Finnish verb conjugation
Verbs in the Finnish language can be divided into six main groups depending on the stem type, both for formal analysis and for teaching the language to non-native speakers. All six types have the same set of personal endings, but the stems assume different suffixes and undergo (slightly) different changes when inflected.
Please refer to the article on Finnish language grammar for more about verbs and other aspects of Finnish grammar.
Tables of conjugation
Tables of conjugation are given here for the regular verb (of type I,) puhua, to speak, as used in the formal, written language. Verb conjugation in the everyday spoken language is somewhat different.
Basic tenses in the indicative mood
| indicative mood | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| active voice | present tense | imperfect | perfect | pluperfect | ||||||
| per. | no. | pron. | affirmative | negative | affirmative | negative | affirmative | negative | affirmative | negative |
| 1st | sg. | minä | puhun | en puhu | puhuin | en puhunut | olen puhunut | en ole puhunut | olin puhunut | en ollut puhunut |
| 2nd | sinä | puhut | et puhu | puhuit | et puhunut | olet puhunut | et ole puhunut | olit puhunut | et ollut puhunut | |
| 3rd | hän | puhuu | ei puhu | puhui | ei puhunut | on puhunut | ei ole puhunut | oli puhunut | ei ollut puhunut | |
| 1st | pl. | me | puhumme | emme puhu | puhuimme | emme puhuneet | olemme puhuneet | emme ole puhuneet | olimme puhuneet | emme olleet puhuneet |
| 2nd | te | puhutte | ette puhu | puhuitte | ette puhuneet | olette puhuneet | ette ole puhuneet | olitte puhuneet | ette olleet puhuneet | |
| 3rd | he | puhuvat | eivät puhu | puhuivat | eivät puhuneet | ovat puhuneet | eivät ole puhuneet | olivat puhuneet | eivät olleet puhuneet | |
| passive voice | puhutaan | ei puhuta | puhuttiin | ei puhuttu | on puhuttu | ei ole puhuttu | oli puhuttu | ei ollut puhuttu | ||
The present, imperfect, perfect, and pluperfect correspond fairly well to English: "speaks", "spoke", "has spoken", and "had spoken", resp., or in the passive voice, "it is spoken", "it was spoken", "it has been spoken", and "it had been spoken". Note the auxiliary verb ei used for negation, usually with the naked stem of the main verb, but with the past participle in the negative imperfect. Finnish lacks a true future tense, so normally the present tense must suffice for future time as well.
Conditional and potential mood
| conditional mood | potential mood | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| active voice | present tense | perfect | present tense | perfect | ||||||
| per. | no. | pron. | affirmative | negative | affirmative | negative | affirmative | negative | affirmative | negative |
| 1st | sg. | minä | puhuisin | en puhuisi | olisin puhunut | en olisi puhunut | puhunen | en puhune | lienen puhunut | en liene puhunut |
| 2nd | sinä | puhuisit | et puhuisi | olisit puhunut | et olisi puhunut | puhunet | et puhune | lienet puhunut | et liene puhunut | |
| 3rd | hän | puhuisi | ei puhuisi | olisi puhunut | ei olisi puhunut | puhunee | ei puhune | lienee puhunut | ei liene puhunut | |
| 1st | pl. | me | puhuisimme | emme puhuisi | olisimme puhuneet | emme olisi puhuneet | puhunemme | emme puhune | lienemme puhuneet | emme liene puhuneet |
| 2nd | te | puhuisitte | ette puhuisi | olisitte puhuneet | ette olisi puhuneet | puhunette | ette puhune | lienette puhuneet | ette liene puhuneet | |
| 3rd | he | puhuisivat | eivät puhuisi | olisivat puhuneet | eivät olisi puhuneet | puhunevat | eivät puhune | lienevät puhuneet | eivät liene puhuneet | |
| passive voice | puhuttaisiin | ei puhuttaisi | olisi puhuttu | ei olisi puhuttu | puhuttaneen | ei puhuttane | lienee puhuttu | ei liene puhuttu | ||
The conditional mood corresponds mostly to "would" or "should" or to the past subjunctive in English. (Finnish lacks a subjunctive mood.) The potential mood is rather rare, and corresponds to "may" or "might" in English. The perfect forms of these moods are easily understood as "would have", "should have", "might have", etc.
