Fortress of Luxembourg
| Fortress of Luxembourg | |
|---|---|
|
Fortress of Luxembourg, prior to its demolition in 1867 | |
|
The "Bock" promontory in 1867 | |
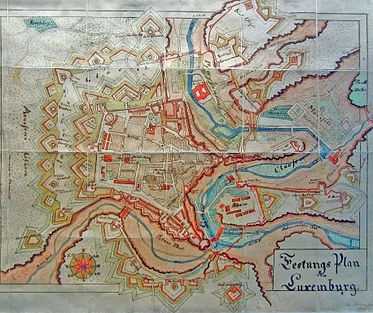
 Fortress of Luxembourg | |
| Coordinates | 49°37′N 6°08′E / 49.61°N 6.13°E |
| Type | Fortress |
| Site information | |
| Open to the public | Yes |
| Condition | Mostly demolished |
| Site history | |
| Built | 15th to 19th centuries |
| In use | Until 1867 |
| Demolished | 1867-1883 |
| Battles/wars | Siege of Luxembourg (1684), Siege of Luxembourg (1794–95) |
|
City of Luxembourg: its Old Quarters and Fortifications | |
| Name as inscribed on the World Heritage List | |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 1994 (18th Session) |
The Fortress of Luxembourg refers to the former fortifications of Luxembourg City, the capital of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, which were mostly demolished in 1867. The fortress was of great strategic importance for the control of the Left Bank of the Rhine, the Low Countries, and the border area between France and Germany.
The fortifications were built gradually over nine centuries, from soon after the city's foundation in the tenth century until 1867. By the end of the Renaissance, Luxembourg was already one of Europe's strongest fortifications, but it was the period of great construction in the 17th and 18th centuries that gave it its fearsome reputation. Due to its strategic location, the fortress became caught up in Europe-wide conflicts between the major powers such as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, the War of the Reunions or the French Revolutionary Wars, and it underwent changes in ownership, sieges, and major alterations, as each new occupier—the Spanish, French, Austrians, and Prussians—made their own improvements and additions.
The fortress acquired the historical epithet of "Gibraltar of the North" as a result of its apparent impregnability. In 1795, when the city surrendered after a 7-month blockade and siege by the French, with its walls still unbreached, the French politician and engineer Lazare Carnot declared Luxembourg "the best [fortress] in the world, apart from Gibraltar".[1]
The city's great significance for the Franco-German frontier led to the 1866 Luxembourg Crisis, almost resulting in a war between France and Prussia over possession of the German Confederation's main western fortress. The 1867 Treaty of London required Luxembourg's fortress to be torn down and for Luxembourg to be placed in perpetual neutrality, signalling the end of the city's use as a military site. Since then, the remains of the fortifications have become a major tourist attraction for the city. In 1994, the fortress remains and the city's old quarter were listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
From Roman fortification to medieval castle
In Roman times, two roads crossed on the plateau above the Alzette and Pétrusse rivers, one from Arlon to Trier, and another leading to Thionville. A circular wooden palisade was built around this crossing, which could provide protection to the farmers of the region in case of danger. Not far from this, on the Bock promontory, was the small Roman fortification Lucilinburhuc – this name later turned into Lützelburg, and later still into Luxembourg.[2][3]
After the Romans had left, the fortification fell into disrepair, until in 963 Count Siegfried of the House of Ardennes, acquired the land in exchange for his territories in Feulen near Ettelbrück from St. Maximin's Abbey in Trier. On the Bock promontory, he built a small castle, which was connected to the plateau through a drawbridge. In time, a settlement grew on the plateau. Knights and soldiers were billeted here on the rocky outcrop, while artisans and traders settled in the area beneath it, creating the long-standing social distinction between the upper and the lower city. The settlement had grown to a city by the 12th century, when it was protected by a city wall adjacent to the current Rue du Fossé. In the 14th century, a second city wall was built, which also incorporated the land of the Rham Plateau. A third one later incorporated the urban area as far as today's Boulevard Royal.[4]
Development and use as fortress
The reinforcement of the fortifications which had begun in 1320 under John the Blind continued until the end of the 14th century. In 1443 Philip the Good and his Burgundian troops took the city in a surprise attack by night. This started a period of foreign occupation for Luxembourg, which had been elevated to a Duchy in 1354. Integrated into the territory of the Netherlands, it would be drawn into the duel between Valois-Bourbons and Habsburgs over the next few centuries, and was ruled by the French, Burgundians, and the Spanish and Austrian Habsburgs. During this time the fortress was continually expanded and extended, and fitted to the military requirements of the day. The casemates, constructed by the Spanish and Austrians, are of particular note.[5]
By marriage, the fortress passed in 1447 to the Austrian Habsburgs along with all Burgundian possessions. In 1542, the French troops of Francis I took the fortress, which was soon retaken by troops of the Holy Roman Empire. Around 1545, Italian and Dutch engineers under Holy Roman Emperor Charles V built the first bastions, linked by curtain walls, on the site of the current Boulevard Roosevelt and Boulevard Royal. The ditch was enlarged from 13 to 31 metres. Ravelins were also added.[6]
Spanish occupation
Later, when the Spanish occupied the city, the aggressive policy of French King Louis XIV from 1670 led to the construction of additional fortifications. With a French attack seeming imminent, the Spanish engineer Louvigny constructed several fortified towers in front of the Glacis from 1672, such as the Redoubts Peter, Louvigny, Marie and Berlaimont; he also built the first barracks in the city. This formed a second line of defence around the city. Louvigny also envisaged constructing works on the other side of the Pétrusse and Alzette valleys, but the Spaniards lacked the funds for this. He had, however, anticipated what the French would do after 1684.[6]
Expansion under Vauban

After the successful siege by Louis XIV in 1683-1684, French troops regained the fortress under the renowned commander and military engineer Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban. From 1684 to 1688, Vauban immediately started a massive re-building and expansion project for the fortifications, using more than 3,000 men.[5] Advance fortifications were placed on the heights around the city: the crownwork on Niedergrünewald, the hornwork on Obergrünewald, the "Cornichon de Verlorenkost", the Fort Bourbon and several redoubts. He greatly expanded the military's hold over the urban space by integrating Pfaffenthal into the defences, and large barracks were built on the Rham and Saint-Esprit plateaux.[6] After the War of the Spanish Succession and the Peace of Ryswick, the fortress came under Spanish control from 1698,[7] then passed to French administration again in 1701.
