including children)
- 8 – 26 February, Operation Hornung (Lenin, Hancewicze; 12,897 people, including children)
- Until 9 February, Operation Erntefest II (Słuck, Kopyl; 2,325 people, including children)
- 15 February – end of March, Operation Winterzauber (Oświeja, Latvian border; 3,904 people, including children)
- 22 February – 8 March, Operation Kugelblitz (Połock, Oświeja, Dryssa, Rossony; 3,780 people, including children)
- Until 19 March, Operation Nixe (Ptycz, Mikaszewicze, Pińsk; 400 people, including children)
- Until 21 March, Operation Föhn (Pińsk; 543 people, including children)
- 21 March – 2 April, Operation Donnerkeil (Połock, Witebsk; 542 people, including children)
- 1 – 9 May, Operation Draufgänger II (Rudnja and Manyly forest; 680 people, including children)
- 17 – 21 May, Operation Maigewitter (Witebsk, Suraż, Gorodok; 2,441 people, including children)
- 20 May – 23 June, Operation Cottbus (Lepel, Begomel, Uszacz; 11,796 people, including children)
- 27 May – 10 June, Operation Weichsel (Dniepr-Prypeć triangle, South-West of Homel; 4,018 people, including children)
- 13 – 16 June, Operation Ziethen (Rzeczyca; 160 people, including children)
- 25 June – 27 July, Operation Seydlitz (Owrucz-Mozyrz; 5,106 people, including children)
- 30 July, Mozyrz massacre (501 people, including children)
- Until 14 July, Operation Günther (Woloszyn, Lagoisk; 3,993 people, including children)
- 13 July – 11 August, Operation Hermann (Iwie, Nowogródek, Woloszyn, Stołpce; 4,280 people, including children)
- 24 September – 10 October, Operation Fritz (Głębokie; 509 people, including children)
- 9 October – 22 October, Stary Bychów massacre (1,769 people, including children)
- 1 November – 18 November, Operation Heinrich (Rossony, Połock, Idrica; 5,452 people, including children)
- December, Spasskoje massacre (628 people, including children)
- December, Biały massacre (1,453 people, including children)
- 20 December – 1 January 1944, Operation Otto (Oświeja; 1,920 people, including children)
1944
- 14 January, Oła massacre (1,758 people, including children)
- 22 January, Baiki massacre (987 people, including children)
- 3 – 15 February, Operation Wolfsjagd (Hłusk, Bobrujsk; 467 people, including children)
- 5 – 6 February, Barycz (near Buczacz) massacre (126 people, including children)
- Until 19 February, Operation Sumpfhahn (Hłusk, Bobrujsk; 538 people, including children)
- Beginning of March, Berezyna-Bielnicz massacre (686 people, including children)
- 7 – 17 April, Operation Auerhahn (Bobrujsk; c. 1,000 people, including children)
- 17 April – 12 May, Operation Frühlingsfest (Połock, Uszacz; 7,011 people, including children)
- 25 May – 17 June, Operation Kormoran; Wilejka, Borysów, Minsk; 7,697 people, including children)
- 2 June – 13 June, Operation Pfingsrose (Talka; 499 people, including children)
- June, Operation Pfingstausnlug (Sienno; 653 people, including children)
- June, Operation Windwirbel (Chidra; 560 people, including children)
Estonia
- The Holocaust in Estonia
- Murders of children by Karl Linnas
1941
- 2 November, Mass murder of children in Pärnu synagogue (34 children)
1942
- 27 March Murder of Pliner children (Holocaust in Estonia; 3 children)
France


- Le Paradis massacre
- Wormhoudt massacre
- Murders of children in the Drancy internment camp
- Maillé massacre
- Maillé, Indre-et-Loire
- Oradour-sur-Glane
- Tulle murders
1944
- 10 June, Oradour-sur-Glane massacre (205 children)
- Ardenne Abbey massacre of British and Canadian troops by Waffen-SS
- Ascq massacre April 1944
Germany