Imperative mood and miscellaneous tenses
| imperative mood | indicative mood | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| active voice | present tense | perfect | present prospective | imperfect prospective | ||||||
| per. | no. | pron. | affirmative | negative | affirmative | negative | affirmative | negative | affirmative | negative |
| 1st | sg. | minä | — | — | — | — | olen puhuva | en ole puhuva | olin puhuva | en ollut puhuva |
| 2nd | sinä | puhu | älä puhu | ole puhunut | älä ole puhunut | olet puhuva | et ole puhuva | olit puhuva | et ollut puhuva | |
| 3rd | hän | puhukoon | älköön puhuko | olkoon puhunut | älköön olko puhunut | on puhuva | ei ole puhuva | oli puhuva | ei ollut puhuva | |
| 1st | pl. | me | puhukaamme | älkäämme puhuko | olkaamme puhuneet | älkäämme olko puhuneet | — | — | — | — |
| 2nd | te | puhukaa | älkää puhuko | olkaa puhuneet | älkää olko puhuneet | — | — | — | — | |
| 3rd | he | puhukoot | älkööt puhuko | olkoot puhuneet | älkööt olko puhuneet | — | — | — | — | |
| passive voice | puhuttakoon | ei puhuttako — älköön puhuttako | olkoon puhuttu | älköön olko puhuttu | on puhuttava | ei ole puhuttava | oli puhuttava | ei ollut puhuttava | ||
The first and third person imperative forms here correspond to English "let us speak", "let him not speak", "let it not be spoken", etc. The perfect imperative is still valid, if somewhat awkward and contrived, e.g. as in English "let it (not) have been spoken". The first person plural imperative puhukaamme sounds rather formal and archaic, so in everyday speech, the passive present indicative puhutaan, is used instead, although this may not quite be considered correct. There are many variations of the imperative forms: in old writings, one may also see the forms puhukaat or puhukaatte for the second person plural, puhukaan for the third person plural, or puhuttakaan for the passive. In the passive or third person, the imperative is sometimes used for the present or perfect subjunctive of other languages, a mood which is lacking in Finnish.
The present prospective and the imperfect prospective correspond best to "I am to speak" and "I was to speak" in English. It is not correct Finnish to use these tenses in the plural: the plural form of the present participle, puhuvat, would be confusing if used in this sense, as it resembles too closely the third person plural present indicative. Despite the apparently equivalent use of the present participle, the grammatical aspect of these tenses is prospective rather than continuous or progressive as in English.
Verbs of obligation in the agent construction
Verbs of obligation such as täytyä, tarvita, pitää, and tulla, with the meanings "must", "need to", "ought to", "shall", respectively are often used in the agent form of construction in which the verb is not conjugated for person but is in the impersonal third person singular. In this construction
- the person(s) bearing the obligation is regarded as the 'agent' (not the subject) and is in the genitive case
- the verb of obligation is in the impersonal third person singular regardless of the plurality and person of the agent.
- This is followed by another verb or verb phrase in which the verb is in the short from first infinitive (i.e. the dictionary form) and which is then regarded as the sentence's subject.[1]
- Heidän täytyy puhua minun kanssani = They must speak with me;
- Minun täytyy puhua heidän kanssansa = I must speak with them;
- Sinun ei tarvitse tehdä tuota = you don't need to do that;
- Ei sinun pidä tappaman = thou shalt not kill.[2]
- sinun pitäisi tulla huomenna = you should come tomorrow.
There is no equivalent of this type of construction in English.
The verb täytyä can only be used in this construction and therefore has no other personal forms. The other verbs can carry personal endings in other forms of construction with normal subject, verb, and object in which the obligation is less strong or in which the verb takes on a different meaning altogether.
- (Minä) tarvitsen apua I need help—expressing need without obligation
- (Minä) pidän hänestä I like him/her—verb has a different meaning
Infinitives and participles
In Finnish there are five infinitive forms,[3] and past and present participles for both active and passive voices.[4]
Infinitive I
First infinitive is the dictionary form of the verb, e.g., puhu-a = "to speak" (stem puhu), and it corresponds in meaning and function to the English infinitive introduced by the particle "to". The suffix of the first infinitive depends on the type of the verb stem. With so-called "vowel" stems, (see verbs of Type I, below), the first infinitive suffix is -a/-ä, whereas with "consonantal" stems, (e.g., Types IV-VI), the suffix is most often -ta/-tä. With vowel stems that consist of a single open syllable ending in a long vowel or a diphthong, or longer stems that end in such syllables, (Type II), the infinitive suffix is -da/-dä, e.g., saa-da = "to get", syö-dä = "to eat", reagoi-da = "to react". The first infinitive of consonantal stems always has the weak consonant grade in the stem, e.g., karata = "to flee" < stem karkaa-.
