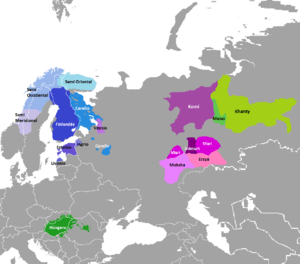
Finno-Ugric languages
| Finno-Ugric | |
|---|---|
| Finno-Ugrian | |
| Geographic distribution: | Eastern, Central and Northern Europe, North Asia |
| Linguistic classification: |
|
| Subdivisions: | |
| ISO 639-2 / 5: | fiu |
| Glottolog: | None |
|
The Finno-Ugric languages. | |
Finno-Ugric (/ˌfɪnoʊˈjuːɡrɪk/ or /ˌfɪnoʊˈuːɡrɪk/),[1] Finno-Ugrian or Fenno-Ugric is a traditional grouping of all languages in the Uralic language family except the Samoyedic languages. Its commonly accepted status as a subfamily of Uralic is based on criteria formulated in the 19th-century and is often criticized by contemporary linguists.[2] The three most-spoken Uralic languages, Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian, are all included in Finno-Ugric.
Linguistic roots common to both branches of the traditional Finno-Ugric language tree (Finno-Permic and Ugric) are distant. About 200 words with common roots in all main Finno-Ugric languages have been identified by philologists including 55 about fishing, 15 about reindeer, and three about commerce.
The term Finno-Ugric, which originally referred to the entire family, is sometimes used as a synonym for the term Uralic, which includes the Samoyedic languages,[3] as commonly happens when a language family is expanded with further discoveries.
Status
The validity of Finno-Ugric as a genetic grouping is under challenge,[4] with some feeling that the Finno-Permic languages are as distinct from the Ugric languages as they are from the Samoyedic languages spoken in Siberia, or even that none of the Finno-Ugric, Finno-Permic, or Ugric branches has been established. Received opinion has been that the easternmost (and last-discovered) Samoyed had separated first and the branching into Ugric and Finno-Permic took place later, but this reconstruction does not have strong support in the linguistic data. In the past, and occasionally today as well, the term Finno-Ugric was used for the entire Uralic language family.
Origins
Attempts at reconstructing a Proto-Finno-Ugric protolanguage—that is, a common ancestor of all Uralic languages except for the Samoyedic languages—are largely indistinguishable from Proto-Uralic, suggesting that Finno-Ugric might not be a historical grouping but a geographical one, with Samoyedic being distinct due to lexical borrowing rather than actually being historically divergent. It has been proposed that the area where Proto-Finno-Ugric was spoken reached between the Baltic Sea and the Ural mountains.[5]
Traditionally, the main set of evidence for the genetic proposal of Proto-Finno-Ugric has come from vocabulary. A large amount of vocabulary (e.g. the numerals "one", "three", "four" and "six"; the body-part terms "hand", "head") is only reconstructed up to the Proto-Finno-Ugric level, while only words with a Samoyedic equivalent have been reconstructed for Proto-Uralic. This methodology has been criticised, as no coherent explanation other than inheritance has been presented for the origin of most of the Finno-Ugric vocabulary (though a small number has been explained as old loanwords from Proto-Indo-European or its immediate successors). The Samoyedic group has undergone a longer period of independent development, and its divergent vocabulary could be due to mechanisms of replacement such as language contact. (The Finno-Ugric group is usually dated to approximately 4000 years of age, the Samoyedic a little over 2000.) Proponents of the traditional binary division note, however, that the invocation of extensive contact influence on vocabulary is at odds with the grammatical conservatism of Samoyedic.
The consonant *š (voiceless postalveolar fricative, [ʃ]) has not been conclusively shown to occur in the traditional Proto-Uralic lexicon, but it is attested in some of the Proto-Finno-Ugric material. Another feature attested in the Finno-Ugric vocabulary is that *i now behaves as a neutral vowel with respect to front-back vowel harmony, and thus there are roots such as *niwa- "to remove the hair from hides".[6]
Regular sound changes proposed for this stage are few and remain open to interpretation. Sammallahti (1988)[6] proposes five, following Janhunen's (1981) reconstruction of Proto-Finno-Permic:
- Compensatory lengthening: development of long vowels from the cluster of vowel plus a particular syllable-final element, of unknown quality, symbolized by *x
- Raising of short *o to *u in open syllables before a subsequent *i
- E.g. *lomi → *lumi "snow" (→ Finnish lumi, Hungarian archaic lom "frost", etc.)
