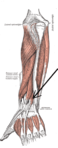Extensor indicis muscle
In human anatomy, the extensor indicis [proprius] is a narrow, elongated skeletal muscle in the deep layer of the dorsal forearm, placed medial to, and parallel with, the extensor pollicis longus. Its tendon goes to the index finger, which it extends.
Origin and insertion
It arises from the distal third of the dorsal part of the body of ulna and from the interosseous membrane. It runs through the fourth tendon compartment together with the extensor digitorum, from where it projects into the dorsal aponeurosis of the index finger.
[1]
Opposite the head of the second metacarpal bone, it joins the ulnar side of the tendon of the extensor digitorum which belongs to the index finger.
Like the extensor digiti minimi (i.e. the extensor of the little finger), the tendon of the extensor indicis always runs on the ulnar side of the tendon of the common extensor digitorum. Both these extensors lack the oblique bands (connexus intertendinei) interlinking the tendons of the extensor digitorum on the dorsal side of the hand.
[2]
Action
The extensor indicis extends the index finger, and by its continued action assists in extending (dorsiflexion) the wrist and the midcarpal joints.[1]
Because the index finger and little finger have separate extensors, these fingers can be moved more independently than the other fingers.
[2]
Additional images
| The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the back of the wrist. (Extensor indicis proprius visible going into second digit.) |
| Bones of left forearm. Posterior aspect. |
| Posterior surface of the forearm. Deep muscles. |
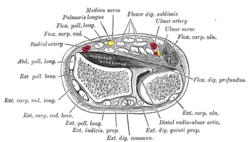
| Transverse section across the wrist and digits. |
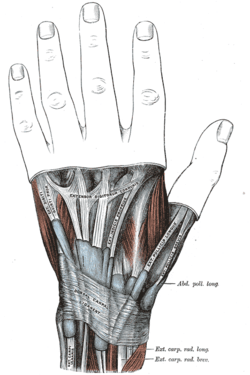
| Muscles of hand. Posterior view. |
| Muscles of hand. Posterior view. |
|
Notes
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Platzer, Werner (2004). Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System (5th ed.). Thieme. ISBN 3-13-533305-1.
- Ross, Lawrence M. (ed.); Lamperti, Edward D. (ed.) (2006). Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System. Thieme. ISBN 1-58890-419-9.
External links
|
|---|
| | Shoulder | |
|---|
| Arm
(compartments) | |
|---|
| | Forearm | |
|---|
| | Hand | | lateral volar | |
|---|
| | medial volar | |
|---|
| | intermediate | |
|---|
| | fascia | |
|---|
|
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- head
- neck
- arms
- chest and back
- diaphragm
- abdomen
- genital area
- legs
- Muscle tissue
- Physiology
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Myopathy
- Soft tissue
- Connective tissue
- Congenital
- abdomen
- muscular dystrophy
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Injury
- Symptoms and signs
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Drugs
- anti-inflammatory
- muscle relaxants
|
|---|
|
|