First infinitive can be used in a sentence similarly to the English infinitive, standing for a subject or a direct object, without any additional inflection. It is also governed by modal verbs like saattaa "might" or voida "be able to", e.g., saattaa mennä = "might go" or voi hakea = "can fetch".
First infinitive has a so-called "long form", having the ending of the nominal translative case and an obligatory possessive suffix. The long form is usually associated with the literary register. It connotes either extent or intent. Examples:
- muista-a = "to remember"; muista-a-kse-ni = "as far as I can remember" (extent), or "in order that I might remember" (intent), lit. "for my remembering".
- näh-dä = "to see"; näh-dä-kse-en = "as far as he/she/it/they can see" (extent), "so that they could see" (intent).
In spoken Finnish, intent is often expressed with the short form infinitive if the subject is implicit or understood by context, or more explicitly with a subordinate clause containing a conditional verb, e.g., että minä muistaisin. Nevertheless, the long form is still used to signify extent; another example: tietä-ä = "to know", tietä-ä-kse-ni = "as far as I know".
The first infinitive does not generally take on any inflected forms. It appears only in the short (dictionary) form and in the long form, and the long form is not used without a possessive suffix.
Infinitive II
Second infinitive may be formed from the first infinitive by replacing the final 'a/ä' with an 'e'. It occurs in the instructive and inessive cases. If the second infinitive has a subject, then the subject is put in the genitive case; in the inessive case the second infinitive also accepts a possessive suffix if appropriate.
The instructive form conveys manner of action, corresponding approximately with "-ing" or "-ingly" in English, less commonly with "-ande/ende" in Swedish, and very commonly with "-ant" in French. It is parallel in function and meaning to the Russian adverbial participle (as opposed to the adjectival participle). Examples:
- tietäen = "knowingly" (instructive);
- tietäen, että hänen täytyisi puhua = "knowing that he would have to speak" = sachant qu'il aurait besoin de parler in French = зная, что ему следовало бы говорить in Russian
- 'näin puhuen' = "thus speaking" (instructive);
The inessive form conveys co-terminal action; i.e. something happening at the same time as something else; more properly seen as some action whose accomplishment simultaneously brings about the accomplishment of something else. It corresponds approximately in English to the use of "when", "while", or the somewhat archaic or British) "whilst"; strict co-terminality is still expressed in English with "in", (or "by",) the present participle "-ing", and any subject in the possessive case, in a manner exactly analogous to the Finnish, and similarly in French with "en" and the present participle "-ant". Examples
- kuollessa = "in dying" or "while dying" = en mourant in French (inessive) = умирая in Russian
- Varas iski uhrin syödessä aamupalaa = "The thief struck whilst the victim was eating breakfast"
The inessive of this infinitive also has a passive form:
- tiedettäessä = "in being known", said of some fact;
but this is ambiguous and could be taken for the active inessive infinitive II of the causative tiedettää, "to make (someone) know"
- tiedettäessä = "in making (someone) know" or "in making (some fact) known".
Infinitive III
The third infinitive is formed by adding the ending -ma/mä to the hard grade of the present stem, (described below.) It is a noun in its own right, denoting "the act" of a verb, and thus it is fully declineable as a noun, but some of the cases have special or commonly understood meanings. The illative of the third infinitive is a common inchoative, governed by such verbs as ruveta and joutua:
- hän rupesi saarnaamaan = "he began to preach".
- häntä ei mennä neuvomaan = "You don't go and advise him"
The elative is used in the sense of forbidding or discouraging an action.
- poikia kiellettiin polttamasta = "the boys were forbidden from smoking"
The adessive (often with a possessive suffix) is used in the sense of being "just about to" do something, equivalent to the French expression "sur le point de (faire quelque chose)".