- Shortening of long vowels in closed syllables and before a subsequent open vowel *a, *ä, predating the raising of *ää and *ee
- E.g. *ńäxl+mä → *ńäälmä → *ńälmä "tongue" (→ Northern Sami njalbmi, Hungarian nyelv, etc.)
Sammallahti (1988) further reconstructs sound changes *oo, *ee → *a, *ä (merging with original *a, *ä) for the development from Proto-Finno-Ugric to Proto-Ugric. Similar sound laws are required for other languages as well. Thus, the origin and raising of long vowels may actually belong at a later stage,[7] and the development of these words from Proto-Uralic to Proto-Ugric can be summarized as simple loss of *x (if it existed in the first place at all; vowel length only surfaces consistently in the Baltic-Finnic languages.[8]) The proposed raising of *o has been alternately interpreted instead as a lowering *u → *o in Samoyedic (PU *lumi → *lomə → Proto-Samoyedic *jom).[7]
Janhunen (2007, 2009)[9][10] notes a number of derivational innovations in Finno-Ugric, including *ńoma "hare" → *ńoma-la, (vs. Samoyedic *ńomå), *pexli "side" → *peel-ka → *pelka "thumb", though involving Proto-Uralic derivational elements.
Structural features
The Finno-Uralic group is not typologically distinct from Uralic as a whole: the most widespread structural features among the group all extend to the Samoyedic languages as well.
Classification disputes
The relation of the Finno-Permic and the Ugric groups is adjudged remote by some scholars. On the other hand, with a projected time depth of only 3 or 4 thousand years, the traditionally accepted Finno-Ugric grouping would be far younger than many major families such as Indo-European or Semitic, and would be about the same age as, for instance, the Eastern subfamily of Nilotic. But the grouping is far from transparent or securely established. The absence of early records is a major obstacle. As for the Finno-Ugric Urheimat, most of what has been said about it is speculation.
Some linguists criticizing the Finno-Ugric genetic proposal[11] also question the validity of the entire Uralic family, instead proposing a Ural–Altaic hypothesis, within which they believe Finno-Permic may be as distant from Ugric as from Turkic. However, this approach has been rejected by nearly all other specialists in Uralic linguistics. For refutations, see e.g. Aikio 2003; Bakró-Nagy 2003, 2005; De Smit 2003; Georg 2003; Kallio 2004; Laakso 2004; Saarikivi 2004.
Common vocabulary
Loanwords
One argument in favor of the Finno-Ugric grouping has come from loanwords. Several loans from the Indo-European languages are present in most or all of the Finno-Ugric languages, while being absent from Samoyedic; many others also must be for phonological reasons dated as quite old.
Häkkinen (1983) has demonstrated that the alleged Proto-Finno-Ugric loanwords are disproportionally well-represented in Hungarian and the Permic languages, and disproportionally poorly represented in the Ob-Ugric languages. Hence it is possible that such words have been acquired by the languages only after the initial dissolution of the Uralic family into individual dialects, and that the scarcity of loanwords in Samoyedic results from its peripheric location.[12]
Numbers
The following table lists the numbers 1 to 10 in several Finno-Ugric languages. Forms in italic do not descend from the reconstructed forms. Only "2" and "5" have cognates in the Samoyedic languages.
| Number | Baltic Finnic | Samic | Mordvinic | Mari | Permic | Ugric | Proto- Finno- Ugric | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finnish | Estonian | Võro | Livonian | Northern Sami | Inari Sami | Erzya | Moksha | Meadow Mari | Komi | Mansi | Khanty | Hungarian | ||
| 1 | yksi gen. yhden, part. yhtä |
üks gen. ühe, part. üht(e) |
ütś | ikš | okta | ohtâ | vejke | fkä | ikte | ətik | äkwa | ĭt | egy[13] | *ükte |
| 2 | kaksi gen. kahden, part. kahta |
kaks gen. kahe, part. kaht(e) |
katś | kakš | guokte | kyeh´ti | kavto | kaftə | kokət | kɨk | kityg | kät | kettő/két | *kakta |
| 3 | kolme | kolm | kolm | kuolm | golbma | kulmâ | kolmo | kolmə | kumət | kuim | hurum | koləm | három, harm- | *kolme |
| 4 | neljä | neli | nelli | nēļa | njeallje | nelji | ńiľe | nilä | nələt | nəľ | nila | ńelä | négy | *neljä |
| 5 | viisi | viis | viiś | vīž | vihtta | vittâ | veƭe | vetä | wizət | vit | ät | wet | öt | *viite |
| 6 | kuusi | kuus | kuuś | kūž | guhtta | kuttâ | koto | kotə | kuðət | kvajt | hot | kut | hat | *kuute |
| 7 | seitsemän | seitse | säidse | seis | čieža | čiččâm | śiśem | sisäm | šəmət | sizim | sat | tapət | hét | N/A |
| 8 | kahdeksan | kaheksa | katõsa | kōdõks | gávcci | käävci | kavkso | kafksə | kandaš(e) | kəkjamɨs | ńololow | nəvət | nyolc | N/A |
| 9 | yhdeksän | üheksa | ütesä | īdõks | ovcci | oovce | vejkse | veçksə | indeš(e) | əkmɨs | ontolow | yaryaŋ | kilenc | N/A |
| 10 | kymmenen | kümme | kümme | kim | logi | love | kemeń | keməń | lu | das | low | loŋət | tíz | *luke |
The number '2' descends in Ugric from a front-vocalic variant *kektä.
