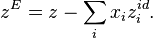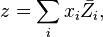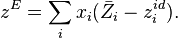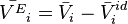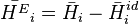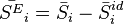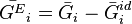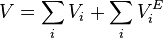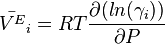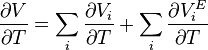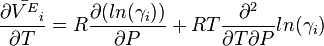Excess molar quantity
Excess molar quantities are properties of mixtures which characterize the nonideal behaviour of real mixtures. They are the difference between the partial molar property of a component in a real mixture and that of the component in an ideal mixture. By definition, excess properties of a mixture are related to those of the pure substances in an ideal mixture by:
Here  denotes the pure substance,
denotes the pure substance, 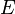 the excess molar property, and
the excess molar property, and 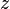 corresponds to the specific property under consideration. From the definition of partial molar properties,
corresponds to the specific property under consideration. From the definition of partial molar properties,
substitution yields:
For volumes, internal energies and enthalpies the excess quantities are identical to the mixing quantities. They can be expressed as functions of derivatives of the activity coefficients.
Examples
The volume of a mixture from the sum of the excess volumes of the components of a mixture is given by the formula:
Relation to activity coefficients
The excess molar volume of the component i is connected to its activity coefficient.
Derivatives to state parameters
Thermal expansivities
Deriving by temperature the thermal expansivities of the components in a mixture can be related to the expansivity of the mixture:
Equivalently:
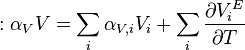
Substituting the temperature derivative of the excess molar volume
one can relate activity coefficients to thermal expansivity.
See also
- Ideal solution
- Apparent molar property
- Heat of mixing
- Volume concentration
- Virial expansion
References
Frenkel, Daan; Smit, Berend (2001). Understanding Molecular Simulation : from algorithms to applications. San Diego, California: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-267351-4.