Geography of Kosovo
| Geography of Kosovo | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Continent | Europe |
| Region | Balkans |
| Coordinates | 42°36′00″N 20°51′00″E / 42.6000°N 20.8500°E |
| Area | Ranked 166th |
| • Total | 10.908 km2 (4.212 sq mi) |
| • Land | 99% |
| • Water | 1% |
| Borders | |
| Highest point |
Gjeravica, 2,656 m (8,714 ft) |
| Lowest point |
White Drin, 297 m (974 ft) |
| Longest river |
White Drin, 122 km (76 mi) |
| Largest lake |
Lake Gazivoda 9.2 km2 (4 sq mi) |
| Climate | Continental |
| Terrain | Mountainous |
| Natural Resources | coal, zinc, lead, silver, chromium, etc. |
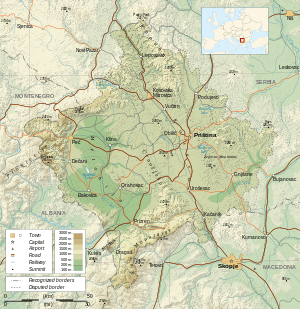
Kosovo is a landlocked country situated in Southeastern Europe, in the center of Balkan Peninsula. With an area of 10.908 km2 (4 sq mi), it is one of the smallest countries in Europe by area, but one of the most populated, with a population of 1,859,203 (2014 estimate) inhabitants (159/km2).
Considering its small size, Kosovo has a great variety of topographical features. It is surrounded by mountains: the Sharr Mountains are located in the south and southeast, bordering Macedonia, while the Kopaonik Mountains rise in the north. The southwest borders with Montenegro and Albania are also mountainous, and are home to the country's highest peak, Gjeravica, 2,656 m (8,714 ft) high. The central region is mainly hilly, but two large plains spread over Kosovo's west and east, respectively, Metohija plain and Kosovo plain.[1]
In the terms of hydrography, Kosovo has limited water resources. The main rivers in the country are the White Drin, running towards the Adriatic Sea, the South Morava in the Goljak area, and Ibar in the north. Sitnica, a tributary of Ibar, is the longest river lying completely within Kosovo. There are several small natural lakes but the country's most important lakes are artificial. The biggest lakes are Gazivoda, Radonjić, Batlava and Badovac. Kosovo also does have a large number of karst springs, thermal and mineral water springs.[2]
Area and boundaries
Kosovo is in the central part of the Western Balkans, Southeastern Europe and it borders Albania to the southwest, Macedonia to the southeast, Montenegro to the west, and Serbia to the north and east. It lies between latitudes 42° and 43° N, and longitudes 20° and 22° E.[3]

The total surface of the territory of Kosovo is 10.908 km2 (4 sq mi), making it the 169th largest country in the world,[3] with a border length as follows:
| Length of borders of Kosovo .[4] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Length | ||
| Albania | 113.551 km (70.557 mi) | ||
| Republic of Macedonia | 170.772 km (106.113 mi) | ||
| Montenegro | 79.165 km (49.191 mi) | ||
| Serbia | 380.068 km (236.163 mi) | ||
| Total | 743.556 km (462.024 mi) | ||
Elevation extremes:
- highest point: Gjeravica 2,656 m (8,714 ft)
- lowest point: White Drin River 297 m (974 ft)
Topography


Although Kosovo has relatively small territory it has a very varied relief. Framed along its borders by high mountain ranges, such as Sharr Mountains to the south and southeast, Prokletije to the west, Kopaonik to the north and Goljak to the east, Kosovo's relief is clearly defined by two main plains in the inner part, Dukagjini to the south-west and Kosovo plain to the north-eastern part. Between Dukagjini and Kosovo plains, in the center of the country, is located Drenica Valley, a smaller hilly region surrounded by Çiçavica mountains to the northeast and Kozmaç to the southwest. There are also several other small valleys like Anamorava, Podujevo valley, Ibar Valley, etc.
Sharr mountain range
The Šar Mountains are located in the south and south-east of the country, bordering the Republic of Macedonia and Albania. With an area of 1100 km2, they represent approximately 1/10 part of total Kosovo territory.[5] The mountains border the Kosovo Plain to the north-east through the valley of the River Lepenci while in the north-west Lumëbardh of Prizren river defines the boundary with Dukagjini Valley. Sharr mountain range extends to Macedonia in southern part and also to Albania in south-west.
This is one of the region's most popular tourist and skiing resorts, with Brezovica and Prevalac as the main tourist centres. Most of the territory of Sharr mountains in Kosovo is declared as National Park.
Accursed Mountains