Agentive Participle
In Finnish, the passive participle cannot be used when the agent is expressed. For this purpose, Finnish uses forms ending in -ma/mä that are formally identical to the third infinitive. (Some authors include it as one of the uses of the third infinitive, while others list it under the special name "agentive participle"). The agentive participle is never used when the agent is not expressed, and must be used in all situations where one wishes to use the passive and express the agent:
- Talo on Pekan maalaama = "The house was painted by Pekka"
- Pekan maalaama talo = "the house painted by Pekka"
- Talo on (sinun) maalaamasi = "The house was painted by you"
As expected for a participle, it agrees with the head noun; in the following, the ending -mia and kirjeita 'books' are in the partitive plural:
- pojan viime viikolla Japanista ystävilleen kirjoittamia kirjeitä = "(some of) the letters written by the boy to his friends last week from Japan"
Infinitive IV
The fourth infinitive is formed just like the third, but with the ending -minen, which is declined like all other Finnish nouns in -nen. It is also a noun, but its meaning is more "the process" rather than the very act of a verb. This often corresponds to "-ation" words in English:
- käyminen = "(the process of) going", which can mean "fermentation" among other things.
The use of this form as a proper infinitive, rather than an "action noun" is generally restricted to forms such as the following, where it implies a sort of obligation:
- minun on tekeminen jotakin = "it is up to me to do something"
- on tekeminen jotakin = "something ought to be done"
- heidän ei ole kysymistä ... = "theirs is not to ask ..."
- tästä ei ole puhumista = "this is not to be spoken of";
or this construction, where the finite verb is repeated in the partitive with a possessive suffix:
- hän puhui puhumistaan = "he talked and talked".
Infinitive V
The rarely used fifth infinitive is a "diminutive" of the third infinitive. It is apparently used only in the adessive plural with a possessive suffix, indicating that at some point in time the action of the verb is "but little" accomplished:
- olin puhumaisillani = "I was just starting to speak".
Present participles
Active
The active present participle is formed by adding -va/vä to the hard grade of the present indicative stem of the verb.
- tulevat päivät ovat tuulisia = "the coming days are (going to be) windy"
(In the nominative plural this form nearly always coincides with the third person plural present indicative.)
Passive
There is also a passive present participle formed by adding the same ending to the passive stem.
- puhuttava = "to be spoken of"
This form is also ambiguous: it could equally well be the active present participle of the causative puhuttaa, "to cause (someone) to speak", thus:
- puhuttava = (active) "making (someone) speak"
- puhutettava = (passive) "being made to speak"
Past participles
Active
The active past participle is usually formed by adding -nut/nyt to the short stem, omitting any epenthetic vowel. Verbs of type III (ending in -lla/llä, -rra/rrä, and -sta/stä) assimilate the n of this ending, thus:
- tullut = "(one that has) come";
- purrut = "(one that has) bitten";
- pessyt = "(one that has) washed".
The stem of the active past participle, for all other cases but the nominative singular, ends in -nee-, which may be likewise assimilated. See tables of conjugation.
Agentive
See Agentive Participle above.
Passive
The passive past participle has the ending -tu/ty or -ttu/tty to the soft grade of the stem. For a verb of type I, a final -a/ä- of the stem is replaced by -e- for the passive past participle.
- antaa = "to give"; annettu = "(that has been) given".
The passive past participle is subject to consonant gradation:
- tt → t;
and for verbs of type III:
- lt → ll,
 nt → nn,
nt → nn, rt → rr,
rt → rr,  st → st.
st → st.
- annettu = (that has been) given; annetut = "(that have been) given", (pl.);
- purtu "(one that has been) bitten", graded as purru-, e.g. purrun "of that which has been bitten".
- pesty = "(that has been) washed", unchanged in soft grade, e.g. pestyt hiukset = "hair that has been washed" (pl. of hius, "a single hair").
Derived passive forms
Without exception, all other passive forms of the verb may be derived from the passive past participle in a regular manner, by replacing the final -u/y with the following endings:
- in the hard grade:
- '-iin': passive imperfect; annettiin "was given"
- '-ava':: passive present participle; annettava "that which is (to be) given"
- '-aisiin/äisiin': passive conditional; annettaisiin "would be given"
- '-aisi/äisi': passive conditional connegative with negative verb ei; ei annettaisi "would not be given"
- '-aneen/äneen': passive potential; annettaneen "might be given"
- '-ane/äne': passive potential connegative; ei annettane "might not be given"
- '-akoon/äköön', '-akaan/äkään': passive imperative; annettakoon "shall be given"
- '-ako/äkö': passive imperative connegative; ei annettako "shall not be given"
- in the soft grade:
- '-aan/ään': passive present indicative; annetaan "is given"
- '-a/ä': passive present indicative connegative with negative verb ei; ei anneta "is not given".