Austrian period
After the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, the Dutch replaced the French for two years, after which Austrian troops regained it in 1715, remaining there for 80 years.[5] The fortress of Luxembourg now formed one of the main strategic pillars in the defence of the Austrian Netherlands against French expansion. For this reason, Vauban's fortifications were reinforced and extended. It was under Charles VI and Maria Theresa that the fortress expanded the most in terms of surface area: the Austrian engineers added lunettes and several exterior forts (Olizy, Thüngen, Rubamprez, Rumigny, Neipperg, Wallis, Rheinsheim, Charles), closed off the valley with locks, and dug casemates into the rock. The fortress now had a triple line of defences on all sides.[6]
French Revolution and Prussian garrison
After an 11-month blockade, the city of Luxembourg was taken by French Revolutionary troops in 1795. The Duchy of Luxembourg was now integrated as the "Département des Forêts" into the French Republic and later the French Empire.[5] In 1815, after Napoleon's final defeat, the Congress of Vienna elevated Luxembourg to a Grand Duchy, now ruled in personal union by the King of the Netherlands. At the same time, Luxembourg became a member of the German Confederation, and the Luxembourgish fortress became a "federal fortress". To this effect, the Dutch King-Grand Duke essentially agreed to share responsibility for the fortress with Prussia, one of two major German powers. While the Dutch King remained fully sovereign, Prussia received the right to appoint the fortress governor, and the garrison would be made up of 1/4 Dutch troops and 3/4 Prussian troops.[8] As a result, until 1867 around 4,000 Prussian officers, NCOs and men were stationed amongst a community of about 10,000 civilian residents.[9] The Prussians modernised the existing defences and added yet more advance forts, Fort Wedell and Fort Dumoulin. There were even plans to build a fourth line of defences, several kilometres from the city, to keep potential attackers even further at bay. This was not to take place, however.[6]
In the 1830, the southern provinces of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands broke off to form the Kingdom of Belgium. At the outbreak of this Belgian Revolution, most Luxembourgers joined the rebels, and from 1830 to 1839 almost all of Luxembourg was administered as part of Belgium. The fortress and city of Luxembourg, held by the Dutch and Prussian troops, was the only part of the country still loyal to the Dutch King William I. The stand-off was resolved in 1839, when the Treaty of London awarded the western part of Luxembourg to Belgium, while the rest (including the fortress) remained under William I.[10]:XVI
Layout
In its final form, the fortress of Luxembourg consisted of three fortress walls, taking up about 180 ha (440 acres) at a time when the city covered only 120 ha (300 acres). Inside, there were a large number of bastions, with 15 forts in the centre, and another nine on the outside. A web of 23 km (14 mi) of underground passages (casemates) connected over 40,000 m2 (430,000 sq ft) of bomb-proof space. The epithet "Gibraltar of the North" compared the fortified city to the impregnable rock of Gibraltar. The fortress of Luxembourg was in fact never taken by force: in 1443, Philip the Good had taken it without opposition while subsequently the fortress was taken by siege leading to starvation.
