Fábrica Argentina de Aviones
Coordinates: 31°26′35.6″S 64°16′20.9″W / 31.443222°S 64.272472°W
 | |
| Sociedad Anónima | |
| Industry | Aerospace, Defense |
| Founded | 1927 |
| Headquarters | Córdoba, Argentina |
Key people | Matías Julián Savoca (chairman)[1] |
| Products | Aircraft, aircraft components, aircraft maintenance and services |
Number of employees | 1,600 (as of June 2014) |
| Website | www.fadeasa.com.ar |
The Fábrica Argentina de Aviones SA (FAdeA), officially Fábrica Argentina de Aviones "Brigadier San Martín" S.A., is Argentina's main aircraft manufacturer. Founded on 10 October 1927 and located in Córdoba, for most of its existence it was known as Fábrica Militar de Aviones (FMA), until its privatization in the 1990s to Lockheed Martin. In 2010 the concession ended and is now wholly owned by the Argentine government.
History


Formed on October 10, 1927 and on July 18, 1928 ends the construction and testing begins on the track the first domestically produced aircraft: the license built Avro 504 Gosport training aircraft equipped with a 100 hp (75 kW) Gnome engine. It had a speed of 140 km/h with a flying endurance of 2 hours.
The factory is known for producing the first jet fighter aircraft in Latin America: the Pulqui I (1947) and the Pulqui II (1950) under the direction of engineers Emile Dewoitine (French) and Kurt Tank (German) respectively.
Privatization (1995)
FMA was closed in 1995 and was privatized by the government of Carlos Menem and from 1995 until March 2009 it belonged concession to LMAASA (Lockheed Martin Aircraft Argentina SA, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin Corporation). Under the terms of the privatization agreement LMAASA would operate it for 25 years and could be renewed for two 10 year periods.
Nationalization (2010)
During the government of Cristina Fernández de Kirchner the factory was nationalized in August 2009 after paying ARS $67 million. The text of the expropriation law provides that "the State shall not return to get rid of a majority stake in the power or decision-making factory." [2][3]
It was renamed after Argentine Air Force Brigadier es:Juan Ignacio San Martín a military engineer who laid the foundations of the aeronautics industry at Córdoba when he directed the Instituto Aerotécnico, the forerunner of the FMA, in the 1940s.
The United States Department of State announced that effective December 18, 2009, Lockheed Martin Aircraft Argentina would be renamed to Fábrica Argentina de Aviones "Brigadier San Martin" S.A. and divested to the Government of Argentina.[4]
Aircraft design and production





