Fruit tree propagation

Fruit tree propagation is usually carried out vegetatively (non-sexually) by grafting or budding a desired variety onto a suitable rootstock.
Perennial plants can be propagated either by sexual or vegetative means. Sexual reproduction begins when a male germ cell (pollen) from one flower fertilises a female germ cell (ovule, incipient seed) of the same species, initiating the development of a fruit containing seeds. Each seed, when germinated, can grow to become a new specimen tree. However, the new tree inherits characteristics of both its parents, and it will not grow "true" to the variety of either parent from which it came. That is, it will be a fresh individual with an unpredictable combination of characteristics of its own. Although this is desirable in terms of producing novel combinations from the richness of the gene pool of the two parent plants (such sexual recombination is the source of new cultivars), only rarely will the resulting new fruit tree be directly useful or attractive to the tastes of humankind. Most new plants will have characteristics that lie somewhere between those of the two parents.
Therefore, from the orchard grower or gardener's point of view, it is preferable to propagate fruit cultivars vegetatively in order to ensure reliability. This involves taking a cutting (or scion) of wood from a desirable parent tree which is then grown on to produce a new plant or "clone" of the original. In effect this means that the original Bramley apple tree, for example, was a successful variety grown from a pip, but that every Bramley since then has been propagated by taking cuttings of living matter from that tree, or one of its descendants.
Methods
The simplest method of propagating a tree vegetatively is rooting or taking cuttings. A cutting (usually a piece of stem of the parent plant) is cut off and stuck into soil. Artificial rooting hormones are sometimes used to improve chances of success. If the cutting does not die from rot-inducing fungi or desiccation first, roots grow from the buried portion of the cutting to become a new complete plant. However although this works well for some plants (such as figs and olives), for most fruit tree cultivars this method has much too low a success rate to be commercially viable. Root cuttings (pieces of root cut off and induced to grow a new trunk) are also not used to propagate fruit trees, although this method is successful with some herbaceous plants.
A refinement on rooting is layering. This is rooting a piece of a wood that is still attached to its parent and continues to receive nourishment from it. The new plant is severed only after it has successfully grown roots. Layering is the technique most used for propagation of clonal apple rootstocks.
The most common method of propagating fruit trees, suitable for nearly all species, is grafting onto rootstocks. This in essence involves physically joining part of a shoot of a hybrid cultivar onto the roots of a different but closely related species or cultivar, so that the two parts grow together as one plant. The process of joining the two varieties must ensure maximum contact between the cambium (the layer just below the bark) of each, so that they grow together successfully. Grafting is a preferred method because it not only propagates a new plant of the desired hybrid cultivar, it usually also confers extra advantages as a result of the characteristics of the rootstocks (or stocks), which are selected for characteristics such as their vigour of growth, hardiness and soil tolerance, as well as compatibility with the desired variety that will form the aerial part of the plant (called the scion). For example, grape rootstocks descended from North American grapes allow European grapes to be grown in areas infested with Phylloxera, a soil-dwelling insect that attacks and kills European grapes when grown on their own roots. Two of the most common grafting techniques are "whip and tongue", carried out in spring as the sap rises, and "budding", which is performed around the end of summer.
Bud grafting

See also Shield budding
- Cut a slice of bud and bark from the parent tree.
- Cut a similar sliver off the rootstock, making a little lip at the base to slot the scion into.
- Join the two together and bind.
- In time, the scion bud will grow into a shoot, which will develop into the desired tree.
Whip and Tongue grafting
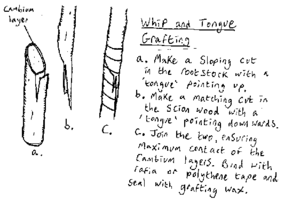
- Make a sloping cut in the rootstock with a "tongue" pointing upwards.
- Make a matching cut in the scion wood with a "tongue" pointing downwards.
- Join the two, ensuring maximum contact of the vascular cambium layers. Bind with raffia or polythene tape or wind around with a 5mm wide strip of elastic band (this is particularly successful because it keeps pressure on the cambium layers to be joined and eventually falls away without cutting into the bark as the tree grows) and seal with grafting wax.