The state of the fortress as of 1867 was as follows:
Grünewald Front
|
Trier Front
|
Thionville Front
|
Longwy Front
|
Land usage
In the Middle Ages, Luxembourg had been a relatively open city, with easy access through 23 gates. The ramparts delimited the urban space but allowed both people and goods to move between the town and the countryside without hindrance. This changed drastically from the mid-16th century, when fortifications cut the city off from the surrounding area.[6]
The defensive buildings, spread out over a large distance, rendered access to the city increasingly difficult: the fortress became a straitjacket for its inhabitants. In the 16th and 17th centuries, the gaps in the old medieval defences were closed off. The Marie gate was buried under Bastion Marie in 1548.[6] The Lampert, Orvis, Beckerich and Jost gates disappeared in the early 17th century under the Berlaimont, Louis, Beck and Jost bastions.[6] The military logic behind the need for an inaccessible fortress contrasted with that in favour of a merchant city, open to the outside. The 1644 closure of the Jews' gate, the city's main access from the West which had facilitated trade with the Netherlands, was a key date in this process.[6] Traffic was obliged to bypass the plain, and enter by the New Gate (Porte-Neuve) built from 1626 to 1636. A traveller coming from France now had to descend into the Grund and come up through the Fishmarket, passing through several gates on the way.[6]
The Spanish government fully recognised that sealing off the city would stifle the economy and result in depopulation at a time when large numbers of civilians were needed to provide for the supply and lodging of the troops. Louvigny in 1671 drew up plans for a new gate on the rue Philippe and a bridge over the Pétrusse valley, both of which would have brought about a considerable increase in trade and transportation. The plans, however, were never realized, probably owing to lack of funds.[6]
The fortress also came to be encircled by a kind of no man's land: the Austrians introduced a security perimeter in 1749, inside of which no permanent construction was allowed. This was in order to keep a clear field of fire, to keep the view unobstructed, and so as not to provide cover to attackers. Under the Prussians, the perimeter was extended to 979 m (3,212 ft) from the external lines of fortification.[6] Luxembourg's first railway station, built in 1859 on the Plateau Bourbon, fell within the perimeter, and therefore had to be constructed out of wood.[6]
The growth of the fortress also meant the loss of agricultural land: from the Middle Ages, gardens, orchards, fields and meadows had formed a green belt around the city, and these disappeared progressively to make way for fortifications.[6] The urban population, however, depended on this area for the city's supply of vegetables, fruit and fodder. The swallowing-up of agricultural fields accelerated when the Austrians extended the Glacis. Commander Neipperg had the earth removed down to the rock, a distance of 600 m (2,000 ft) from the fortress, so that attackers laying siege would have no opportunity to dig trenches.[6] The rocky desert that surrounded the city was now called the "bare fields" (champs pelés). Expropriations of land were often executed without discussion: the military would invoke the threat of war and a state of emergency, seizing plots of land without any compensation. In 1744, the garrison confiscated a plot of land close to the Eich gate in order to extend the defences. This land, and its garden of 48 fruit trees, belonged to three orphaned sisters, aged 9, 15 and 20, for whom the orchard was the only means of subsistence. The confiscation plunged them into destitution: when the soldiers chopped down the trees and the girls attempted to at least collect the firewood, they were chased off.[6]
It was not until the late 18th century that the authorities changed their attitude: the government in Brussels decided that compensation should be paid for confiscated property. The Austrians started to compensate for the previous decades' injustices by making payments to those who had been expropriated, or to their descendants.[6]
Military rule
Entering or exiting the city meant passing under the watchful eye of the soldiers on guard duty. At dusk, the gates would be shut, not to be re-opened until sunrise. Fear of an attack was not the only reason for closing the gates at night. In fact, for extended periods, especially in the late 18th century, there was little likelihood of being attacked. Yet even in times of good relations with the neighbouring French, the doors were shut: above all the military authorities feared their troops deserting. This was a constant plague for the Austrian army, as for all Ancien Régime garrisons. Each year, a tenth of the troops would be lost to desertion, often escaping under the cover of darkness. In 1765, barbed wire was placed on the ramparts, to make night-time escapes more difficult. Paradoxically, the gate closure became more a matter of keeping the garrison inside than of protecting the city itself.[6] However, those still outside the walls would have to hurry home when they heard the Zapestreech—signalling the imminent gate closure—if they wanted to avoid being locked out for the night. The Luxembourgish legend of Saint Nicholas (see below) refers to this.[6]
Living conditions and relations between garrison and inhabitants
Lodging among civilians

In 1787, the citizens of Luxembourg stated in a petition that they had "the sad privilege of living in a fortress, a privilege that is inseparable from the lodging of soldiers". Living in a fortress city had serious disadvantages: the ramparts set serious limits on the amount of space available while the inhabitants had to share this small area with large numbers of troops. The further back one goes in history, the more difficult it is to locate exact numbers of both inhabitants and garrisoned soldiers.[9]
For the Spanish period, in 1684 the Prince of Chimay had 2,600 soldiers under his command (1,700 infantry and 900 cavalry). The military population was not limited to troops: many soldiers and officers also had wives and children. In 1655, in the upper town alone, a third of the 660 soldiers were listed as married, and about half of these families had children. Then there were also the servants employed by the officers. The total military population of the upper town in was therefore 1,170, almost twice as many as the number of actual troops.[9]
Under the Austrian occupation, some 2,700 troops were stationed in the fortress in 1722, as compared to 4,400 in 1741 and 3,700 in 1790. In times of crisis or war, the garrison might be increased dramatically, as in 1727-1732 when the Austrians feared a French attack and 10,000 soldiers were stationed inside the fortress or in camps in the surroundings (while the civilian population was only 8,000).[9] In the 19th century, there were 4,000 Prussian troops garrisoned in a city of about 10,000-13,000 residents.[9]
All of these had to be housed somewhere. Until 1672, when the first barracks were constructed, all officers, troops, and their wives and children, lived with the civilian inhabitants, leading to drastic overpopulation. A magistrate in 1679 noted that there were only 290 houses in the city, many of them tiny, owned by poor artisans with large families. These people, who barely eked out a living from one week to the next, only just had enough beds to sleep in themselves, never mind providing accommodation for a large number of soldiers who were "crammed one on top of the other, experiencing first-hand the poverty and misery of their landlords".[9] The military's lists of billets give an idea of the cramped conditions in which troops and civilians co-existed: the butcher Jacques Nehr (listed in 1681) had a wife and five children. A room on the first floor of his house contained two married sergeants and three children. A second room housed a married soldier with his child, two gunners, and an infantryman. A dragoon lived above the stables. This was not an isolated case, and the justiciar and aldermen (échevins) repeatedly protested to the government about the intolerable living arrangements.[9]