The numbers '9' and '8' in Finnic through Mari are considered to be derived from the numbers '1' and '2' as '10–1' and '10–2'. One reconstruction is *yk+teksa and *kak+teksa respectively, where *teksa cf. deka is an Indo-European loan; notice that the difference between /t/ and /d/ is not phonemic, unlike in Indo-European. Another analysis is *ykt-e-ksa, *kakt-e-ksa, with *e being the negative verb.
Finno-Ugric Swadesh lists
100-word Swadesh lists for certain Finno-Ugric languages can be compared and contrasted at the Rosetta Project website: Finnish, Estonian, Hungarian, Erzya.
Peoples
The Finno-Ugric peoples is a presumed historic group of those peoples who currently speak Finno-Ugric languages. Like the speakers of Indo-European languages, Finno-Ugric peoples include multiple races.
The four largest ethnicities speaking Finno-Ugric languages are the Hungarians (14.5 million), Finns (6.5 million), Estonians (1.1 million), and Mordvins (0.85 million). Three (Hungarians, Finns, and Estonians) inhabit independent nation-states, Hungary, Finland, and Estonia, while the Mordvins have an autonomous Mordovian Republic within Russia. The traditional area of the indigenous Sami people is in Northern Fenno-Scandinavia and the Kola Peninsula in Northwest Russia and is known as Sápmi. Some other Finno-Ugric peoples have autonomous republics in Russia: Karelians (Republic of Karelia), Komi (Komi Republic), Udmurts (Udmurt Republic), Mari (Mari El Republic), and Mordvins (Moksha and Erzya; Republic of Mordovia). Khanty and Mansi peoples live in the Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug of Russia, while Komi-Permyaks live in Komi-Permyak Okrug, which formerly was an autonomous okrug of Russia, but today is a territory with special status within Perm Krai.
Population genetics
The linguistic reconstruction of the Finno-Ugric language family has led to the postulation that the ancient Proto–Finno-Ugric people were ethnically related, and that even the modern Finno-Ugric-speaking peoples are ethnically related.[14] Such hypotheses are based on the assumption that heredity can be traced through linguistic relatedness,[15] although it must be kept in mind that language shift and ethnic admixture, a relatively frequent and common occurrence both in recorded history and most likely also in prehistory, confuses the picture and there is no straightforward relationship, if at all, between linguistic and genetic affiliation. Still, the premise that the limited community of speakers of a proto-language must have been ethnically homogeneous remains accepted.[10]
Modern genetic studies have shown that the Y-chromosome haplogroup N3, and sometimes N2, is almost specific though certainly not restricted to Uralic or Finno-Ugric speaking populations, especially as high frequency or primary paternal haplogroup.[16][17] These haplogroups branched from haplogroup N, which probably spread north, then west and east from Northern China about 12,000–14,000 years before present from father haplogroup NO (haplogroup O being the most common Y-chromosome haplogroup in Southeast Asia).
Some of the ethnicities speaking Finno-Ugric languages are:
(Baltic Finnic)
("Volgaic")
(Permic)
(Ugric)
See also
- Finnic peoples
- Finnic languages
- Ugric peoples
- Volga Finns
- Comb Ceramic culture
- Uralic languages
- Uralo-Siberian languages
- Old Hungarian script
- Old Permic script
- Proto-Finnic language
- Proto-Uralic homeland hypotheses
References
- ↑ Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 11th Edition. Retrieved September 04, 2012 from website:http://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/Finno-Ugric
- ↑ Tapani Salminen, "The rise of the Finno-Ugric language family." In Carpelan, Parpola, & Koskikallio (eds.), Early contacts between Uralic and Indo-European: linguistic and archaeological considerations. Mémoires de la Société Finno-Ougrienne 242; Helsinki 2001. 385–396.