The FMA has produced numerous innovative aircraft prototypes, but the state of the Argentine economy has usually prevented most of them from entering large-scale production. Nevertheless the FMA has managed to put several aircraft types of more conventional designs into full productions. It also engaged in production of licensed aircraft from other countries.
The prefixes used for the aircraft locally developed (and produced) are:
- Ae, for "Dirección General de Aerotécnica", on the first period (1927–1936);
- F.M.A., for "Fábrica Militar de Aviones", on the second period (1938–1943);
- I.Ae., for "Instituto Aerotécnico", on the third period (1943–1952);
- IA, meaning not specified, on the fourth (current) period (1952 to present).
List of aircraft manufactured or projected
| Year | Model | Built | Obs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Started as Instituto Aerotécnico | |||
| 1928 | Avro 504K "Gosport" | 31 | Biplane basic trainer, license-built. First aircraft produced by FMA. |
| 1930 | Dewoitine D.21 | 35 | Monoplane fighter, license-built. |
| 1931 | FMA AeC.1 | 1 | Civil tourism aircraft prototype (initial version); basic trainer (later version). First national design. |
| 1932 | FMA AeC.2 | 2 | Civil tourism aircraft |
| 1932 | FMA AeME.1 | 7 | basic military trainer |
| 1933 | FMA AeT.1 | 3 | Transport/commercial aircraft |
| 1934 | FMA AeMO.1 | 41 | Observation monoplane |
| 1934 | FMA AeMOe.1 | 6 | Derivative of the AeMO.1, observation and training |
| 1934 | FMA AeMOe.2 | 61 | Variant of the AeMOe.1, observation and training |
| 1934 | FMA AeC.3 | 16 | Civil aircraft. |
| 1935 | FMA AeMB.1 | 1 | First bomber aircraft built by FMA |
| 1935 | FMA AeMB.2 | 14 | First bomber aircraft built by FMA |
| 1935 | FMA AeMS.1 | 1 | Ambulance aircraft |
| 1936 | FMA AeC.3G | 1 | Tourism aircraft. |
| 1936 | FMA AeC.4 | 1 | Improved prototype version of the C.3G |
| Name changed to Fabrica Militar de Aviones | |||
| 1940 | Curtiss Hawk 75O | 20 | License built version of the US monoplane fighter Curtiss Hawk 75[5] |
| 1940 | Focke-Wulf Fw 44J Stieglitz | 190 | License built version of the German biplane trainer |
| 1940 | FMA I.Ae.20 El Boyero | 130 | Tourism aircraft, series built by "Industrias Petrolini" |
| 1943 | FMA I.Ae.21 | 1 | Advanced trainer aircraft prototype, based on the North American NA-16-1P fuselage. |
| 1943 | FMA I.Ae.22 DL | 206 | Advanced trainer aircraft |
| 1945 | FMA I.Ae.23 | 1 | Basic trainer prototype, based on the Focke-Wulf Fw44J |
| 1945 | FMA I.Ae.25 Mañque | 1 | Assault/Transport glider. |
| 1946 | FMA I.Ae.24 Calquín | 100 | Attack/Light bomber |
| 1947 | FMA I.Ae.27 Pulqui | 1 | Jet fighter prototype, first of its kind built in Latin America. |
| 1947 | FMA I.Ae.31 Colibrí | 3 | Two-seat Trainer aircraft |
| 1948 | FMA I.Ae.30 Ñancú | 1 | Fighter/Attack prototype |
| 1949 | FMA I.Ae.32 Chingolo | 1 | Tourism/Trainer aircraft |
| 1949 | FMA I.Ae.34 Clen Antú | 3+1+3 | Glider, flying wing. Designed by Reimar Horten, also known as the Horten XVa and XVb |
| 1950 | FMA I.Ae.33 Pulqui II | 5 | First swept-wing jet fighter designed in Latin America |
| 1953 | DINFIA IA35 Huanquero | 2+3+20+9(+1+1) | Transport aircraft; variants "Constancia" and "Pandora" executive aircraft. |
| 1953 | FMA I.Ae.41 Urubú | 4 | Flying-wing glider, designed by Reimar Horten, also known as the Horten XVc. |
| 1953 | FMA I.Ae. 43 Pulqui III | 0 | Project, swept-wing supersonic jet fighter |
| FMA I.Ae.36 Cóndor | 0 | Civil passenger transport, designed by Kurt Tank. Project cancelled, no prototypes built. | |
| 1954 | FMA I.Ae.37 | 1 | Supersonic delta-wing interceptor, designed by Reimar Horten. Glider, unpowered prototype only. |
| 1960 | I.Ae. 38 Naranjero | 1 | Flying-wing transport/cargo, designed by Reimar Horten. |
| 1953 | FMA IAe.44 DL.II | 0 | Advanced trainer (project, none built) |
| 1959 | DINFIA IA 45 Querandí | 2 | Executive transport, prototypes only (NOTE: some sources mention "1957" and "1" built) |
| 1957 | FMA I.Ae. 46 Ranquel | 101+116 | 2-seat utility aircraft. Second series, enhanced variant "Super Ranquel". |
| 1960 | FMA I.Ae. 48 | Cancelled | Fighter aircraft |
| 1960 | DINFIA IA 35 Guaraní I | 1 | Approximate date, transport derived from the I.Ae. 35 "Huanquero" |
| 1963 | DINFIA IA 50 Guaraní II | 1+2+18+14 | Transport aircraft, derived from the IA 35 Guaraní I |
| Beechcraft T-34 Mentor | 75 | Trainer, licence built | |
| 1965 | IA 53 Mamboretá | 2 | Agricultural aircraft |
| 1960 | Morane-Saulnier MS.760 Paris | 48 | Trainer, licence built |
| 1975 | FMA IA 58 Pucará | 120 | Counter-insurgency/light attack aircraft |
| 1978 | FMA IA 62 | 0 | military trainer aircraft. none built |
| 1983 | FMA IA 66 Pucará II | 1 | After the 'Malvinas/Falkland' war a revised version of Pucara was designed. It used an IA-58 as base with more powerful engines, single seat design, and better IR protection. The program was cancelled after the prototype was homologated. |
| 1984 | FMA IA 63 Pampa | 20+12 | Advanced trainer. AT-63 currently under production |
| 1990 | (IA 70) Embraer/FMA CBA 123 Vector |
2 | Turboprop 19-passenger regional airliner, only prototypes built before being cancelled [6] |
| IA 67 Córdoba | Light attack bomber project, none built (mid-1980s) | ||
| FMA SAIA 90 | Cancelled | Supersonic air superiority jet fighter project, none built (mid-1980s) | |
| Name changed to Lockheed Martin Aircraft Argentina SA | |||
| 1999 | Lockheed Martin A-4AR Fightinghawk | 18 | other 18 by Lockheed Martin in Pasadena, California. |
| 2003 | Beechcraft T-34 Mentor | Refurbishment of Argentine and Bolivia Air Forces | |
| 2006 | Lockheed C-130 Hercules | Refurbishment of Argentine Air Force and Colombian Air Force aircraft. | |
| Name changed to FAdeA S.A. | |||
| 2009 | FMA IA 63 Pampa | Changing power plant | |
| 2010 | FMA IA 58 Pucará | Changing power plant and avionics | |
| 2013 | FAdeA IA 73 | basic trainer to replace T-34 [7] | |
Gallery
Local designs
-