Living in such close proximity caused numerous frictions between soldiers and residents. In 1679, a magistrate complained that citizens had to give over "three, four, five or six beds, along with linen and blankets" to "soldiers who were most often violent, drunk, and difficult, who mistreated them [...] stole their linen and furniture, and chased them from their own homes".[9] Ruffian soldiers would come home at night drunk, leaving the house doors open being noisy. The Spanish troops were apparently particularly undisciplined. When lodging in barracks was introduced, discipline improved considerably, though conflicts with residents did not disappear entirely. In the 18th century, there were still examples of Austrian officers who moved into rooms more spacious than the ones they had been assigned; others would bring girls of low repute to their house at night, to the alarm of their civilian landlords.[9]
This was all the more galling given that, under the Spaniards and Austrians, the city's inhabitants received no compensation for all this: they were to provide housing to the soldiers free of charge. The government claimed that since the garrison's presence brought trade and business which benefited the city's merchants and artisans, it was only fair for citizens to contribute by lodging the troops.[9] Nor was the burden of quartering troops shared equally, by any means: there were many exemptions, reflecting the social inequality of the Ancien Régime society. The justiciar, the aldermen, lawyers, members of the provincial council, and the nobility were exempt.[9] The magistrates assigned soldiers to houses, and to this effect made lists with very detailed descriptions of houses' interiors. Abuses of power could not be prevented: the authorities were known to assign an excessive number of soldiers to the houses of residents who had been involved in disputes with the city. Citizens tried to wriggle out of these obligations by deliberately not keeping all rooms in their house fit for habitation; the wealthier inhabitants were able to avoid taking in soldiers by paying their way out.[9]
Introduction of barracks

Purpose-built military accommodation was built in Luxembourg from 1672 onwards, with the barracks of Piquet and Porte-Neuve, as well as some huts on the Rham and Saint-Esprit plateaux.[9] The barracks were enlarged and multiplied by Vauban after 1684, and by the Austrians and Prussians over the next two centuries. In 1774, the six barracks housed 7,900 troops, while the military hospital in Pfaffenthal had room for another 200 men.[9] From the late 17th century, it became the norm for troops to reside in barracks; officers, on the other hand, continued to be quartered among civilians right up until the fortress's demolition in 1867. Even in Prussian times in the 19th century, most officers rented a room with their "servis", their accommodation allowance: as a result, the house-owners could at least receive payment.[9]
By this point, under the Prussian garrison, most of the soldiers were only in Luxembourg for short periods in connection with their military service.[11] The aristocratic officers, on the other hand, were under strict social rules, and therefore intermarriages between the civilian population and the garrison soldiers were uncommon, except for non-commissioned officers, who were career soldiers.[11] There was a love-hate relationship between inhabitants and garrison: on the one hand, there was jealousy over the soldiers' exemption from certain taxes and levies; on the other, the soldiers spent their wages in the city, and many businessmen and shopkeepers depended on the military for their livelihood, as did the craftsmen and day labourers who worked on improving or repairing the fortifications.[11]
Both groups were faced with the same poor living conditions in the city: the lack of a clean water supply and of sanitation, which led to outbreaks of cholera and typhus. The barracks were so cramped that often two soldiers had to share a bed; the officers, quartered in the houses of the upper classes, did not experience such problems. Among the inhabitants, there was similar stratification: there was a marked difference between the dark, cramped housing of the poor in the lower town and the fine accommodation enjoyed by the rich who lived in housing in the upper town built by the nobility or the clergy.[11]
Animals
Animals were indispensable in order to maintain and run a fortress, and to feed its garrison. Riding horses, draught horses and workhorses were required while cattle, sheep or other animals were needed for slaughter.[12]
In 1814, the ground floors of the Rham Barracks, the Maria Theresa Barracks, and the riding barracks were renovated for use as stables. Out of the five storage buildings for grain and flour which had been built by 1795, the one in the upper town was used as a stable. Together, these had a capacity of 386 horses.[12] By late 1819, the artillery required a new riding arena to train a large number of new horses that were being delivered. For this, they wanted to use the garden of an old monastery on the Saint-Esprit Plateau. By 1835, an indoor riding arena in the lower yard of the plateau had been completed. This had enough room to train a squadron, and in war time could be used as a livestock shed or as a fodder store.[12]
Apart from the riding horses of the cavalry detachment and officers, a large number of draught horses belonged to the artillery and military engineers for ensuring supplies. In case of emergency or when large-scale transport was necessary, contracts were signed with private haulage companies. Just for the mill in the Cavalier Camus, which made enough flour daily for 1,500 portions of bread, 24 horses were required.[12] For the rapid reinforcement of endangered fortress sections or to support a breakout, horsed units of artillery were ready. In 1859, Luxembourg had eight horse guns with 38 horses. There was also a need for additional horses to transport the ammunition, as well as for riding and as reserves.[12]
Storage space for the animals' fodder had to be found. Oats were stored in the remaining churches after 1814. Straw posed a problem, due to the danger of its catching fire. It was to be stored either in the trenches of the Front of the plain, in Pfaffenthal, or in the lower quarters of the Grund and Clausen.[12] The livestock for slaughter were to be accommodated among the inhabitants, with the gardens in the Grund and Pfaffenthal being reserved for cattle.[12]
Animals could also be a source of income for the military: already under the French, the fortress authorities sold off the grazing rights on the grassy areas of the Glacis. Due to lax supervision of grazing, however, by 1814, some of the folds were no longer recognisable as such.[12]
Luxembourg crisis and demolition
After the Prussian victory in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, the German Confederation was dissolved. In its place, under Prussian leadership, the North German Confederation was founded, which did not include Luxembourg. Nevertheless, Prussian troops remained in the fortress. Before the war, the Prussian chancellor Otto von Bismarck had signalled to the French government of Napoleon III that Prussia would not object to French hegemony in Luxembourg, if France stayed out of Prussia's conflict with Austria, to which Napoleon agreed. After the war, the French offered King William III 5,000,000 guilder for his personal possession of Luxembourg, which the cash-strapped Dutch monarch accepted in March 1867. Prussian objections to what was now portrayed as French expansionism provoked the Luxembourg Crisis, and the threat of a war between the major powers was averted only by the London Conference and the Second Treaty of London. This declared Luxembourg to be a neutral state, and required the fortress to be torn down, and the Prussian garrison to leave within three months.