The region of Kosovo's mountainous area, including the highest peak Gjeravica, at 2,656 m (8,714 ft) above sea level, is located in the south-west and western part of the country, bordering Albania and Montenegro.
Kopaonik Mountain Range
The Kopaonik mountains are located in the north. The central region of Drenica, Crnoljeva and the eastern part of Kosovo, known as Goljak, are mainly hilly areas.
Plains
There are two main plains in Kosovo. The Metohija basin is located in the western part of the Kosovo, and the Plain of Kosovo occupies the eastern part. Between the two basins there is low hills area of Drenica.
The plain of Kosovo is on average higher that the plain of Metohija for about 100 metres (328 ft).
Average height of the plain of Kosovo is 550 m (1,804 ft) and the average height of the plain of Metohija is 450 m (1,476 ft).
Rugova Valley and Canyon
One of Kosovo's most prominent geological features is the Rugova Canyon in the Alpet Shqiptare. The 25 km (16 mi) long canyon near the border with Montenegro was formed by the flow of the Pećka Bistrica. The canyon was declared a Protected National Monument in 1988, and will be included in a proposed Bjeshket e Nemuna/Prokletije National Park, approved by the Kosovo Parliament in 2003.
Gadime Cave
Gadime Cave is a cave composed of Paleozoic marble, located in the village of Donje Gadimje on the eastern side of the Kosovo Valley. The northern passage contains displays of aragonite speleothems in a variety of rare formations.[6][7]
Bodies of water
Although Kosovo is landlocked, there are several notable rivers and lakes within its borders. The main rivers are the White Drin, running towards the Adriatic Sea, with the Erenik among its tributaries, the Sitnica, the South Morava in the Goljak area, and Ibar in the north. The main lakes are Gazivoda Lake (380 million m³) in the north-western part, Radoniq lake (113 million m³) in the south-west part, Batlava Lake (40 million m³) and Badovc Lake (26 million m³) in the north-east part. Other smaller scenic lakes include Zemra Lake, Đeravica Lake and Liqenat Lake. Kosovo is also home to the following waterfalls:
- The 25 metres (82 ft) Drin Waterfall is located at the mouth of the White Drin River.
- The Mirusha Waterfalls are a series of falls on the Miruša River (a tributary of the Drin) in the municipality of Mališevo in western Kosovo, on the Metohija region.
In the Bifurcation of Nerodimka river, it contains the only example in Europe (and one of only two in the world) where a river divides with the resultant water flows ending up in different seas (the Black Sea and the Aegean)
Climate
Kosovo is located between the Mediterranean Sea and mountainous regions of Southeast Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. This geographic location gives the country its large annual temperature range. Summer temperature highs can reach +30 °C (86 °F), winter's temperatures as low as −10 °C (14 °F).[8] According to the Strahler classification map the climate in Kosovo is considered moist continental.[9] The country experiences warm summers and cold and snowy winters.
See also
References
- ↑ Kosovo Travel Guid
- ↑ Independent Commission for Mines and Minerals of Kosovo
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 , CIA - The World Factbook
- ↑
- ↑ http://www.parksdinarides.org/en/kosovo/sharri
- ↑ Mermerna Pecina, Tony Oldham, 2002
- ↑ Around Kosovo: It's Better to See it Once Than Hear About it 100 Times, Valerii Petrushka
- ↑ Geography
- ↑ Strahler & Strahler. (2006).Introducing Physical Geography, Boston:John Wiley & Sons Inc.
External links
-
 Wikimedia Atlas of Kosovo
Wikimedia Atlas of Kosovo -
 Geography of Kosovo travel guide from Wikivoyage
Geography of Kosovo travel guide from Wikivoyage - Visit Kosovo - Tourism Website
- Kosovo Caves Gadimje
| ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||