Overview of main verb types
The following table shows the basic changes and marks for conjugating each of the types of Finnish verbs.
| Type | Example | 1. Pers. Pres. | 3. Pers. Imp. | Participle | Passive | Passive Imp. | Infinitive ends in | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-a | puhua | puhun | puhui | puhunut | puhutaan | puhuttiin | -oa, -ua/yä | to speak |
| I-b | oppia | opin | oppi | oppinut | opitaan | opittiin | -ea/eä, -ia/iä | to learn |
| I-c | antaa | annan | antoi | antanut | annetaan | annettiin | -aa, 1. vowel a/e/i | to give |
| I-d | johtaa | johdan | johti | johtanut | johdetaan | johdettiin | -aa, 1. vowel o/u | to lead |
| I-e | kieltää | kiellän | kielsi | kieltänyt | kielletään | kiellettiin | -ää | to forbid |
| II-a | saada | saan | sai | saanut | saadaan | saatiin | (long vowel)+da/dä | to get |
| II-b | syödä | syön | söi | syönyt | syödään | syötiin | (diphthong)+da/dä | to eat |
| III | tulla | tulen | tuli | tullut | tullaan | tultiin | -lla/llä, -nna/nnä, -rra/rrä, -sta/stä |
to come |
| IV | haluta | haluan | halusi | halunnut | halutaan | haluttiin | -uta/ytä | to want |
| V | tarvita | tarvitsen | tarvitsi | tarvinnut | tarvitaan | tarvittiin | -ita/itä | to need |
| VI | paeta | pakenen | pakeni | paennut | paetaan | paettiin | -eta/etä | to flee |
Type I verbs
These are verbs whose infinitive forms end in vowel + a/ä, for example puhua = "to speak", tietää = "to know". This group contains a very large number of verbs. Here is how tietää conjugates in the present indicative:
- minä tiedän = I know
- sinä tiedät = you (singular) know
- hän/se tietää = (s)he/it knows
- me tiedämme = we know
- te tiedätte = you (plural/formal) know
- he/ne tietävät = they know
The personal endings are -n, -t, -(doubled final vowel), -mme, -tte, -vat. The inflecting stem is formed by dropping the final -a/ä of the infinitive, and has a strong-grade consonant in the third-person forms and weak-grade elsewhere. Note that for third person plural, this is an exception to the general rule for strong grade.
Past Tense
In the simple case (which applies to most type I verbs), the imperfect indicative is formed by inserting the characteristic marker i between the stem and the personal endings, which are the same as in the present tense except that the vowel does not double in the 3rd person singular:
- puhun = "I speak", puhuin = 'I spoke'
- puhut = "you speak", puhuit = 'you spoke'
- puhuu = "(he) speaks", puhui = '(he) spoke'
- puhumme = "we speak", puhuimme = 'we spoke' and so on.
However, the insertion of the i often has an effect on the stem. Of type I verbs, one notable exception is tietää:
- tiedän = 'I know', tiesin = 'I knew'
ymmärtää = 'to understand' also follows this pattern. Changes of stem for other verb types will be discussed in the relevant sections below.
Passive
- Present passive
- The present passive is formed by adding -taan to the inflecting stem of the verb with the consonant in its weak form:
- puhua
 puhu-
puhu-  puhutaan
puhutaan - If the vowel at the end of the stem is a or ä it is changed to e before the -taan ending:
- tietää
 tiedä-
tiedä-  tiede
tiede 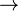 tiedetään
tiedetään
- Past passive
- This is formed in the same way as the present passive, except that the ending is -ttiin, hence puhuttiin = 'it was spoken', tiedettiin = 'it was known'.
- Note the presence of the same i marker in the past passive as in the imperfect indicative. Note also the presence of the extra t.
- Conditional passive
- This is formed in the same way as the present passive, except that the ending is -ttaisiin, hence puhuttaisiin = 'it would be spoken', tiedettäisiin = 'it would be known'.
- Note the presence of the isi conditional marker.
- Potential passive
- This is formed in the same way as the present passive, except that the ending is -ttaneen, hence puhuttaneen = 'it may be spoken', tiedettäneen = 'it may be known'.