Generally, it was usual for decommissioned fortresses to pass into the ownership of the cities concerned. In Luxembourg, however, an eagerness to comply with the Treaty of London and a fear of being caught up in a future Franco-German war caused the government to undertake the project on behalf of the city. The sale of the land of the fortress would fund the costs of demolition and of the urban development of the city. An international commission inspected the demolition work in 1883, bringing to light the government's inexperience with such work. The state had to decide between "keeping everything" and "razing everything". Military defensive works had to be interrupted by roads; military remains converted into cellars or warehouses had to be destroyed.[13]:336
The demolition of the fortress, with its casemates, batteries, barracks, and so on, took 16 years, from 1867 to 1883, and cost 1,5 million francs. The process was somewhat chaotic: often parts of the fortress were simply blown up, the usable materials carried off by local residents, and the rest was covered up with earth. Social concerns were not absent from the enterprise. The old barracks served as lodgings for the workers employed in the demolition work. No qualification was required to participate in this work: during times of economic downturn, additional demolition projects on the fortress gave work to the unemployed. The dismantling became a grandiose spectacle, and a celebration of new technologies and ambitious projects.[13]:337 It was decided, however, to preserve some buildings for future generations (see below).
Luxembourg achieved full independence in 1890 after the death of the Dutch king William III. He was succeeded in the Netherlands by his daughter Wilhelmina but as the succession laws of Luxembourg allowed only male heirs, the personal union came to an end. The Luxembourgers chose the German Duke Adolphe of the House of Nassau-Weilburg as their Grand Duke.
Expansion of the city
This demolition work, which might be seen today as the destruction of a historic monument, was at the time seen as an act of liberation. The fortress was the very visible symbol of foreign domination, and additionally the various masters of the fortress forbade the building of new houses, so as not to influence the defensive military strategy at the heart of the fortress. When the corset of the fortifications had disappeared, the city could expand for the first time since the 14th century. In the West the Boulevard Royal was built, adjacent to the Municipal Park. In the south, the new Adolphe Bridge opened up the Bourbon Plateau for development, with its Avenue de la Liberté. Here, a harmonious blend of houses, imposing edifices (the Banque et Caisse d'Épargne de l'État, the ARBED building, the central railway station) and squares such as the Place de Paris were built.[14]
Additionally, the residential quarters of Limpertsberg and Belair were created.
Legacy
Remains and later use
.jpg)
Parts of the fortress were not destroyed, but simply rendered unfit for military use. Many old walls and towers still survive, and still heavily influence the view of the city. Some of the remaining elements of the fortress are the Bock promontory,[15] Vauban towers, the "Three Towers" (one of the old gates),[16] Fort Thüngen, the towers on the Rham plateau,[17] the Wenceslas Wall,[18] the old cavalry barracks in Pfaffenthal,[19] the Holy Ghost citadel, the casemates of the Bock and the Pétrusse,[20][21] the castle bridge, and some of the Spanish turrets.[22] For its tourism industry, the city currently depends very heavily on its location as well as promoting the remains of the fortress and the casemates.[23] The Wenzel and Vauban circular walks have been set up to show visitors the city's fortifications.[24][25][26][27] The old fortifications and the city have been classed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1994.[2]
The old Fort Thüngen on the Kirchberg plateau has been heavily restored, and now houses a fortress museum.[28]
Fort Lambert, on the Front facing the plain, was covered over with earth after 1867. On this site, the Avenue Monterey was built. In 2001, construction work on an underground car park under the Avenue Monterey uncovered part of the Fort – one of its redoubts – which can now be seen by the public.[29]
Bastion Beck is now the Place de la Constitution, where the iconic Gëlle Fra statue is located.[30]
Place names
Many street and building names in the city still serve as a reminder of the city's former military function, the defensive works, and of the foreign troops and administrators in Luxembourg:
- Rue du Fort Rheinsheim, and the nearby "Salle Rheinsheim" of the Centre Convict (a meeting-place for religious and cultural organisations); also the headquarters of the "S.A. Maria Rheinsheim", which administers the real estate of the Catholic Church in Luxembourg[31]
- Rue Louvigny and the Villa Louvigny, which was built on the remains of Fort Louvigny, named after Jean Charles de Landas, Count of Louvigny, who was chief engineer and also interim governor of the fortress in the 1670s[32]
- Rue du Fossé (fossé: ditch)
- Place d'Armes
 Street sign for Rue Louvigny. The explanation reads "Military engineer in the Spanish period, 1675".