- Action T4
- Murders of children in the Hadamar Clinic (NS-Tötungsanstalt Hadamar) mostly by Irmgard Huber
- Murders of children by Hans Heinze
- Otmar Freiherr von Verschuer#Involvement in Nazi human experimentation
1945
- 8 April - The Celle Massacre
- 13 April - Gardelegen Massacre
- 20 April - Murder of 20 children by Alfred Trzebinski
Greece
(see also List of massacres in Greece)
- Massacre of Kondomari (Crete, 60 men, mainly elder)
- Razing of Kandanos (Crete, 180, including women children)
- Holocaust of Viannos (Crete, 500+, including women children)
- Distomo massacre (Central Greece, 218, including women children)
- Drakeia massacre (Thessaly, 118 men)
- Holocaust of Kedros (Crete, 164, including women children)
- Kommeno (Epirus, 317, including women children)
- Massacre of Kalavryta (Peloponnese, 1,200+, including women children)
- Massacre of the Acqui Division (Kefalonia, 5,000, Italian anti-fascist troops)
- Mesovouno massacre (Macedonia, 268, including women and children)
- Paramythia executions (Epirus, 201, including women children)
- The Massacre of Chortiatis (Macedonia, 146, including women children)
- Executions of Kaisariani (Athens, 200+, all civilians)
- Massacre of Mousiotitsa (Epirus, 153, including women children)
- Executions of Kokkinia (Athens, 300+, all civilians, assisted by Security Battalions)
- Alikianos executions (Crete, 118, all civilians)
- Razing of Anogeia (Crete, unknown, including women and children)
In addition, more than 90 villages and towns are recorded from the Hellenic network of martyr cities.[24] During the triple German, Italian and Bulgarian, occupation about 800,000 people lost their lives in Greece (see World War II casualties).
Italy

- List of massacres in Italy
- Ardeatine massacre
- Boves massacre
- Marzabotto massacre
- Sant'Anna di Stazzema massacre
1944
- 29 June, Civitella-Cornia-San Pancrazio massacre (Tuscany; 203 people, including children)
- 12 August, Sant'Anna di Stazzema massacre (560 people, including children)
- 29 September – 5 October, Marzabotto massacre (250 children)
Latvia
1941
- 30 November and 8 December, Rumbula massacre (25,000 people, including children)[25]
Lithuania
1941
- 13 July – 21 August Daugavpils massacre by Einsatzkommando 3 (9,585 people, including children)[26]
- July – August 1944, Ponary massacre (c. 100,000 people, including children)
- 18 August – 22 August, Kreis Rasainiai massacre (1,020 children)
- 19 August, Ukmerge massacre (88 children)
- Summer-autumn-winter, Complete murder of native Jewish population in Estonia (900 individuals, including 101 children)
- 1 September, Marijampolė massacre (1,404 children)
- 2 September, Wilno massacre (817 children)
- 4 September, Čekiškė massacre (60 children)
- 4 September, Seredžius massacre (126 children)
- 4 September, Veliuona massacre (86 children)
- 4 September, Zapyškis massacre (13 children)
- 6 September – 8 September, Raseiniai massacre (415 children)
- 6 September – 8 September, Jurbork massacre (412 people, including children)
- 29 October, Kaunas massacre (4,273 children)
- 25 November, Kauen-F.IX massacre (175 children)
Netherlands
1940
- 14 October, Rotterdam bombing (nearly 1,000 people were killed and 85,000 made homeless.)
1944
- 1 October, Putten raid (552 deaths)
- 5 November, Heusden Town Hall Massacre (134 people, including 74 children)
Norway
- Attempted deportation of children of Jewish Children's Home in Oslo
Poland
- The Holocaust in Poland
- Borów massacre (103 children)
- Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany
- German AB-Aktion in Poland
- Gmina Aleksandrów, Lublin Voivodeship
- Gmina Besko
- Gmina Gidle
- Gmina Kłecko
- Gmina Ryczywół
- Gmina Siennica
- Huta Pieniacka massacre
- Intelligenzaktion Pommern
- Jedwabne pogrom
- Jeziorko woodland cemetery
- Kidnapping of Polish children by Nazi Germany
- Krasowo-Częstki massacre (83 children)
- Lviv pogroms
- Massacres of Poles in Volhynia
- Michniów massacre (48 children)
- Murders of children by Josef Mengele
- Pacification Operations in German occupied Poland
- Planned destruction of Warsaw
- Ponary massacre
- Operation Tannenberg
- Szczecyn massacre (71 children)
- Valley of Death (Bydgoszcz)
1942
- 2 July, murder of children of Lidice in the Kulmhof extermination camp (82 children)
1943
- 12 March, Murder of Czesława Kwoka in KZ Auschwitz-Birkenau (1 child)
- 23 May, Kielce cemetery massacre (45 children)
- 3 August, Szczurowa massacre (93 people, including children)
- 29 September, Ostrówki massacre (246 children)
- 29 September, Wola Ostrowiecka massacre (220 children)
1944


