Federal Assembly (Switzerland)
| Federal Assembly German: Bundesversammlung French: Assemblée fédérale Italian: Assemblea federale Romansh: Assamblea federala | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type |
Bicameral |
| Houses |
Council of States National Council |
| Leadership | |
President of the National Council | |
President of the Council of States | |
| Structure | |
| Seats |
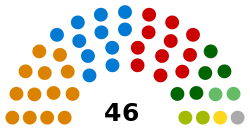
246 200 National Council 46 Council of States |
 | |
National Council political groups |
Government parties (167) Opposition parties (33) |
 | |
Council of States political groups |
Government parties (41) |
| Elections | |
National Council last election | 23 October 2011 |
Council of States last election | 23 October 2011 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Federal Palace of Switzerland, Bern | |
| Website | |
|
www | |
The Federal Assembly (German: Bundesversammlung, French: Assemblée fédérale, Italian: Assemblea federale, Romansh: Assamblea federala), is Switzerland's federal legislature. It meets in Bern in the Federal Palace.
The Federal Assembly is bicameral, being composed of the 200-seat National Council and the 46-seat Council of States. The houses have identical powers. Members of both houses represent the cantons, but, whereas seats in the National Council are distributed in proportion to population, each canton has two seats in the Council of States, except the six 'half-cantons' which have one seat each. Both are elected in full once every four years, with the last election being held in 2011.
The Federal Assembly possesses the federal government's legislative power, along with the separate constitutional right of citizen's initiative. For a law to pass, it must be passed by both houses. The Federal Assembly may come together as a United Federal Assembly in certain circumstances, including to elect the Federal Council, the Federal Chancellor, a General (Swiss generals are only selected in times of great national danger), or federal judges.
Composition
The Federal Assembly is made up of two chambers:
- the National Council, with 200 seats
- the Council of States, with 46 councillors.
Seats in the National Council are allocated to the cantons proportionally, based on population. In the Council of States, every canton has two seats (except for the former "half-cantons", which have one seat each).
United Federal Assembly
On occasions the two houses sit jointly as the "United Federal Assembly" (German: Vereinigte Bundesversammlung, French: Assemblée fédérale, Chambres réunies, Italian: Assemblea federale plenaria, Romansh: Assamblea federala plenara). This is done to:
- elect members of the Federal Council, the Federal Chancellor, the General and federal judges;
- arbitrate in the event of conflicts between federal authorities;
- issue pardons; or
- listen to special announcements
The United Federal Assembly is presided by the National Council's Presidency.
Groups
.svg.png) |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Switzerland |
|
Federal Assembly
|
|
Administrative divisions
|
|
Politics portal |
Parties can cooperate in groups, allowing smaller parties access to rights as part of a caucus. These groups must have at least five members and must be maintained across both chambers.[1] Being a member of a formal group gives members the right to sit on committees, and those that aren't members can't speak in most debates. Each group receives a fixed allowance of €112,000, whilst each member of a group also receives an additional €20,800 a year each.[1]
Since March 2009, there have been six groups in the Federal Assembly. The latest group to form was the Conservative Democratic Party which split off the Swiss People's Party in 2008. The Christian Democrats/EPP/glp Group (CEg) was formed after the 2007 elections, out of the former Christian Democratic (C) and EPP (E) groups. The current FTP/Liberal group (RL) was formed in 2003 out of the former FDP (R) and Liberal (L) groups; since the 2009 fusion of the Free Democrati and Liberal Parties, RL is once again a single-party group. In 2011, the CEg was disbanded, the Green Liberals formed their own faction (GL) and the three Christian parties formed the Christian-Evangelical Group (CE).
Currently (as of 2012), the seven factions are composed as follows:
| Group | Parties | NC | CS | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| People's Faction (V) | Swiss People's Party | 54 | 5 | 62 | |
| Ticino League | 2 | 0 | |||
| Independent | 0 | 1 | |||
| Social Democrats Faction (S) | Social Democratic Party | 46 | 11 | 57 | |
| Christian-Evangelical Faction (CE) | Christian Democratic People's Party | 28 | 13 | 44 | |
| Evangelical People's Party | 2 | 0 | |||
| Christian Social Party | 1 | 0 | |||
| FDP.The Liberals Faction (RL) | FDP.The Liberals | 30 | 11 | 41 | |
| Green Faction (G) | Green Party | 15 | 2 | 17 | |
| Green Liberal Faction (GL) | Green Liberal Party | 12 | 2 | 14 | |
| BDP Faction (BD) | Conservative Democratic Party | 9 | 1 | 10 | |
| Without Faction | Geneva Citizens' Movement | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
See also
- Swiss federal election, 2011
- Swiss federal election, 2007
- Hotel Bellevue Palace
- Federal Diet of Switzerland
Notes and references
Bibliography
- The Swiss Confederation – a brief guide 2010. Swiss Confederation. 2010. p. 19.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||