Street sign for Rue Louvigny. The explanation reads "Military engineer in the Spanish period, 1675". - Rue Jean-Georges Willmar, named after a governor of Luxembourg (1815-1830)[33]
- Rue Vauban (in Clausen), after Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, the French military engineer who massively expanded Luxembourg's fortifications[34]
- The Glacis and the Rue des Glacis, a glacis being a slope of earth in front of defensive fortifications
- Boulevard Kaltreis (in Bonnevoie), used to be colloquially called "op der Batterie", as the French troops besieging the city had positioned their artillery here in 1794[35]
- On the Plateau Bourbon:
- Rue du Fort Bourbon[36]
- Rue du Fort Elisabeth [37]
- Rue du Fort Wallis[38]
- Rue du Fort Neipperg, after Wilhelm Reinhard von Neipperg, an Austrian general who was governor of Luxembourg five times in the 18th century[39]
- Rue Bender, after Blasius Columban von Bender, governor from 1785 to 1795[40]
- Rue du Fort Wedell
- On the Kirchberg plateau:
- Rue des Trois Glands and Rue du Fort Thüngen; the Fort, which has been mostly reconstructed, consists of three towers, hence nicknamed the "Three Acorns" (French: Trois Glands)[41]
- Rue du Fort Berlaimont[42]
- Rue du Fort Niedergrünewald
Culture
A local version of a legend of Saint Nicholas (D'Seeche vum Zinniklos) refers to the danger of being shut outside the fortress gates for the night. Three boys were playing outside, and were far away from the city when the curfew was sounded: it was too late for them to return home. They sought refuge with a butcher who lived outside the city. At night-time, however, the butcher killed them to turn them into aspic. Luckily, a few days later, Saint Nicholas also found himself shut out of the city, and also went to the butcher's house. He found the children, and was able to bring them back to life.[6]
Jean Racine, the famous French dramatist, was in Luxembourg in 1687 as the historiographer of Louis XIV and inspector of the fortress.[43]
There are several elaborate maps and views of the fortress made before 1700. In 1598, Georg Braun and Franz Hogenberg published the oldest known view of Luxembourg City, a copper engraving that appeared in Civitates orbis terrarum (Cologne, 1598). Half a century later, the Dutch cartographer Joan Blaeu, drawing on Braun's work, published his "Luxemburgum" in the second volume of his Stedeboek (Amsterdam, 1649). Van der Meulen provides another view of Luxembourg from Limpertsberg where he depicts French troops taking the city in 1649.[44]
In more modern times, the British Romantic landscape artist J. M. W. Turner (1775-1851) painted several scenes of the fortress, both paintings and sketches, after visiting in 1824 and 1839. Johann Wolfgang von Goethe visited the city in 1792, and left a number of sketches of the fortress. Christoph Wilhelm Selig, a member of the Hessian garrison (1814-1815), painted several watercolours. Later, the fortress served as a model for the Luxembourgers Michel Engels and Nicolas Liez and Jean-Baptiste Fresez. Even after the dismantling of (most of) the fortifications in 1867, the spectacular remains have still been used as motifs by artists such as Joseph Kutter or Sosthène Weis.
-

Georg Braun, Franz Hogenberg: Luxembourg City (1598)
-

Joan Blaeu: Luxembourg City (1649)
-

Van der Meulen: Prise de Luxembourg (1649)
-

Christoph Wilhelm Selig: Luxembourg from Pfaffenthal (1814)
-
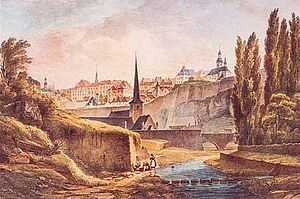
Jean-Baptiste Fresez: Luxembourg from the Alzette River (c. 1828)
-

J. M. W. Turner: Luxembourg (1834)
-

J. M. W. Turner: Citadel of St Esprit, Luxembourg (c. 1839)
-

Nicolas Liez: View of Luxembourg from the Fetschenhof (1870)
-
Sosthène Weis: Bock rock (1938)
See also
- Fort Thüngen
- Siege of Luxembourg (1684)
- Siege of Luxembourg (1794–95)
- Fortresses of the German Confederation
Footnotes
- ↑ Kreins, Jean-Marie. Histoire du Luxembourg. 3rd edition. Paris: Presses Universitaires de France, 2003. ISBN 978-2-13-053852-3. p. 64
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "City of Luxembourg: its Old Quarters and Fortifications". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 11 October 2013.
- ↑ Lodewijckx, Marc (1 January 1996). Archaeological and historical aspects of West-European societies: album amicorum André Van Doorselaer. Leuven University Press. pp. 379–. ISBN 978-90-6186-722-7.