Apple rootstocks
One reason for grafting onto rootstocks is that this enables the grower to determine the tree's eventual size. Apple tree size classes number from one to ten in increasing height and breadth.[1] A "1" is a dwarf which can be productive and as short as 3 feet (0.91 m) with proper pruning. A "10" is the standard sized tree with no dwarfing and will grow to 20 feet (6.1 m) tall and wide or more, dependent upon the variety chosen. In general the class range is (1) 10-20% of full size, (2) 20-30%, (3) 30-40% and so forth to size 10 which is 100% of full size.
The following are a selection of apple tree rootstocks. They are referred to by numbers prefixed by letters indicating the developer of the rootstock.
| Very Small | Small | Medium | Large | Very Large |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P22, M27, G65 | G11, M9, G16, Bud. 9, Mark | M26, G935, G202, G30, MM102, Interstems, M7, M116 | MM106 | MM111, Bud. 118, M25 |
| 6 ft/2m | 8 ft/2.5m | 10 ft/3m | 14 ft/4m | 18 ft/5m |
"Bud 118" A winter hardy early bearing replacement for MM 111 bred in the Soviet Union. Full sized tree unless allowed to bear young which will stunt its growth. Hardy to USDA zone 3.
"Bud 9" A winter- hardy, early- bearing replacement for M9 bred in the Soviet Union. Dwarf tree resistant to crown rot and less susceptible to drought than most other dwarfing stocks. Produces large fruit, is precocious and hardy to USDA zone 3.
"M" designates Malling series developed stocks. East Malling Research is a pioneer in the development of dwarfing rootstocks. East Malling Research Station in Kent, England collected clones of the Paradise stocks from France in 1912 from which 24 "M" were designated with no particular order to the rootstock characteristics other than where they were located in the garden at the time the numbers were assigned. In other words, M.2 is a larger tree than M.9, while M.27 is smaller than M.26.[2]
"MM" designates Malling-Merton stocks developed from joint breeding program by John Innes Institute, in Merton, England, & East Malling Research Station in the early 1950s.[3] The "MM" series was developed primarily to provide resistance to Woolly Apple Aphid(Eriosomatinae) infestation.[4]
"EMLA" designates East Malling / Long Ashton research stations who took the "M" stocks and developed virus free versions. For example., EMLA 7 is M 7 with a guaranteed virus-free stock.[5] EMLA characteristics are often different from the parent "M" rootstock. Note that nearly all the apple rootstocks in the industry are now virus free.[2]
"CG" or "G" designates Cornell-Geneva stocks which are those developed via the Cornell and USDA collaboration at the New York Agricultural Experiment Station in Geneva, NY. The "G" is the old designation. All newer stocks are "CG" followed by numbers that actually provide some information about the stock. As one might surmise, this is a huge improvement in the classical naming scheme which has no identification method at all.[6]
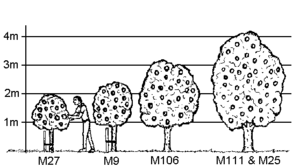
- M.27 Malling 27: A very dwarfing rootstock. Unless the central leader is supported, the tree will be very small. Often only used as an intermediate stem piece on MM.106 or MM.111. If handled and spaced properly, it can be a very productive stock for a vertical axe system.[5] Trees can be grown three to four feet tall and produce about 45 fruit, roughly 2 pecks, depending on fruit cultivar.[7]
- M.9: Very dwarfing - Reaches a height of 8 to 10 ft (2.4 to 3.0 m), coming into fruit after 3 to 4 years, reaching full capacity of 50 to 65 pounds (23 to 29 kg) after 5 to 6 years. It will grow under average soil conditions, but needs a good rich soil to thrive. A good choice where space is limited and fertility is high. Permanent staking is required, as is routine feeding and watering. Trees on this rootstock always require leader support. The rootstock is very susceptible to fire blight and can develop burr knots.[5]