Prototype AeC.1 (1931)
-

AeT.1 (1933)
-

FMA 20 El Boyero (1940)
-

Prototype FMA 21 trainer (1943)
-

I.Ae. 22 DL advanced trainer (1944)
-

I.Ae. 23 trainer prototype, based on the FW-44J Stieglitz (1944)
-

I.Ae. 24 Calquin attack aircraft, c.1950
-
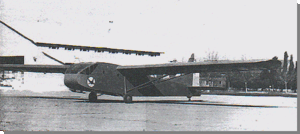
Prototype I.Ae. 25 Mañque glider (1945)
-

I.Ae. 30 Ñancú (1948)
-

IAe.31 Colibrí (1947)
-

I.Ae. 34 Clen Antú, tailless glider designed by Reimar Horten, late 1940s
-

Model I.A. 36 Cóndor, airliner designed by Kurt Tank, early 1950s
-

FMA I.Ae. 37 fighter prototype (1953)
-

IAe.41 Urubú flying wing glider (1953)
-

IA 45 Querandi light transport prototype (1957)
-

IA 53 Mamboretá agricultural aircraft prototype (mid-1960s)
-

IA-59, prototype Unmanned aerial vehicle, early 1970s
-

FMA IA 63 Pampa, Paris Air Show, 1991
-
_(PT-ZVE).jpg)
CBA 123 / IA 70 prototype, Farnborough 1990
-

FAdeA I.A. 73 Unasur I mock-up
Manufactured under license
-

Curtiss Hawk 75O
-

FW-44J Stieglitz
-
_MS-760_Paris_Lofting-2.jpg)
Morane-Saulnier MS-760 Paris, Mendoza, 2005
See also
- Other aircraft manufacturers in Argentina
References
Notes
- ↑ "FAdeA AUTORIDADES". Retrieved 11 July 2014.
- ↑ Back at the hands of the state
- ↑ (Spanish)Ministerio de Defensa - República Argentina
- ↑ Lockheed Martin Aircraft Argentina SA to Fábrica Argentina de Aviones “Brigadier San Martin” S.A.
- ↑ Padin 1999, pp. 9, 15
- ↑ CBA123/IA 70
- ↑ La Fábrica Argentina de Aviones fabricará un nuevo avión de entrenamiento para pilotos
Bibliography
- Bellomo, Sergio; Cordon Aguirre, Arturo; Marino, Atilio; Núñez Padin, Jorge (1999). Núñez Padin, Jorge Felix, ed. Curtiss Hawk. Serie Fuerza Aérea Argentina (in Spanish) 5. Bahía Blanca, Argentina: Fuerzas Aeronavales.
- Arreguez, Angel Cesar (2008). Mansur, Sergio Luis, ed. Fabrica Militar de Aviones: Cronicas y Testimonios (in Spanish) (Second ed.). Cordoba, Argentina: Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnologia de la Provincia de Cordoba. ISBN 978-987-24620-0-0.
Further reading
- (Spanish) FÁBRICA MILITAR DE AVIONES: CRÓNICAS Y TESTIMONIOS, retrieved 2010-01-18 (PDF file available for download). Published in 2007 by Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología de la Provincia de Córdoba, Argentina (Córdoba's Province Science and Technology Ministry)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fábrica Militar de Aviones. |
- (Spanish) Official site
- FMA history
- (Spanish) Aeromilitaria.com.ar
- "Former Lockheed Martin Argentina plant relaunched as FAdeA" FlightGlobal
| ||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||