- Note the presence of the ne potential marker.
Type II verbs
Verbs whose first infinitive ends in vowel + da, for example juoda = 'to drink', syödä = 'to eat'. This is a fairly large group of verbs, partly because one way in which foreign borrowings are incorporated into the Finnish verb paradigms is to add oida, for example, organisoida = 'to organise'.
Another important verb of this type is voida = 'to be able/allowed to'.
The stem is formed by removing da with no vowel doubling in the third person singular: juon, juot, juo, juomme, juotte, juovat.
Imperfect indicative
For these verbs whose stems end in two vowels, the first of the vowels is lost when the i is added in the imperfect: juon = 'I drink', join = 'I drank' etc.
There is an exception to this rule if the stem already ends in an i - for example voida or the -oida verbs mentioned earlier. In this case the stem does not change between present and imperfect indicative, so the imperfect forms are the same as the present forms, and the distinction between them must be made from context.
Passive
Passives in this group are formed in the same way as for group II verbs:
- syödä
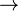 syödään, syötiin, syötäisiin
syödään, syötiin, syötäisiin - juoda
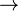 juodaan, juotiin, juotaisiin
juodaan, juotiin, juotaisiin
Type III verbs
These are verbs whose first infinitive ends in two consonants + a, for example mennä = 'to go'. Another way of looking at these verbs is that they have verb stems ending in a consonant to which a vowel must be added (either e for the present tense or i for the past tense) before the personal ending. The final consonant of the stem is generally emphasised by length of pronunciation in the infinitive and participle forms and orthographically written as a double consonant. Where the consonant ending of the stem is -s, however, the dictionary form of the verb ends with -stä or -sta. This is another large group of verbs.
Present indicative
The stem is formed by removing the a and its preceding consonant. Then add e followed by the personal endings: menen, menet, menee, menemme, menette, menevät.
Imperfect indicative
The i of the imperfect is added directly to the stem formed as for the present tense, then the personal endings are added: pestä = 'to clean', pesen = 'I clean', pesin = 'I cleaned' etc.
Passive
- Present passive
- In this group, the passive has the same -aan ending as for group I verbs, but no t; the easiest way to form the passive is to extend the vowel on the end of the first infinitive and then add n:
- mennä
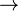 mennään
mennään
All other forms of the passive are related to the present passive in the same way as for type I verbs, including the 'extra t', except that since there was no t to start with, the passive forms only have one! Also the double consonant before the ending becomes single.
- mennä
 mennään
mennään  mentiin, mentäisiin
mentiin, mentäisiin - olla
 ollaan
ollaan  oltiin (see below), oltaisiin
oltiin (see below), oltaisiin
Type IV verbs
This, and the following two groups, have the first infinitive that ends in a vowel + ta/tä. Most commonly, type IV verbs end with ata/ätä, ota/ötä, uta/ytä, but other vowels are possible. Examples are tavata = "to meet", pilkata = "to mock", vastata = "to answer", haluta = "to want", tarjota = "to offer".
The stem used in present indicative conjucation is formed by dropping the -ta/-tä suffix from the infinitive form and adding a/ä. In conjugation, the normal personal ending is added; the final vowel is doubled in the 3rd person singular, unless the stem already ends in aa/ää:
- halua-n, halua-t, halua-a, halua-mme, halua-tte, halua-vat
- tapaa-n, tapaat, tapaa, tapaa-mme, etc.
- pilkkaa-n, pilkkaa-t, pilkkaa, pilkkaa-mme, etc.
- vastaa-n, vastaa-t, vastaa, vastaa-mme, etc.
- tarjoa-n, tarjoa-t, tarjoa-a, tarjoa-mme, etc.
The consonant in the stem appears in strong grade.
Imperfect indicative
The imperfect stem can be obtained from the infinitive by changing the final t to s, followed by the usual imperfect marker i; the stem consonant appears in strong grade. Examples with personal endings: halusi-n = "I wanted", tapasi-t = "you met", vastasi, "he answered", etc.
Passive
Passives in this type are formed in the same fashion as for type I verbs; as in type I, the stem consonant appears in the weak grade. Examples:
- haluta
 halutaan, haluttiin, haluttaisiin
halutaan, haluttiin, haluttaisiin - tavata
 tavataan, tavattiin, tavattaisiin
tavataan, tavattiin, tavattaisiin - vastata
 vastataan, vastattu, vastattiin, etc.
vastataan, vastattu, vastattiin, etc.