- G.41 Geneva 41, released in 2005, produces trees the size of M.9. The rootstock was developed from a cross between M.27 and Robusta 5 made in 1975. Resistant to Crown|Collar|Root rot(Phytophthora) and fire blight.[5]
- M.26: Dwarfing - Similar to M9 in effect, although somewhat more vigorous and generally stronger, with a higher expected eventual yield of 65–75 pounds (29–34 kg) and height of 8 to 10 ft (2.4 to 3.0 m). A good choice where soil quality is average and compact growth is required. Comes into fruit after 3 to 4 years, reaching full cropping capacity after 5 to 6 years. Staking needed for first five years of its life. It is susceptible to collar rot and fire blight and should not be planted in a wet site. Certain varieties when grafted onto this rootstock may exhibit signs of graft union incompatibility, i.e., the union breaks.[5]
- G.11 Geneva 11 is the second release of the Cornell breeding program similar in size to M.26 (Class 4), but more productive. Has the advantage of being resistant to fire blight and crown rot as well as only rarely producing suckers or burr knots.[5]
- G.202 Geneva 202(CG 4202) is a semidwarfing rootstock that produces a tree in class 5 slightly larger than M.26(Size Class 4) and is more productive than M.26. It was developed from a cross of M.27 (Size Class 1) and Robusta 5 to be fire blight and Phytophthora resistant as well as having resistance to woolly apple aphids. In a 9-year study with the scion cultivar of the "Liberty" apple, G.202 was about 50 percent smaller than M.7, but had much greater production efficiency.[5]
- M.7 Malling 7 rootstock produces a semidwarf tree of Class 6[1] that is freestanding in deep well drained soils but in rocky, steep, or shallow soils, it tends to lean. The rootstock may sucker profusely and is susceptible to collar rot(Phytophthora).[5]
- MM.106: Semi-dwarfing — Sometimes referred to as semi-vigorous, this is the most widely used of rootstocks. It is probably the best choice for the average garden under average conditions, being tolerant of a wide range of soils, and producing a tree with an eventual size of 14 to 18 ft (4.3 to 5.5 m). Trees on this stock begin producing fruit within three to four years, and yield 90 to 110 pounds (41 to 50 kg) after some seven or eight years. MM106 is very suitable for use with weaker varieties that would produce under sized bushes with more dwarfing rootstocks. Can be trained as a half standard tree, but is rather too vigorous for cordons unless the soil is poor. Requires staking for the first five years or so of its life. Trees on MM.106 are highly susceptible to collar rot especially when planted in soils that remain wet(poor percolation).[5]
- M.111 : Vigorous — Not generally suitable for garden scale growing, being both too large and spreading (18–25 ft), and too slow to come into cropping. They are however suitable for growing as specimen standards in the large garden, or for producing medium-sized bushes on poorer soils. Begins to fruit after six or seven years, reaching full capacity of 160 to 360 lb (73 to 163 kg) after eight to nine years. It is not winter hardy in United States zone 3 unless it receives abundant snow cover. Bud 118 was developed in the Soviet Union to replace MM 111, Bud 118 is winter hardy in zone 3 and very precocious. (Early bearing). Planting depth of this rootstock is critical. The union should be no higher than 1 to 2 inches above the final soil line.[5]
- M.25: Very vigorous — Suitable for a grassed orchard, and to grow on as a full standard. Plant 20 ft (6.1 m) apart, makes a tree of 15 to 20 ft (4.6 to 6.1 m) or more height and spread, eventually yielding 200 to 400 lb (91 to 181 kg) per tree. This rootstock is primarily used in UK and is rarely seen in the United States where M.111(size Class 8)[1] is used for this size tree.
- Seedling: Very vigorous trees produced on a rootstock grown from seed. There is greater variability than with the vegetatively propagated rootstocks. Apples used for production of seedling rootstocks include "Dolgo" and "Antonovka", which are both extremely hardy and vigorous.
