Exposure range
In photography, exposure range may refer to any of several types of dynamic range:
- The Light sensitivity range of photographic film, paper, or digital camera sensors.
- The luminosity range of a scene being photographed.
- The opacity range of developed film images
- The reflectance range of images on photographic papers.
The exposure range of a device is usually expressed in stops, which are equivalent to 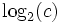 where c is the medium or device's contrast ratio. For example, average Digital Video (DV) has a contrast ratio of 45:1, so its exposure range is roughly 5.5 stops. Film has an exposure range of approximately 14 stops.
where c is the medium or device's contrast ratio. For example, average Digital Video (DV) has a contrast ratio of 45:1, so its exposure range is roughly 5.5 stops. Film has an exposure range of approximately 14 stops.
Exposure is usually controlled by changing the lens aperture (the amount of light it gathers), the shutter speed (how long light is gathered) or sensitivity (how strongly the film or sensor responds to light). Changing exposure does not change the exposure range.

A graduated neutral density filter can be also used to improve the reproduction of the exposure range of the scene, by darkening bright parts of the image. A graduated filter will reduce the extreme highlights of an image, such as a clear, open sky as well as sunlight. The filter is usually an even gradation of neutral gray to clear, covering the top third to half of the filter in gray. Therefore, it mostly affects the top third to half of the frame's exposure, leaving the highlights in the bottom half to two-thirds unaffected. Often these filters are the square gelatin, polycarbonate, or glass type. A mounting kit such as a square frame receptacle mounted to interchangeable screw-in rings will hold the filter at an appropriate orientation. These can be mounted to the end of an SLR lens camera in the same fashion as a polarizing lens, UV filter, and various other screw-in type filters for SLR and DSLR cameras.
See also
- Exposure latitude
- High dynamic range imaging