Geography of Angola
| Geography of Angola | |
|---|---|
  | |
| Continent | Africa |
| Region | Southern Africa |
| Coordinates | 12°30′S 18°30′E / 12.500°S 18.500°E |
| Area | Ranked 22nd |
| • Total | 1,246,700 km2 (481,400 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 1,600 km (990 mi) |
| Borders |
Land boundaries: 5,369 km DROC 2,646 km Republic of Congo 231 km Namibia 1,427 km Zambia 1,065 km |
| Highest point | Mount Moco, 2,620 m |
| Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean, 0 m |
| Longest river | Congo River, 4,344 m |
| Terrain | narrow coastal plains, hills and mountains, high plains |
| Natural Resources | petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, uranium |
| Natural Hazards | occasional heavy rainfall with accompanying floods |
| Environmental Issues | deforestation, overgrazing of meadows, air pollution, waste disposal |
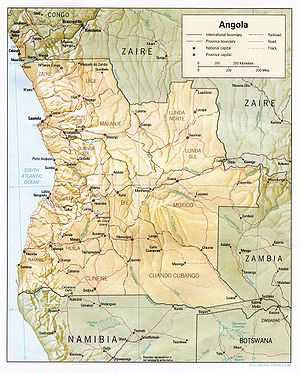
Angola is located on the western Atlantic Coast of southern Africa between Namibia and the Republic of the Congo. It also is bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia to the east. The country consists of a sparsely watered and somewhat sterile coastal plain extending inland for a distance varying from 50 to 160 km (31 to 99 mi). Slightly inland and parallel to the coast is a belt of hills and mountains and behind those a large plateau.
Geology

The rock formations of Angola are met with in three distinct regions:
- the littoral zone,
- the median zone formed by a series of hills more or less parallel with the coast,
- the central plateau.
The central plateau consists of ancient crystalline rocks with granites overlain by non-fossiliferous sandstones and conglomerates of Paleozoic age. The outcrops are largely hidden under laterite. The median zone is composed largely of crystalline rocks with granites and some Palaeozoic unfossiliferous rocks. The littoral zone contains the only fossiliferous strata. These are of Tertiary and Cretaceous ages, the latter rocks resting on a reddish sandstone of older date. The Cretaceous rocks of the Dombe Grande region (near Benguella) are of Albian age and belong to the Acanthoceras mamillari zone. The beds containing Schloenbachia inflata are referable to the Gault. Rocks of Tertiary age are met with at Dombe Grande, Mossamedes and near Loanda. The sandstones with gypsum, copper and sulfur of Dombe are doubtfully considered to be of Triassic age. Recent eruptive rocks, mainly basalts, form a line of hills almost bare of vegetation between Benguella and Mossamedes. Nepheline basalts and liparites occur at Dombe Grande. The presence of gum copal in considerable quantities in the superficial rocks is characteristic of certain regions.
Location
Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Namibia and Democratic Republic of the Congo
Geographic coordinates: 12°30′S 18°30′E / 12.500°S 18.500°E
Map references: Africa
Area
- total: 1,246,700 km2 (481,354 sq mi)
- land: 1,246,700 km2 (481,354 sq mi)
- water: 0 km2 (0 sq mi)
country comparison to the world: 30
Area comparative
- Australia comparative: smaller than the Northern Territory
- Canada comparative: slightly smaller than the Northwest Territories
- United Kingdom comparative: 5 times bigger than the UK
- United States comparative: slightly less than twice the size of Texas
Capital
Major cities
- Amboim (Porto Amboim)
- Bailundo (Vila Teixeira da Silva)
- Benguela (São Felipe de Benguella) - port - railhead
- Caála (Vila Robert Williams)
- Calandula (Duque de Bragança)
- Camacupa (Vila General Machado)
- Chibia (Vila João de Almeida)
- Ganda (Vila Mariano Machado)
- Huambo (Nova Lisboa) - rail
- Kuito (Silva Porto)
- Kuvango (Vila da Ponte)
- Lubango (Sá da Bandeira)
- Luena (Vila Luso)
- Massango (Forte República)
- Mbanza Congo (São Salvador do Congo)
- Menongue (Serpa Pinto) - railhead
- Namibe (Moçâmedes) - port - railhead
- N'Dalatando (Vila Salazar) - rail
- N'Giva (Vila Pereira d'Eça)
- Saurimo (Vila Henrique de Carvalho)
- Soyo (Santo António do Zaire)
- Sumbe (Novo Redondo)
- Tombua (Porto Alexandre)
- Uíje (Carmona)
- Other Towns in Angola
Land boundaries
- total: 5,369 km
- border countries: Democratic Republic of the Congo 2,646 km (of which 225 km is the boundary of discontiguous Cabinda Province), Republic of the Congo 231 km, Namibia 1,427 km, Zambia 1,065 km
Coastline: 1,600 km
Maritime claims:
- territorial sea: 22 km (12 nmi)
- contiguous zone: 44 km (24 nmi)
- exclusive economic zone: 370 km (200 nmi)
Climate
Like the rest of tropical Africa, Angola experiences distinct, alternating rainy and dry seasons. The coastal strip is tempered by the cool Benguela Current, resulting in a climate similar to coastal Peru or Baja California. It is semiarid in the South and along the coast to Luanda. There is a short rainy season lasting from February to April. Summers are hot and dry, while winters are mild. The north has a cool, dry season. The climate is greatly influenced by the prevailing winds, which arc W., S.W. and S.S.W. Two seasons are distinguished - the cool, from June to September; and the rainy, from October to May. The heaviest rainfall occurs in April, and is accompanied by violent storms. The far north and Cabinda enjoy rain throughout much of the year.