- ↑ Tommola, Hannu (2010). "Finnish among the Finno-Ugrian languages". Mood in the Languages of Europe. John Benjamins Publishing Company. p. 155. ISBN 978-90-272-0587-2.
- ↑ Salminen, Tapani (2002): Problems in the taxonomy of the Uralic languages in the light of modern comparative studies; the clade has also been abandoned by Ethnologue.
- ↑ Campbell, Lyle (2004). Historical linguistics: an introduction. MIT Press. p. 405. ISBN 978-0-262-53267-9.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Sammallahti, Pekka (1988). "Historical Phonology of the Uralic languages". In Denis, Sinor. The Uralic languages – Description, history and foreign influences. BRILL. pp. 478–554. ISBN 978-90-04-07741-6.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Häkkinen, Jaakko 2009: Kantauralin ajoitus ja paikannus: perustelut puntarissa. – Suomalais-Ugrilaisen Seuran Aikakauskirja 92. http://www.sgr.fi/susa/92/hakkinen.pdf
- ↑ Aikio, Ante (2012), "On Finnic long vowels, Samoyed vowel sequences, and Proto-Uralic *x", Suomalais-Ugrilaisen Seuran toimituksia 264, ISSN 0355-0230
- ↑ Janhunen, Juha (2007), "The primary laryngeal in Uralic and beyond" (PDF), Suomalais-Ugrilaisen Seuran toimituksia 253, ISSN 0355-0230, retrieved 2010-05-05
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Janhunen, Juha (2009), "Proto-Uralic – what, where and when?" (PDF), Suomalais-Ugrilaisen Seuran toimituksia 258, ISBN 978-952-5667-11-0, ISSN 0355-0230
- ↑ especially Angela Marcantonio
- ↑ Häkkinen, Kaisa (1983). Suomen kielen vanhimmasta sanastosta ja sen tutkimisesta (PhD) (in Finnish). Turun yliopisto. ISBN 951-642-445-7.
- ↑ According to Zaich, Gábor (2006). Etimológiai szótár (in Hungarian). p. 167. ISBN 978-963-7094-01-9., the Hungarian word for "one" is an internal development, i.e. it is not related to the Proto-Finno-Ugric *ükte
- ↑ Sámuel Gyarmathi (1983). Grammatical Proof of the Affinity of the Hungarian Language with Languages of Fennic Origin: (Gottingen Dieterich, 1799). John Benjamins Publishing. ISBN 978-90-272-0976-4.
- ↑ Where do Finnish come from?
- ↑ European Journal of Human Genetics – Abstract of article: A counter-clockwise northern route of the Y-chromosome haplogroup N from Southeast Asia towards Europe
- ↑ Journals Home
Further reading
- Aikio, Ante (2003). Angela Marcantonio, The Uralic Language Family: Facts, Myths and Statistics. (Book review.) In: Word – Journal of the International Linguistic Association 3/2003: 401–412.
- Bakró-Nagy Marianne 2003. Az írástudók felelőssége. Angela Marcantonio, The Uralic Language Family. Facts, myths and statistics. In: Nyelvtudományi Közlemények 100: 44–62. (Downloadable: )
- Bakró-Nagy Marianne 2005. The responsibility of literati. Angela Marcantonio, The Uralic Language Family. Facts, myths and statistics. In: Lingua 115: 1053–1062. (Downloadable: )
- Etymologisches Wörterbuch des Ungarischen: Register. 1997. ISBN 978-963-05-6227-0.
- Björn Collinder (1977). Fenno-Ugric Vocabulary: An Etymolog. Buske Verlag. ISBN 978-3-87118-187-0.
- Campbell, Lyle: Historical Linguistics: An Introduction. Edinburgh University Press 1998.
- Márta Csepregi; Gábor Bereczki (2001). Finnugor kalauz. ISBN 978-963-243-862-7.
- De Smit, Merlijn 2003: A. Marcantonio: The Uralic language family. Facts, myths and statistics (review). In: Linguistica Uralica 2003, 57-67.
- Encyclopædia Britannica 15th ed.: Languages of the World: Uralic languages. Chicago, 1990.
