Febrifugine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
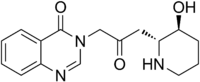
| IUPAC name
3-{3-[(2R,3S)-3-Hydroxypiperidin-2-yl]-2-oxopropyl}quinazolin-4(3H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 24159-07-7 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL479432 |
| ChemSpider | 8027405 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 9851692 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C16H19N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 301.34 g·mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Febrifugine is a quinazolinone alkaloid first isolated from the Chinese herb Dichroa febrifuga, but also found in the garden plant Hydrangea.[1] Laboratory synthesis of febrifugine determined that the originally reported stereochemistry was incorrect.[2]
Febrifugine has antimalarial properties and the halogenated derivative halofuginone is used in veterinary medicine as a coccidiostat.
References
- ↑ McLaughlin, N. P.; Evans, P. (2010). "Dihydroxylation of Vinyl Sulfones: Stereoselective Synthesis of (+)- and (−)-Febrifugine and Halofuginone". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 75 (2): 518–521. doi:10.1021/jo902396m. PMID 20000346.
- ↑ Kobayashi, Shū; Ueno, Masaharu; Suzuki, Ritsu; Ishitani, Haruro; Kim, Hye-Sook; Wataya, Yusuke (1999). "Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Antimalarial Alkaloids Febrifugine and Isofebrifugine and Their Biological Activity". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 64 (18): 6833. doi:10.1021/jo990877k. PMID 11674693.