Terrain
| Land use | (2012) |
|---|---|
| Arable land | 3.93% |
| Permanent crops | 0.23% |
| Other | 95.84% |
Angola has four principal natural regions: the arid coastal lowland, stretching from Namibia to Luanda and characterized by low plains and terraces; green hills and mountains, rising inland from the coast into a great escarpment; a large area of high inland plains of dry savanna, called the high plateau (planalto), which extends eastward and south-east from the escarpment; and rain forest in the north and in Cabinda. The highest point in Angola is Morro de Môco, at 2,620 m. Elevations generally range from 910 to 1,830 m (3,000 to 6,000 ft).
Coastal lowland
The coast is for the most part flat, with occasional low cliffs and bluffs of red sandstone. There is but one deep inlet of the sea - Great Fish Bay (or Baía dos Tigres). Farther north are Port Alexander, Little Fish Bay and Lobito Bay, while shallower bays are numerous. Lobito Bay has water sufficient to allow large ships to unload close inshore. The coastal lowland rises from the sea in a series of low terraces. This region varies in width from about 25 km near Benguela to more than 150 km in the Cuanza River Valley just south of Angola's capital, Luanda, and is markedly different from Angola's highland mass. The Atlantic Ocean's cold, northwardflowing Benguela Current substantially reduces precipitation along the coast, making the region relatively arid or nearly so south of Benguela (where it forms the northern extension of the Namib Desert), and quite dry even in its northern reaches. Even where, as around Luanda, the average annual rainfall may be as much as fifty centimeters, it is not common for the rains to fail. Given this pattern of precipitation, the far south is marked by sand dunes, which give way to dry scrub along the middle coast. Portions of the northern coastal plain are covered by thick brush.
Hills and mountains
The approach to the great central plateau of Africa is marked by the west-central highlands, a series of irregular escarpments and cuestas parallel to the coast at distances ranging from 20 km to 100 km inland as Tala Mugongo (1,300 m or 4,300 ft), Chella and Vissecua (1,600 m or 5,200 ft). The Cuanza River divides the mountain zone into two parts. The northern part rises gradually from the coastal zone to an average elevation of 500 meters, with crests as high as 1,000 to 1,800 meters. South of the Cuanza River, the hills rise sharply from the coastal lowlands and form a high escarpment, extending from a point east of Luanda and running south through Namibia. The highest peak is Mount Moco (2,620 m or 8,600 ft), and the escarpment is steepest in the far south in the Serra da Chella mountain range. In Benguela Province other high points are Loviti (2,370 m or 7,780 ft), in 12° 5' S., and Mt. Elonga (2,300 m or 7,500 ft). South of the Cuanza is the volcanic mountain Caculo-Cabaza (1,000 m or 3,300 ft).
High plateau
The high plateau, with an altitude ranging from 1,200 to 1,800 m (3,900 to 5,900 ft), lies to the east of the hills and mountains and dominates Angola's terrain. It consists of well-watered, wide, rolling plains, and low hills with scanty vegetation. The surface of the plateau is typically flat or rolling, but parts of the Benguela Plateau and the Humpata Highland area of the Huíla Plateau in the south reach heights of 2,500 meters and more. The Malanje Plateau to the north rarely exceeds 1,000 meters in height. The Benguela Plateau and the coastal area in the immediate environs of Benguela and Lobito, the Bié Plateau, the Malanje Plateau, and a small section of the Huíla Plateau near the town of Lubango have long been among the most densely settled areas in Angola. In the east the tableland falls away to the basins of the Congo and Zambezi, to the south in Namibia it merges into a barren sandy desert.
Drainage
The Zambezi River and several tributaries of the Congo River have their sources in Angola. A large number of rivers originate in the central uplands, but their patterns of flow are diverse and their ultimate outlets varied. A number flow in a more or less westerly course to the Atlantic Ocean, providing water for irrigation in the dry coastal strip and the potential for hydroelectric power, only some of which had been realized by 1988. Two of Angola's most important rivers, the Cuanza (Kwanza) and the Cunene (Kunene), take a more indirect route to the Atlantic, the Cuanza flowing north and the Cunene flowing south before turning west. The Cuanza is the only river wholly within Angola that is navigable—for nearly 200 kilometers from its mouth- -by boats of commercially or militarily significant size. The Congo River, whose mouth and western end form a small portion of Angola's northern border with Zaire, is also navigable.
