Flavokavain B
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
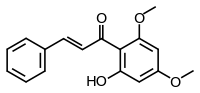
| IUPAC name
(E)-1-(2-Hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-phenyl-propenone | |
| Other names
2'-hydroxy-4',6'-dimethoxychalcone Flavokawain B | |
| Identifiers | |
| 2059845 | |
| 1775-97-9 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 5356121 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C17H16O4 |
| Molar mass | 284.31 g·mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Flavokavain B is a flavokavain found in the kava plant.[1] In 2010 a paper was published identifying it as a hepatotoxin.[2] Another paper published in 2013 suggests that Flavokavain B might be effective in killing bone cancer cells by pointing out evidence of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by Flacokavain B treatment with less toxicity than the standard treatments.[3] Flavokavain B has been demonstrated to possess potent apoptotic abilities.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Dharmaratne, H. Ranjith W.; N. P. Dhammika Nanayakkara; Ikhlas A. Khan (February 2002). "Kavalactones from Piper methysticum, and their 13C NMR spectroscopic analyses". Phytochemistry 59 (4): 429–33. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(01)00443-5. PMID 11830162.
- ↑ Zhou P., Gross S., Liu J.-H., Yu B.-Y., Feng L.-L., Nolta J., Sharma V., Piwnica-Worms D., Qiu S.X 'Flavokawain B, the hepatotoxic constituent from kava root, induces GSH-sensitive oxidative stress through modulation of IKK/NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways . FASEB Journal 2010 24:12 (4722-4732)
- ↑ "Flavokawain B, a kava chalcone, inhibits growth of human osteosarcoma cells through G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis". Molecular Cancer 12: 55. 2013. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-12-55. PMC 3681603. PMID 23764122.
- ↑ Ramez N. Eskander1, Leslie M. Randall1, Toshinori Sakai, Yi Guy, Bang Hoang, Xiaolin Zi. "Flavokawain B, a novel, naturally occurring chalcone, exhibits robust apoptotic effects and induces G2/M arrest of a uterine leiomyosarcoma cell line".
External links
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||