- ↑ "History of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg", Grand Duché de Luxembourg. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "Du château à la forteresse", Ville de Luxembourg. (in French) Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 6.16 6.17 6.18 6.19 Thewes, Guy. "Le «grand renfermement»: La ville à l'âge de la forteresse." (in French) Ons Stad, No. 99, 2012. p. 10-13
- ↑ "Treaty of Ryswick". Encyclopedia Britannica 1911.
- ↑ Engelhardt, Friedrich Wilhelm. Geschichte der Stadt und Festung Luxemburg: Seit ihrer ersten Entstehung bis auf unsere Tage. Luxembourg: Rehm, 1830. p. 284-285
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 9.8 9.9 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 Thewes, Guy. "Le logement des soldats dans la forteresse de Luxembourg." (in French) Ons Stad, No. 102, 2013. p. 14-17
- ↑ Fyffe, Charles Alan. A History of Modern Europe, 1792-1878. Popular edition, 1895. Retrieved 1 November 2013.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Jungblut, Marie-Paule. "Das Leben in der Bundesfestung Luxemburg 1815-1867." (in German) Ons Stad, No. 43, 1993. p. 6-7
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 12.7 Bruns, André. "Tiere in der Festung." (in German) Ons Stad, No. 97, 2011. p. 48-49
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Philippart, Robert. "La Ville de Luxembourg: De la ville forteresse à la ville ouverte entre 1867 et 1920." (in French) In: Émile Haag. Une réussite originale - Le Luxembourg au fil des siècles. Luxembourg: Binsfeld, 2011.
- ↑ "History - After the dismantling of its fortress". Luxembourg City Tourist Office. Retrieved 11 October 2013.
- ↑ "Bock Promontory". Luxembourg City Tourist Office, 2013.
- ↑ "Les 3 tours". (in French) Service des Sites et Monuments Nationaux, 2010.
- ↑ "Rham Plateau". Luxembourg City Tourist Office, 2013.
- ↑ "Wenceslas Wall". Luxembourg City Tourist Office, 2013.
- ↑ "Ancienne caserne de cavalerie (Pfaffenthal)". (in French) Service des Sites et Monuments Nationaux, 2009.
- ↑ "Petrusse Casemates". Luxembourg City Tourist Office, 2013.
- ↑ "Bock Casemates". Luxembourg City Tourist Office, 2013.
- ↑ "Spanish Turret" Luxembourg City Tourist Office, 2013.
- ↑ "After the dismantling of its fortress". Luxembourg City Tourist Office, 2013.
- ↑ "Itinéraire culturel Wenzel". (in French) Service des Sites et Monuments Nationaux, 2010.
- ↑ "Itinéraire culturel Vauban". (in French) Service des Sites et Monuments Nationaux, 2010.
- ↑ "Promenades - The Wenzel Circular Walk". Luxembourg City Tourist Office, 2013.
- ↑ "Promenades - The Vauban Circular Walk". Luxembourg City Tourist Office, 2013.
- ↑ Historique du bâtiment (in French) Musée Dräi Eechelen, 2012.
- ↑ Redoute Lambert - Parking Monterey (in French) Service des sites et monuments nationaux, 2009.
- ↑ Bastion Beck - Place de la Constitution (in French) Service des sites et monuments nationaux, 2009.
- ↑ Beck, Henri. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Rheinsheim (Rue du Fort) (in German) Ons Stad, No. 54, 1997. p. 32
- ↑ Friedrich, Evy. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Louvigny (Rue) (in German) Ons Stad, No. 21, 1986. p. 34
- ↑ Beck, Fanny. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Willmar (Rue Jean-Georges)". (in German) Ons Stad, No. 102, 2013. p. 71
- ↑ Beck, Fanny."Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Vauban (Rue)". (in German) Ons Stad, No. 92, 2009. p. 67
- ↑ Friedrich, Evy. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Kaltreis (Boulevard)". (in German) Ons Stad, No. 16, 1984. p. 26
- ↑ Friedrich, Evy. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Bourbon (Rue du Fort)". (in German) Ons Stad, No. 4, 1980. p. 36
- ↑ Friedrich, Evy; Holzmacher, Gaston. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Elisabeth (Rue du Fort)". (in German) Ons Stad, No. 8, 1981. p. 27
- ↑ Beck, Fanny. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Wallis (Rue du Fort)". (in German) Ons Stad, No. 95, 2010. p. 55
- ↑ Friedrich, Evy; Beck, Henri. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Neipperg (Rue du Fort)". (in German) Ons Stad, No. 29, 1988. p. 30
- ↑ Friedrich, Evy. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Bender (Rue). (in German) Ons Stad, No. 3, 1980. p. 27
- ↑ Beck, Fanny. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Trois Glands (Rue des)". (in German) Ons Stad, No. 88, 2008. p. 68
- ↑ Friedrich, Evy. "Was bedeuten die Straßennamen der Stadt? - Berlaimont (Rue du Fort)". (in German) Ons Stad, No. 3, 1980. p. 29
- ↑ "Arts et culture au Luxembourg: Une culture ouverte sur le monde." Service information et presse du gouvernement luxembourgeois, 2009.
- ↑ Mersch, Jacques. "Luxembourg: vues ancienne". Luxembourg: Editions Paul Bruck, 1977. (in French)
References and further reading
- Bruns, André. Luxembourg as a Federal Fortress 1815-1860. Wirral: Nearchos Publications, 2001.
