German Green Belt
The German Green Belt (Grünes Band Deutschland in German) is a project of Bund Naturschutz (BUND), one of Germany's largest environmental groups. The project began in 1989 facing a forbidding, 870-mile network of fences and guard towers once ran the length of Germany, separating East and West. Now, one of the world’s most unique nature reserves is being created along the old “Death Strip,” turning a monument to repression into a symbol of renewal.[1]
East and West Border
Construction and Purpose
The Berlin Wall (German: Berliner Mauer) was a barrier that divided Berlin from 1961 to 1989,[1] constructed by the German Democratic Republic (GDR, East Germany) starting on 13 August 1961, that completely cut off (by land) West Berlin from surrounding East Germany and from East Berlin until it was opened in November 1989.[2] In practice, the Wall served to prevent the massive emigration and defection that marked East Germany and the communist Eastern Bloc during the post-World War II period.
Becoming the "Green Belt"
History
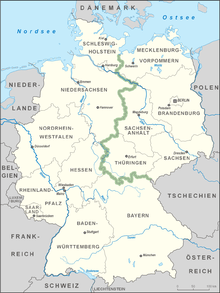
On the former inner German border, there is a strip of land approximately 1400 km long (with an area of more than 100 km²) that remained nearly untouched since the construction of the Berlin Wall. The government of GDR wanted a distance between the fence and the actual border, in order to arrest or even shoot people who managed to pass the fence. It stretches from Travemünde on the Baltic to the Czech border, near Hof in Bavaria. A number of endangered species can be found there.
Planning and Implementation
The Bund Naturschutz wants to exert pressure on the Bundesländer to designate several areas as nature reserves and has appealed for donations from the public to enable Bund Naturschutz to acquire properties along the Green Belt.
In 2001 and 2002, the areas and the different species living there were catalogued, with financial support from the German Federal Ministry of the Environment. At a conference on "Perspectives of the Green Belt" in Bonn in July 2003, Mikhail Gorbachev became the patron of the project. There is also the wider vision of a European Green Belt.
2005 the planned transfer of the land to five German states was part of the coalition agreement. 2008, the plan was successfully implemented in Thuringia. The 763 km long section of the Green Belt in the state of Thuringia has its own mission statement for conservation and design.
The negotiations between the German Federal Government and the states of Brandenburg, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt have not yet been completed. Regardless the BUND acquired private property in the Green Belt, which formed a total of 580 acres in 2011.
Route
Beyond the German Borders
Extension of the Green Belt beyond the German borders to reflect the larger "Iron Curtain" of the former Soviet states.
Conservation
There are a number of valuable habitats in the Green Belt. The Whinchat, the red-backed Shrike, the Black Stork, the Kingfisher and the European Otter are some of the species that can be found there.
See also
References
- ↑ schwägerl, Christian. http://e360.yale.edu/feature/along_scar_from_iron_curtain_a_green_belt_rises_in_germany/2390/. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
External links
- www.bund.net - Bund Naturschutz webpage about the Green Belt (German)