- 28 February, Huta Pieniacka massacre
- 28 – 29 February, Korosciatyn Massacre (c. 150 people, including children)
- 2 June, Murder of Yekusiel Yehudah Halberstam's children (9 children)
- 4–August 25, Ochota massacre (c. 10,000 people, including children)
- 5 – 8 August, Wola massacre (40,000[27] up to 100,000[28] people, including children)
Russia
- The Holocaust in Russia
- Commissar Order
- German war crimes during the Battle of Moscow
- German war crimes against Soviet civilians
Serbia
1941
- 20–21 October Kragujevac massacre (2300-5000 civilians killed, including 217 children)
Ukraine
- The Holocaust in Ukraine
- Babi Yar
- Drobytsky Yar
- Lviv pogroms
- Massacres of Poles in Volhynia
1941
- June, Czechow massacre (6 children)
- 29 – 30 September, Babi Jar massacre (33,771 people, including children: List of victims of the Babi Yar massacre)
1943
- 1 – 2 March 1943, Koriukivka massacre
- 29 September, Wola Ostrowiecka massacre (220 children)
1944
- 28 February, Huta Pieniacka massacre
- 28 – 29 February, Korosciatyn Massacre (c. 150 people, including children)
-

Asperg. Sinti and Roma people about to be deported, 22 May 1940.
-

Asperg. Sinti and Roma children about to be deported, 22 May 1940.
-
Iaşi. Jewish bodies, 29 June 1941.
-

Reichskommissariat Moskau. Jewish women and children been forced out of their homes. A soldier in Romanian uniform is marching along as a guard, 17 July 1941.
-

Members of the 21st Latvian Police Battalion assemble a group of Jewish women for execution on a beach near Liepāja, 1941.
-

Warsaw ghetto, 1940/1943.
-

Warsaw Ghetto Uprising – Photo from Jürgen Stroop Report to Heinrich Himmler from May 1943. The original German caption reads: "Askaris used during the operation". Two Askari or Trawniki guards, peer into a doorway past the bodies of Jewish children killed during the suppression of the Warsaw ghetto uprising.
-

Eichmann and his officers were responsible for the murder of most of the Jewish population in the ghettos of the territory of Czechoslovakia, and for the transport of men, women and children of all nationalities to extermination camps, for example KZ Auschwitz-Birkenau, May–June 1944.
-

Polish civilians murdered by German SS forces (Oskar Dirlewanger) in Warsaw Uprising, August 1944.
-

Collecting bodies after bombing, during Warsaw Uprising. Picture of the courtyard of Tamka 23 street where Tomaszewski was taken after being wounded on 8 September 1944.
-

Minsk, 1941/1944.
-

This boy's dead, burning body shows damage done by a V-2 on a main intersection in Antwerp, on a main supply line to the Netherlands, 1944.
-

