FABP1
| Fatty acid binding protein 1, liver |
|---|
PDB rendering based on 2f73. |
| Available structures |
| PDB |
Ortholog search: PDBe, RCSB |
| List of PDB id codes |
|
2F73, 2L67, 2L68, 2LKK, 2PY1, 3B2H, 3B2I, 3B2J, 3B2K, 3B2L, 3STK, 3STM, 3STN, 3VG2, 3VG3, 3VG4, 3VG5, 3VG6, 3VG7
|
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Symbols | FABP1 ; FABPL; L-FABP |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 134650 MGI: 95479 HomoloGene: 1106 IUPHAR: 2531 ChEMBL: 5421 GeneCards: FABP1 Gene |
|---|
|
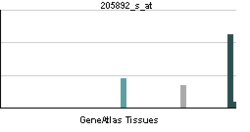
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
|
| More reference expression data |
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse | |
|---|
| Entrez | 2168 | 14080 | |
|---|
| Ensembl | ENSG00000163586 | ENSMUSG00000054422 | |
|---|
| UniProt | P07148 | P12710 | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001443 | NM_017399 | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001434 | NP_059095 | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 2:
88.42 – 88.43 Mb | Chr 6:
71.2 – 71.21 Mb | |
|---|
| PubMed search | | | |
|---|
|
Fatty acid-binding protein 1 (FABP1) also known as liver-type fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FABP1 gene.[1][2][3]
Function
FABP1 encodes the fatty acid-binding protein found in liver. Fatty acid binding proteins are a family of small, highly conserved, cytoplasmic proteins that bind long-chain fatty acids and other hydrophobic ligands. FABP1 and FABP6 (the ileal fatty acid binding protein) are also able to bind bile acids. It is thought that FABPs roles include fatty acid uptake, transport, and metabolism.[3]
References
- ↑ Chen SH, Van Tuinen P, Ledbetter DH, Smith LC, Chan L (Jul 1986). "Human liver fatty acid binding protein gene is located on chromosome 2". Somat Cell Mol Genet 12 (3): 303–6. doi:10.1007/BF01570790. PMID 3012800.
- ↑ Weickert MO, Loeffelholz CV, Roden M, Chandramouli V, Brehm A, Nowotny P, Osterhoff MA, Isken F, Spranger J, Landau BR, Pfeiffer AF, Mohlig M (Oct 2007). "A Thr94Ala mutation in human liver fatty acid-binding protein contributes to reduced hepatic glycogenolysis and blunted elevation of plasma glucose levels in lipid-exposed subjects". Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293 (4): E1078–84. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00337.2007. PMID 17698986.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Entrez Gene: FABP1 fatty acid binding protein 1, liver".
Further reading
- Glatz JF, Börchers T, Spener F, van der Vusse GJ (1995). "Fatty acids in cell signalling: modulation by lipid binding proteins.". Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 52 (2–3): 121–7. doi:10.1016/0952-3278(95)90010-1. PMID 7784447.
- Kaikaus RM, Chan WK, Ortiz de Montellano PR, Bass NM (1993). "Mechanisms of regulation of liver fatty acid-binding protein". Mol. Cell. Biochem. 123 (1–2): 93–100. doi:10.1007/BF01076479. PMID 8232272.
- Londraville RL (1997). "Intracellular fatty acid-binding proteins: putting lower vertebrates in perspective". Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 29 (6): 707–20. PMID 9070383.
- Börchers T, Hohoff C, Buhlmann C, Spener F (1997). "Heart-type fatty acid binding protein - involvement in growth inhibition and differentiation". Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 57 (1): 77–84. doi:10.1016/S0952-3278(97)90496-8. PMID 9250612.
- Carroll SL, Roth KA, Gordon JI (1990). "Liver fatty acid-binding protein: a marker for studying cellular differentiation in gut epithelial neoplasms". Gastroenterology 99 (6): 1727–35. PMID 1699834.
- Sweetser DA, Birkenmeier EH, Klisak IJ et al. (1987). "The human and rodent intestinal fatty acid binding protein genes. A comparative analysis of their structure, expression, and linkage relationships". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (33): 16060–71. PMID 2824476.
- Chan L, Wei CF, Li WH et al. (1985). "Human liver fatty acid binding protein cDNA and amino acid sequence. Functional and evolutionary implications". J. Biol. Chem. 260 (5): 2629–32. PMID 3838309.
- Lowe JB, Boguski MS, Sweetser DA et al. (1985). "Human liver fatty acid binding protein. Isolation of a full length cDNA and comparative sequence analyses of orthologous and paralogous proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 260 (6): 3413–7. PMID 3838313.
- Murphy EJ (1998). "L-FABP and I-FABP expression increase NBD-stearate uptake and cytoplasmic diffusion in L cells". Am. J. Physiol. 275 (2 Pt 1): G244–9. PMID 9688651.
- Wolfrum C, Börchers T, Sacchettini JC, Spener F (2000). "Binding of fatty acids and peroxisome proliferators to orthologous fatty acid binding proteins from human, murine, and bovine liver". Biochemistry 39 (6): 1469–74. doi:10.1021/bi991638u. PMID 10684629.
- Wolfrum C, Borrmann CM, Borchers T, Spener F (2001). "Fatty acids and hypolipidemic drugs regulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha - and gamma-mediated gene expression via liver fatty acid binding protein: a signaling path to the nucleus". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (5): 2323–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.051619898. PMC 30137. PMID 11226238.
- Schroeder F, Atshaves BP, Starodub O et al. (2001). "Expression of liver fatty acid binding protein alters growth and differentiation of embryonic stem cells". Mol. Cell. Biochem. 219 (1–2): 127–38. doi:10.1023/A:1010851130136. PMID 11354243.
- Zimmerman AW, van Moerkerk HT, Veerkamp JH (2001). "Ligand specificity and conformational stability of human fatty acid-binding proteins". Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 33 (9): 865–76. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(01)00070-X. PMID 11461829.
- Mésange F, Sebbar M, Capdevielle J et al. (2003). "Identification of two tamoxifen target proteins by photolabeling with 4-(2-morpholinoethoxy)benzophenone". Bioconjug. Chem. 13 (4): 766–72. doi:10.1021/bc015588t. PMID 12121132.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
PDB gallery |
|---|
| | 2f73: Crystal structure of human fatty acid binding protein 1 (FABP1) |
|
|
|
|
|---|
| | Fatty acid | |
|---|
| | Hormone | |
|---|
| | Metal/element | |
|---|
| | Vitamin | |
|---|
| | Other | |
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Proteins
- Membrane
- Globular
- Antibodies
- Fibrous
|
|---|
|
|