North of the Lunda Divide the Kwango and many other streams flow north from the tableland to join the Kasai River (one of the largest affluents of the Congo), which in its upper course forms for fully 300 mi (480 km) the boundary between Angola and the Congo. South of the divide some rivers flow into the Zambezi River system and thence to the Indian Ocean, others to the Okavango River (as the Cubango River is called along the border with Namibia and in Botswana) and thence to Lake Ngami and the Okavango Swamp in Botswana. The tributaries of the Cubango River and several of the southern rivers flowing to the Atlantic are seasonal, completely dry much of the year.
Land use and hazards
Natural resources: petroleum, diamonds,[1] iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, uranium
Irrigated land: 855.3 km² (2005)
Total renewable water resources: 148 km3 (35.5 cu mi) (2011)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
- total: 0.71 km3 (0.17 cu mi)/yr (45%/34%/21%)
- per capita: 40.27 m3 (52.67 cu yd)/yr (2005)
Natural hazards: locally heavy rainfall causes periodic flooding on the plateau
Environment - current issues
Overuse of pastures and subsequent soil erosion attributable to population pressures; desertification; deforestation of tropical rain forest, in response to both international demand for tropical timber and to domestic use as fuel, resulting in loss of biodiversity; soil erosion contributing to water pollution and silting of rivers and dams; inadequate supplies of potable water
Environment - international agreements:
- party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78)
- signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Flora and fauna
Both flora and fauna are those characteristic of the greater part of tropical Africa. As far south as Benguela the coast region is rich in oil palms and mangroves. In the Northern part of the province are dense forests. In the South towards the Kunene are regions of dense thorn scrub. Rubber vines and trees are abundant, but in some districts their number has been considerably reduced by the primitive methods adopted by native collectors of rubber. The species most common are various root rubbers, notably the Carpodinus chylorrhiza. This species and other varieties of carpodinus are very widely distributed. Landolphias are also found. The coffee, cotton and Guinea pepper plants are indigenous, and the tobacco plant flourishes in several districts. Among the trees are several which yield excellent timber, such as the tacula (Pterocarpus tinctorius), which grows to an immense size, its wood being blood-red in colour, and the Angola mahogany. The bark of the musuemba (Albizzia coriaria) is largely used in the tanning of leather. The mulundo bears a fruit about the size of a cricket ball covered with a hard green shell and containing scarlet pips like a pomegranate.
The fauna includes the lion, leopard, cheetah, elephant, giraffe, rhinoceros, hippopotamus, buffalo, zebra, kudu and many other kinds of antelope, wildpig, ostrich and crocodile. Angola previously served as a habitat for the endangered African Wild Dog,[2] which is now deemed to be extinct within the entire country, stemming from human activities during the period 1965 to 1991. Among fish are the barbel, bream and African yellow fish.
Ecoregions of Angola
The following ecoregions have been described in Angola:
- Angolan Scarp savanna and woodlands, the steep coastal escarpment.
- Angolan montane forest-grassland mosaic, the inland slopes of the central highlands which are covered in grassland and contain the remaining patches of mountain woodland;
- Angolan Miombo woodlands, much of the large inland plain, indeed most of central Angola.
- Angolan Mopane woodlands, an area in the south, mostly comprising Cunene Province and extending across the border into neighbouring Namibia.
(more to add here)
Geography - note: the province of Cabinda is an exclave, separated from the rest of the country by the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Angola, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
Angola
- Northernmost Point - unnamed point on the border with Republic of the Congo (north of the town Caio Bemba, Cabinda province (an Angolan exclave)
- Easternmost Point - unnamed location on a river section of the border with Zambia (north of the town Sapeta in Zambia), Moxico province
- Southernmost Point - on the point where the Cunene River section of the border with Namibia terminates at the Caprivi Strip (immediately north of the town Andara in Namibia, Cuando Cubango province
- Westernmost Point - Baía dos Tigres island, Namibe Province
Angola (mainland)
- Northernmost Point - a point on the border with the Democratic Republic of Congo immediately to the north-west of the town Luvo, Zaire Province
- Easternmost Point - unnamed point on a river section of the border with Zambia (north of the town Sapeta in Zambia), Moxico province
- Southernmost Point - on the point where the Cunene River section of the border with Namibia terminates at the Caprivi Strip (immediately north of the town Andara in Namibia, Cuando Cubango province
- Westernmost Point - unnamed headland west of Tombua (Porto Alexandre), Namibe
See also
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Library of Congress Country Studies.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Library of Congress Country Studies. This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the CIA World Factbook.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the CIA World Factbook. This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Department of State (Background Notes).
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Department of State (Background Notes). This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Line notes
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||