- Georg, Stefan 2003. Rezension: A. Marcantonio: The Uralic Language Family. Facts, Myths and Statistics. In: Finnisch-Ugrische Mitteilungen Band 26/27.
- Heikki Paunonen; Päivi Rintala (1984). Nykysuomen rakenne ja kehitys: Näkökulmia kielen vaihteluun ja muuttumiseen. ISBN 978-951-717-360-5.
- Kallio, Petri 2004. (Review:) The Uralic Language Family: Facts, Myths, and Statistics (Angela Marcantonio). In: Anthropological Linguistics Vol. 46, no. 4: 486-489.
- Laakso, Johanna: Karhunkieli. Pyyhkäisyjä suomalais-ugrilaisten kielten tutkimukseen (A Bear Tongue. Views on the Research of the Finno-Ugric Languages). Helsinki: SKS, 1999.
- Johanna Laakso (1991). Uralilaiset kansat: tietoa suomen sukukielistä ja niiden puhujista. ISBN 9510164852.
- Laakso, Johanna 2004. Sprachwissenschaftliche Spiegelfechterei (Angela Marcantonio: The Uralic language family. Facts, myths and statistics). In: Finnisch-ugrische Forschungen 58: 296-307.
- Marcantonio, Angela: What Is the Linguistic Evidence to Support the Uralic Theory or Theories? – In Linguistica Uralica 40, 1, pp 40–45, 2004.
- Marcantonio, Angela: The Uralic Language Family: Facts, Myths and Statistics. 2003.
- Marcantonio, Angela, Pirjo Nummenaho, and Michela Salvagni: The "Ugric–Turkic Battle": A Critical Review. In Linguistica Uralica 37, 2, pp 81–102, 2001. Online version.
- Saarikivi, Janne 2004. Review of: Angela Marcantonio. Uralic Language Family: Facts, Myths and Statistics. In: Journal of Linguistics 1/2004. p. 187-191.
- Pekka Sammallahti; Matti Morottaja (1983). Saami-Suoma-Saami Skovlasanikirje =: Inarinsaame-Suomi-Inarinsaame Koulusanakirja. Ruovttueatnan Gielaid Dutkanguovddas. ISBN 978-951-9475-36-3.
- Pekka Sammallahti (1993). Sámi-suoma-sámi sátnegirji: Saamelais-suomalais-saamelainen sanakirja. ISBN 978-951-8939-28-6.
- Sinor, Denis (ed.): Studies in Finno-Ugric Linguistics: In Honor of Alo Raun (Indiana University Uralic and Altaic Series: Volume 131). Indiana Univ Research, 1977, ISBN 978-0-933070-00-4.
- Vikør, Lars S. (ed.): Fenno-Ugric. In: The Nordic Languages. Their Status and Interrelations. Novus Press, pp. 62–74, 1993.
- Wiik, Kalevi: Eurooppalaisten juuret, Atena Kustannus Oy. Finland, 2002.
- Языки народов СССР III. Финно-угорские и самодийские языки (Languages of the Peoples in the USSR III. Finno-Ugric and Samoyedic Languages). Москва (Moscow): Наука (Nauka), 1966. (Russian)
- A magyar szókészlet finnugor elemei. Etimológiai szótár (The Hungarian Vocabulary of Finno-Ugric Origin. Etymological Dictionary). Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó, 1967–1978.
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Finno-Ugrian. |
- Some Finno-Ugrian links A more comprehensive link collection
- Swadesh lists for the Finno-Ugric languages (from Wiktionary's Swadesh-list appendix)
- FAQ about Finno-Ugrian Languages
- Linguistic Shadow-Boxing Johanna Laakso's book review of Angela Marcantonio's "The Uralic language family. Facts, myths and statistics"
- Uralic Linguistics Vs. Voodoo Science! A collection of links about the "new paradigm" debate by Merlijn de Smit
- Numbers in Asian languages Counting to ten in a variety of languages
- Ugri.info Finno-Ugric peoples infobase
- Finno-Ugric Electronic Library by the Finno-Ugric Information Center in Syktyvkar, Komi Republic Interface in Russian and English, texts in Mari, Komi, Udmurt, Erzya and Moksha languages.
- The Finno-Ugrics: The dying fish swims in water The Economist, December 20, 2005
- "Ethnic origins of Finno-Ugric nations and modern Finno-Ugric nationalism in the Russian Federation" by Konstantin Zamyatin
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||