The Malling series and clones have been standard rootstocks for apples for many years and remain the "workhorses" for the commercial industry in the United States[5] and the UK. However, since most of them are susceptible to disease some Malling rootstocks are being replaced by new breeds, including the Cornell-Geneva series, which has resistance to the major problems preventing quality production of apples utilizing organic control systems. One of the newest rootstocks of the "CG" series, only released commercially in 2004, is CG5202(G.202) which adds resistance to the woolly apple aphid, and when combined with highly resistant cultivars such as "Liberty" it is showing great potential.[8][9]
Another desirable characteristic of rootstocks is environmental adaptability. This may be tolerance to wet/dry soil conditions, acidity/alkalinity of soil or even hot/cold air temperature.[2] Rootstocks based on Siberian Crab apple are being used in colder areas for more cold tolerance.[10]
The ability of new rootstocks to modify or augment characteristics of fruit trees is limited and may disappoint in the long term. It takes ten years to get a full picture of the effects of any one rootstock, so a rootstock that appears promising in the first five years of a trial may fail in the last five years. The Mark rootstock was such a stock and has now fallen mostly into disfavor.[5] Another, the G.30, has proved to be an excellent stock for production but it was only after a number of years of trials that it was found to be somewhat incompatible with the cultivar "Gala", so that it is now recommended to be staked and wired.[5]
An industry consortium undertakes trials of different rootstocks, called the "NC-140" trials.[11] These test many pome rootstocks in many different sites across the United States and thereby provide growers a clearer picture of what to expect when growing fruit trees on specific stock, in specific planting methods in their specific area of the. This information has the potential to create economic benefits to both growers and consumers, as well as helping to reduce the need to spray pesticides as frequently as is currently required.[12]
Pear rootstocks
Pears are usually grafted onto quince rootstocks, which produce small to medium-sized trees. Some varieties however are not compatible with quince, and these require double working. This means that a piece of pear graft-work compatible with both the quince rootstock and the pear variety is used as an intermediate between the two. If this is not done the pear and the rootstock could eventually separate at the graft. Varieties that require double working include "Bristol Cross", "Dr Jules Guyot", "Doyenné d' été" and "Williams Bon Chrétien".
- Quince C: Moderately vigorous — Makes a bush pear tree about 8 to 18 ft (2.4 to 5.5 m) tall, bearing fruit within four to eight years. Suitable for highly fertile soils and vigorous varieties, but not where conditions are poor. Used for bush, cordon and espalier growing. Old stocks of Quince C may be infected with a virus, so care should be taken to obtain certified virus free stock. If in doubt, use Quince A as there is not a great amount of difference in vigor between the two.
- Quince A: Medium vigor — Slightly more vigorous than Quince C, this is the most common variety upon which pears are grafted. Bears fruit between four to eight years, making a tree of some 10 to 20 ft (3.0 to 6.1 m) in height and spread. Suitable for all forms of pear trees except standards.
Pear stock: Very vigorous — Pears grafted onto pear rootstocks make very large standard trees, not suitable for most gardens.
Cherries
Until the 1970s, cherries were grown on the vigorous Malling F12/1, Mazzard (Prunus avium), or Maheleb (P. maheleb) rootstocks, which required much space and time before cropping began, thus the growing of cherries was not a realistic option on a garden scale. The introduction of the rootstock "Colt" enabled trees reaching a maximum height of 12 to 15 ft (3.7 to 4.6 m) to be grown, and if trained as a pyramid it is possible to restrict growth to about 10 ft (3.0 m).[13] The popular sweet variety "Stella" can even be successfully grown in a pot on the patio when grafted onto a "Colt" rootstock.[13] A newer rootstock, Gisela 5,[14] is slowly becoming available to gardeners and produces a tree 20% smaller than Colt and 45% smaller than Mahaleb and Mazzard, making netting for bird protection much easier. Furthermore, German Nurseries Consortium (Consortium Deutscher Baumschulen — CDB®) is introducing across the EU their newest most dwarfing Gisela 3 cherry rootstock that has 50% dwarfing qualities in comparison with Mahaleb and Mazzard and is 10% smaller still than Gisela 5 rootstock.
Plums
Plum rootstocks include:
- Pixy — A dwarfing rootstock (Prunus domestica subsp. insititia, or sometimes Prunus insititia) suitable for bush trees planted 8 to 10 ft (2.4 to 3.0 m) apart.
- St. Julien A — A semi-vigorous rootstock suitable for bush and half standards planted 12 to 15 ft (3.7 to 4.6 m) apart. Also suitable for peaches, nectarines and apricots.
- Brompton or Myrobalan B- (Prunus cerasifera) — Suitable for half standards planted 18 to 22 ft (5.5 to 6.7 m) apart. Also suitable for peaches, nectarines and apricots.
- Myro-29C — (Prunus cerasifera) Semi-dwarf rootstock. Shallow, vigorous, good choice for hard soils. Somewhat drought tolerant.
- Citation — Semi-dwarf rootstock. Shallow, vigorous, good choice for hard soils. Prefers a wetter soil.
