Family Violence Prevention and Services Act
This article is about a United States law. For the main article, see Domestic violence in the United States.
The Family Violence Prevention and Services Act (FVPSA) is a United States law, first authorized as part of the Child Abuse Amendments of 1984 (PL 98–457), that provides federal funding to help victims of domestic violence and their dependent children by providing shelter and related help, offering violence prevention programs, and improving how service agencies work together in communities.
- The 24-hour, confidential, toll-free National Domestic Violence Hotline provides support, information, referrals, safety planning, and crisis intervention in more than 170 languages to hundreds of thousands of domestic violence victims each year.
- The Domestic Violence Prevention Enhancements and Leadership Through Alliances (DELTA) Program teaches people ways to prevent violence.
- Formula Grants. This money helps states, territories, and tribes create and support programs that work to help victims and prevent family violence. The amount of money is determined by a formula based partly on population. The states, territories, and tribes distribute the money to thousands of domestic violence shelters and programs.[1][2]
-
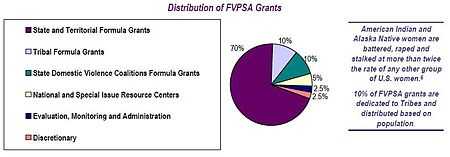
Family Violence Prevention and Services Act (FVPSA) Grants
See also
References
- ↑ Laws on violence against women. Office on Women's Health, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. May 18, 2011. Retrieved November 20, 2011.
- ↑ Family Violence Prevention and Services Act (FVPSA) Program Summary. Office on Women's Health, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Retrieved November 20, 2011.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||