External intercostal muscles
| External intercostal muscles | |
|---|---|
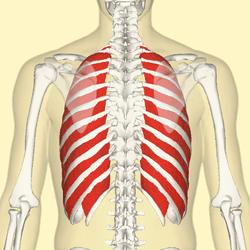 Position of the external intercostal muscles (shown in red) seen from the back. | |
| Details | |
| Latin | musculi intercostales externi |
| lower border of ribs | |
| upper border of rib below | |
| intercostal arteries | |
| intercostal nerves | |
| Actions | Inhalation |
Antagonist | intercostales interni muscles |
| Identifiers | |
| Gray's | p.403 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | m_22/12549368 |
| TA | A04.4.01.012 |
| FMA | 74084 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The external intercostal muscles, or external intercostals (Intercostales externi) are eleven in number on either side.
They extend from the tubercles of the ribs behind, to the cartilages of the ribs in front, where they end in thin membranes, the external intercostal membranes, which are continued forward to the sternum. These muscles work in unison when inhalation occurs. The internal intercostal muscles relax while the external muscles contract causing the expansion of the chest cavity and an influx of air into the lungs.
Each arises from the lower border of a rib, and is inserted into the upper border of the rib below. In the two lower spaces they extend to the ends of the cartilages, and in the upper two or three spaces they do not quite reach the ends of the ribs.
They are thicker than the internal intercostals, and their fibers are directed obliquely downward and laterally on the back of the thorax, and downward, forward, and medially on the front.
Variations
Continuation with the external oblique or serratus anterior: A supracostalis muscle, from the anterior end of the first rib down to the second, third or fourth ribs occasionally occurs.
Additional images
-
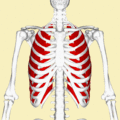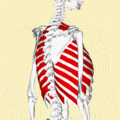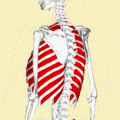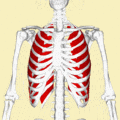
Position of the external intercostal muscles (shown in red). Animation.
-
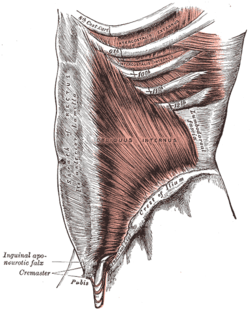
Deep muscles of the chest and front of the arm, with the boundaries of the axilla. (Intercostalis externus labeled at bottom center.)
-
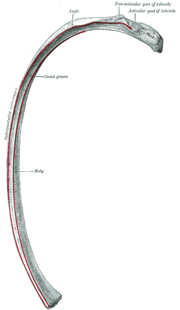
A central rib of the left side. Inferior aspect.
-

Diagram of the course and branches of a typical intercostal nerve.
Related pages
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to External intercostal muscles. |
- -556793779 at GPnotebook
- External+intercostal+muscle at eMedicine Dictionary
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||