Own-root fruit trees
Many species of fruit, e.g., fig, filbert, olive, and pomegranate, are commonly grown on their own roots, as there may be no great advantages to using a special rootstock, or suitable rootstocks may not be readily available. However, even for fruit trees that usually are grown grafted on a rootstock, there can be advantages in growing them on their own roots instead, particularly in the traditional coppicing systems advocated in both sustainable agriculture and permaculture. Disadvantages of using own-root trees can include excessive size and excessive production of wood (thus very long times until the start of fruit production), although training branches horizontally and limiting pruning to summer only may help encourage fruit production at an earlier age.[15][16][17] There is a lack of research on the use of the own root method in large scale systems.
Family trees and fruit salad trees
In addition to propagating trees on rootstocks designed to control size/vigour and confer disease resistance, grafting above the rootstock can be used to provide multiple cultivars of a single species, known as a family tree, or, within certain limits, cultivars of different fruit species on one tree, often known as a fruit salad tree. Family trees typically combine several cultivars (two or three being most common) of apple, pear or a given species of stonefruit on a single rootstock, while fruit salad trees typically carry two or more different species from within a given genus, such as plum, apricot, and peach or mandarin orange, lemon, and lime. Certain combinations, including sour cherry (prunus cerasus)/sweet cherry (prunus avium), although from the same genus, are known to be difficult, although successes have sometimes been reported. Other grafts of this kind can produce the Pomato.
See also
- Fruit tree forms
- Fruit tree pollination
- Orchards
- Plant propagation
- Pruning fruit trees
- Rootstocks
- Vegetative reproduction
- Pomato
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Apple Rootstocks' Fact Sheet Access Page". Nysaes.cornell.edu. 2010-05-11. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Lecture Notes - Horticulture 432". PSU. Archived from the original on 2011-05-23.
- ↑ "Web site - Apple Rootstocks". Tfpg.cas.psu.edu. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "Woolly Apple Aphid". Nysipm.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 5.11 5.12 "Web site - Specific rootstocks". Tfpg.cas.psu.edu. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "William C. Johnson Updates-April 1999". Nysaes.cornell.edu. 2010-05-11. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "MidFEx presents Gene's Backyard Orchard (Introduction) — 97 dwarf apple trees in 2500 square feet". Web.archive.org. 2010-09-25. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "(PDF) NC-140 2006 Annual Report" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "NC-140 Regional Rootstock Research Project New Apple Rootstocks promising for commercial growers From: The Fruit Growers News, 41(5): 6-8". Nc140.org. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ Chittaranjan Kole (29 December 2010). Wild Crop Relatives - Genomic and Breeding Resources: Temperate Fruits. Springer. p. 59. ISBN 978-3-642-16056-1. Retrieved 25 March 2011.
- ↑ "New Apple Rootstocks Promising for Commercial Growers". Nc140.org. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "Home". NC-140. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Hessayon, Dr. D. G., The Fruit Expert, Transworld Publishers Ltd, 1997, p37 ISBN 0-903505-31-2
- ↑ "Use of Gisela 5 for sweet cherries Jef Vercammen,Guy Van Daele and Toon Vanrykel — Lithuanian Institute of Horticulture and the Lithuanian University of Agriculture." (PDF). Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "Phil Corbett video". Youtube.com. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "Orange Pippin apple and orchard resource". Orangepippin.com. 1981-04-16. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ↑ "Phil Corbett website". Cooltemperate.co.uk. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
External links
- Apples from seeds FAQ
- Apple — University of Georgia
- New Apple Rootstocks On the Horizon (2003 report) — Michigan State University Extension
- Apple Rootstock Fact Sheets — Cornell University / USDA-ARS Apple Rootstock Breeding and Evaluation Program
- Performance of Cornell-Geneva Rootstocks Across North America in Multi-Location NC-140 Rootstock Trials (abstract) — International Society for Horticultural Science(ISHS)
- Pyrodwarf, A New Clonal Rootstock For High Density Pear Orchards (abstract) — International Society for Horticultural Science(ISHS)
- Specific rootstocks(apple) — Pennsylvania Tree Fruit Production Guide
- Pears — University of Georgia
- Plums — University of Georgia
- Rootstocks — DWN Dave Wilson Nursery
- Gene Yale's backyard with 176 Apple trees — (ABC) Interview, video and story
- Tutorial: T-Bud and Chip Bud Fruit Tree Grafting Techniques — MidFEx