Type V verbs
All the verbs in this groups have infinitives ending in ita/itä. This type has few members; tarvita = "to need" is a common example.
The indicative stem may be obtained by dropping the final a and adding 'se': tarvitsen, tarvitset, tarvitsee, tarvitsemme, tarvitsette, tarvitsevat.
Imperfect indicative
-si takes the place of -se, but in the third-person singular, there is only one vowel, e.g.:
- tarvitsin, tarvitsit, tarvitsi, tarvitsimme, tarvitsitte, tarvitsivat
Passive
The passive forms of these verbs are built just like those of type IV, since both types end in -ta:
- valita
 valitaan, valittiin, valittaisiin
valitaan, valittiin, valittaisiin - merkitä
 merkitään, merkittiin, merkittäisiin
merkitään, merkittiin, merkittäisiin
Type VI verbs
Almost all verbs of this type have infinitives ending in 'eta' (notable exceptions being parata = "to improve/become better" and huonota = "to deteriorate/become worse". There are not many verbs which fall into this category, and these don't tend to be commonly used. However, it is a fairly common route for turning adjectives into verbs; for example kylmä = "cold", kylmetä = "to get cold".
The present stem for this type is characterized by the insertion of ne after the infinitive stem; as a consequence, the final syllable of the stem is open, and hence the final consonant of the stem is in strong grade. Examples:
- rohje-ta' = "to dare"
- rohkenen = "I dare"
- rohkenet = "you dare"
- rohkenee = 'he/she/it dares' etc.
- pae-ta = "to escape", pakenen = "I escape"
- kylme-tä = "to get cold", kylmenen = "I get cold"
- para-ta = "to improve" (intransitive), paranen = "I improve"
Imperfect indicative
The imperfect indicative of this type of verb is formed by replacing the final "e" of the "ne" stem with the imperfect marker "i". Thus:
- rohkenin = "I dared"
- rohkenit = "you dared"
- rohkeni = "he/she/it dared" etc.
Passive
Passives of this type are formed in the same way as for type IV verbs.
Non-derivable and irregular stems
Standard Finnish has comparatively very few irregular verbs in addition to 'olla' discussed above. However, because the infinitive is an inflected form of the root, the consonant gradation may obscure the root. The root of the word 'juosta' = 'to run' is juoks-; when generating the infinitive, the pattern ks → s is applied: juoks+ta → juosta. Epenthetic 'e' is added for personal forms, e.g. juoksen.
There is a rare pattern where a stem with -k- is rendered as -hdä in the infinitive, but disappears in gradation, e.g.:
- 'tehdä' = 'to do, make': tee-; teen, teet, tekee, teemme, teette, tekevät, etc.
- 'nähdä' = 'to see': näe-; näen, näet, näkee, näemme, näette, näkevät, etc.
That is, teke- and näke- forms are rendered as tehdä and nähdä in the infinitive but are subject to gradation of 'k' in personal forms like teen. In some colloquial forms, the 'e' is rendered as a chroneme instead: nään instead of näen etc.
Spoken language adds some more irregular verbs by assimilative deletion, e.g.:
- tulla - tule - tuu
- mennä - mene - mee
- panna - pane - paa
- olla - ole - oo
Computer program for inflexion and syntax of the Finnish verb
- "Tuuli" available in http://www.wakkanet.fi/%7Epahio/esitteet.html
- Verbix: conjugation of Finnish verbs
Online Finnish Verb Conjugators
http://www.romania-sanakirja.net/online/verbs/conjugate_verb.php http://www.verbix.com/languages/finnish.shtml
Notes and references
- ↑ Pirjo Leino: Suomen kielioppi pg 114 Infinitive Subject. Otava 1989
- ↑ Note the archaic use of the instructive case of the third infinitive. A common error, even for native Finns, is to confuse this with the illative case, tappamaan, which would be incorrect. Nowadays, the first infinitive is used with pitää
- ↑ Savolainen, Erkki. Verkkokielioppi: 2.5.2.2.1 Infinitiivit Finn Lectura 2001
- ↑ Savolainen, Erkki. Verkkokielioppi: 2.5.2.2.2 Partisiipit Finn Lectura 2001