- Coster, J. (1869). Geschichte der Festung Luxemburg seit ihrer Entstehung bis zum Londoner-Traktate von 1867: Mit besonderer Rücksicht auf die strategische Bedeutung und die kriegsgeschichtlichen Ereignisse dieses Platzes. Nebst einem Plan mit sammtl. Festungswerken. V. Bück.
- Deidier (1742). Le parfait ingénieur françois, ou La fortification offensive et défensive; contenant la construction, l'attaque et la défense des places régulieres & irrégulieres, selon les méthodes de monsieur De Vauban, & des plus habiles auteurs de l'Europe, qui ont écrit sur cette science. Charles-Antoine Jombert. pp. 167–.
- Engelhardt, Friedrich Wilhelm (1830). Geschichte der Stadt und Festung Luxemburg: seit ihrer ersten Entstehung bis auf unsere Tage : mit besonderer Rücksicht auf die kriegsgeschichtlichen Ereignisse; nebst Plan der Stadt und statistischer Einleitung. Rehm.
- Engels, Michel. Bilder aus der ehemaligen Bundesfestung Luxemburg. Luxembourg: J. Heintzes Buchhandlung, 1887.
- Jacquemin, Albert. Die Festung Luxemburg von 1684 bis 1867. Luxembourg, 1994.
- Knaff, Arthur (1887). Die Belagerung der Festung Luxemburg durch die Franzosen unter Maréchal de Créqui im Jahre 1684: ein Beitrag zur Geschichte der Festung Luxemburg ; mit einer Karte. Heintze.
- Koltz, Jean-Pierre. Baugeschichte der Stadt und Festung Luxemburg. Luxembourg, Vol. I, 1970.
- Konen, Jérôme (ed.) Kasematten - Auf Spurensuche in der Festungsstadt Luxemburg. Luxembourg: Jérôme Konen Productions, 2013.
- Kutter, Edouard. Luxembourg au temps de la forteresse. Luxembourg: Edouard Kutter, 1967.
- Langini L. Églises du Grand-Duché de Luxembourg, Témoins de l’histoire et de la spiritualité. Luxembourg: Service des Sites et Monuments Nationaux, 1993.
- Musée d'Histoire de la Ville de Luxembourg (ed.). Das Leben in der Bundesfestung Luxemburg (1815-1867). Luxembourg: Imprimerie Centrale, 1993.
- Mersch, François. Luxembourg. Forteresse & Belle Epoque. Luxembourg: Éditions François Mersch, 1976.
- Parent, Michel. Vauban. Paris: Editions Jacques Fréal, 1971.
- Pauly, Michel; Uhrmacher, Martin: "Burg, Stadt, Festung, Großstadt: Die Entwicklung der Stadt Luxemburg". / Yegles-Becker, Isabelle; Pauly, Michel: "Le démantelement de la forteresse". In: Der Luxemburg Atlas – Atlas du Luxembourg. Eds.: Patrick Bousch, Tobias Chilla, Philippe Gerber, Olivier Klein, Christian Schulz, Christophe Sohn and Dorothea Wiktorin. Photos: Andrés Lejona. Cartography: Udo Beha, Marie-Line Glaesener, Olivier Klein. Cologne: Emons Verlag, 2009, ISBN 978-3-89705-692-3.
- Pays, A. S. Du (1863). Itinéraire descriptif, historique, artistique et industriel de la Belgique. Hachette et Cie. pp. 323–.
- Prost, Philippe. La ville en guerre. Édition de l'imprimeur, 1996.
- Rocolle, Pierre. 2000 ans de fortification française. Lavauzelle, 1989.
- Rupprecht, Alphonse. Logements militaires à Luxembourg pendant la période de 1794 à 1814. Luxembourg: Krippler-Muller, 1979.
- Savin, Cyril. Musée de la Forteresse, Conception générale d’aménagement thématique. Luxembourg: Service des Sites et Monuments Nationaux, 1998.
- Thewes, Guy. Luxembourg Forteresse d’Europe, catalogues du Musée d’Histoire de la ville de Luxembourg, Vol. 5. Luxembourg, 1998.
- Tousch, Pol. Episoden aus der Festung Luxemburg: Luxembourg, une forteresse raconte. Luxembourg: Éditions Pol Tousch, 1998. ISBN 2-919971-05-0.
- Trausch, Gilbert. La Ville de Luxembourg, Du château des comtes à la métropole européenne. Fonds Mercator Paribas, 1994. ISBN 978-9-06153-319-1.
- Van der Vekene, Emile. Les plans de la ville et forteresse de Luxembourg édités de 1581 à 1867. 2nd edition. Luxembourg: Saint-Paul, 1996. ISBN 978-2-87963-242-1.
- Watelet, Marcel. Luxembourg Ville Obsidionale, Musée d’Histoire de la ville de Luxembourg. Luxembourg, 1998.
- Zimmer J. Le Passé Recomposé, archéologie urbaine à Luxembourg. Luxembourg, MNHA, 1999.
- Zimmer J. Aux origines du quartier St-Michel à Luxembourg "Vieille ville", De l’église à la ville. Luxembourg, MNHA, 2001.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fortress of Luxembourg. |
- Luxembourg City Tourist Office
- Musée Dräi Eechelen (French), the fortress museum
- Forteresse de Luxembourg (French) on the "Service des sites et monuments nationaux" website
- Fortified Places, Luxembourg