The bodies of Belgian men, women, and children, killed by the German military during their counter-offensive into Luxembourg and Belgium, await identification before burial, 1944.
-
Ghetto Litzmannstadt: Children rounded up for deportation to the Kulmhof extermination camp.
-
Memorial to the murdered children of Lidice.
Sources
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Child Holocaust victims. |
- United States Holocaust Memorial Museum – Article Children during the Holocaust; and online exhibitions Life in the Shadows; and Give Me Your Children
- Holocaust Memorial Album Honoring more than 1.5 Million Souls Under 12 years of age that never returned ... from Holocaust Survivors and Remembrance Project: "Forget You Not"
- Children and the Holocaust
- Nazis kidnap Polish children
Notes
- This article incorporates text from the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, and has been released under the GFDL.
See also
- War crimes of the Wehrmacht
- Nazi crime
- Anti-German sentiment
- Allied war crimes during World War II
- Bombing of Guernica
- British war crimes
- Command responsibility
- Consequences of German Nazism
- Einsatzgruppen
- Generalplan Ost
- German concentration camps
- Italian war crimes
- Japanese war crimes
- German American internment
- List of Axis war criminals
- List of war crimes
- Nazi crimes against ethnic Poles
- Nazi Germany
- Pacification operations in German-occupied Poland
- Soviet war crimes
- United States war crimes
- War crimes trials
- War of Extermination: Crimes of the Wehrmacht 1941-1944
- World War II atrocities in Poland
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to War crimes. |
References
- ↑ Maltz, Judy (Mar 3, 2011). "A picture worth six million names". Haaretz. Retrieved 2013-07-20.
- ↑ Olusoga, David and Erichsen, Casper W (2010). The Kaiser's Holocaust. Germany's Forgotten Genocide and the Colonial Roots of Nazism. Faber and Faber. ISBN 978-0-571-23141-6
- ↑ Levi, Neil; Rothberg, Michael (2003). The Holocaust: Theoretical Readings. Rutgers University Press. p. 465. ISBN 0-8135-3353-8.
- ↑ Mahmood Mamdani, When Victims Become Killers: Colonialism, Nativism, and the Genocide in Rwanda, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 2001, p. 12
- ↑ Allan D. Cooper (2006-08-31). "Reparations for the Herero Genocide: Defining the limits of international litigation". Oxford Journals African Affairs.
- ↑ "Remembering the Herero Rebellion". Deutsche Welle. 2004-11-01.
- ↑ Colonial Genocide and Reparations Claims in the 21st Century: The Socio-Legal Context of Claims under International Law by the Herero against Germany for Genocide in Namibia, 1904-1908 (PSI Reports) by Jeremy Sarkin-Hughes
- ↑ Empire, Colony, Genocide: Conquest, Occupation and Subaltern Resistance in World History (War and Genocide) (War and Genocide) (War and Genocide) A. Dirk Moses -page 296(From Conquest to Genocide: Colonial Rule in German Southwest Africa and German East Africa. 296, (29). Dominik J. Schaller)
- ↑ The Imperialist Imagination: German Colonialism and Its Legacy (Social History, Popular Culture, and Politics in Germany) by Sara L. Friedrichsmeyer, Sara Lennox, and Susanne M. Zantop page 87 University of Michigan Press 1999
- ↑ Walter Nuhn: Sturm über Südwest. Der Hereroaufstand von 1904. Bernard & Graefe-Verlag, Koblenz 1989. ISBN 3-7637-5852-6.
- ↑ Marie-Aude Baronian, Stephan Besser, Yolande Jansen, "Diaspora and memory: figures of displacement in contemporary literature, arts and politics", pg. 33 Rodopi, 2007,
- ↑ Samuel Totten, William S. Parsons, Israel W. Charny, "Century of genocide: critical essays and eyewitness accounts" pg. 51, Routledge, 2004,
- ↑ Dan Kroll, "Securing our water supply: protecting a vulnerable resource", PennWell Corp/University of Michigan Press, pg. 22
- ↑ Telford Taylor (November 1, 1993). The Anatomy of the Nuremberg Trials: A Personal Memoir. Little, Brown and Company. ISBN 0-3168-3400-9. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ↑ Thomas Graham, Damien J. Lavera (May 2003). Cornerstones of Security: Arms Control Treaties in the Nuclear Era. University of Washington Press. pp. 7–9. ISBN 0-2959-8296-9. Retrieved 5 July 2013.
- ↑ Robinson, James J., ABA Journal 46(9), p. 978.
- ↑ Spencer C. Tucker, Priscilla Mary Roberts (October 25, 2005). World War I: A Student Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 1074. ISBN 1-8510-9879-8.
- ↑ Logan Marshall (1915). Horrors and atrocities of the great war: Including the tragic destruction of the Lusitania: A new kind of warfare: Comprising the desolation of Belgium: The sacking of Louvain: The shelling of defenseless cities: The wanton destruction of cathedrals and works of art: The horrors of bomb dropping: Vividly portraying the grim awfulness of this greatest of all wars fought on land and sea: In the air and under the waves: Leaving in its wake a dreadful trail of famine and pestilence. Retrieved 5 July 2013.
- ↑ Chuter, David (2003). War Crimes: Confronting Atrocity in the Modern World. London: Lynne Rienner Pub. p. 300. ISBN 1-58826-209-X.
- ↑ Willmore, John (1918). The great crime and its moral. New York: Doran. p. 340.
- ↑ France: the dark years, 1940-1944 page 273 Julian Jackson Oxford University Press 2003
- ↑ Telford Taylor "When people kill a people" in The New York Times, March 28, 1982
- ↑ "Home - Veterans Affairs Canada". Vac-acc.gc.ca. 2012-03-29. Retrieved 2012-07-09.
- ↑ {{http://www.lamia.gr/el/content/diktyo}}
- ↑ "Complete tabulation of executions carried out in the Einsatzkommando 3 zone up to 1 December 1941". Holocaust-history.org. Retrieved 2012-05-04.
- ↑ "Gesamtaufstellung der im Bereich des EK. 3 bis zum 1. Dez. 1941 durchgeführten Exekutionen". Holocaust-history.org. 2002-09-28. Retrieved 2012-05-04.
- ↑ Muzeum Powstania otwarte, BBC Polish edition, 2 October 2004, Children accessed on 13 April 2007
- ↑ O Powstaniu Warszawskim opowiada prof. Jerzy Kłoczowski, Gazeta Wyborcza – local Warsaw edition, 1998-08-01. Children accessed on 13 April 2007
Further reading
External links
- Movie (on-line)
- Poland under German occupation 1939-1945 on YouTube
- The Atrocities committed by German-Fascists in the USSR


