Euphyes dukesi
| Dukes' skipper | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Lepidoptera |
| Family: | Hesperiidae |
| Genus: | Euphyes |
| Species: | E. dukesi |
| Binomial name | |
| Euphyes dukesi (Lindsey, 1923)[2] | |
| Subspecies[3] | |
| |
 | |
| Generalized range.[4] | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Dukes' skipper (Euphyes dukesi) is a butterfly of the Hesperiidae family. It lives the eastern United States and a small portion of southern Ontario, Canada, in three distinct populations.[3] Preferred habitats are shaded wetlands (woodland or coastal swamps, marshes, and ditches), with various species of sedge plants it uses as host plants for its larvae.[3]
Description
They have short, rounded wings with a wingspan of 32 to 38 millimetres (1.3 to 1.5 in).[3] The wings of both sexes are deep brown on top, and the underside of the hindwings are light brown with pale yellow rays. They're similar in appearance to other Euphyes, but "the single yellowish streak on the hindwing beneath is unmistakable."[5] Females are slightly larger than males and have a hindwing band with two to three pale yellowspots, while males have a black stigma on the forewing.[3] Caterpillars have a light green body with black head.[3]
For male genitalia have “five toothed processes at the terminus of the aedoeagus.”[6]
Naming
The species was named for W. C. Dukes of Mobile, Alabama in Arthur Ward Lindsey's original 1923 description of the species, “in acknowledgment of his unselfish efforts to advance our knowledge of the Lepidoptera of Alabama.”[7] The first specimen was collected by Dukes on August 6, 1922 in Mobile County, Alabama.[6][7]
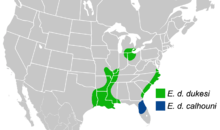
Distribution
Dukes' skipper is found in scattered locations around the eastern United States and a small portion of southeastern Canada.[8] There are three distinct regionally clustered populations:
- Along the Atlantic Coast from southeastern Virginia to northern peninsular Florida.[8]
- The lower Mississippi Valley from central Missouri and southern Illinois south to the Gulf Coast.[8]
- Extreme southwestern Ontario, southeastern Michigan, northeastern Indiana, and northern Ohio.[8]
Its full distribution consists of the Canadian province of Ontario and the following US states: AL, AR, FL, GA, IL, IN, KY, LA, MI, MO, MS, NC, OH, SC, TX, VA.[9]
The split distribution between coastal plains and the Great Lakes area is unusual for North American butterflies, and it's hypothesized that it may be due to population displacements during the Pleistocene glacial intervals, followed by dispersal through the vegetational corridors of the Mississippi and Mohawk Valleys when the ice sheets retreated.[4]
Life Cycle
Eggs are laid singly under the leaves of the host plants on which the larvae feed.[2][3] Larvae molt several times and diapause to overwinter in their fourth instar, feed again and molt once more in the spring, then pupate for about two weeks before emerging as adults.[2][3] Its adult lifespan is estimated at three weeks, and its total lifespan from hatching is about a year or less.[3]
Broods
The species ranges from univoltine in the north to trivoltine in the south, with flight periods lasting approximately one month. In northern populations, the species typically has a single brood around July. From western Kentucky and Virginia southward, it has one brood around June and a second brood around August to September. In Florida, the subspecies E. dukesi calhouni may have more than two broods, from mid-May through October.
Food
Host plants used by larva are restricted to various sedges of the genera Carex and Rhynchospora.[2][3] These include hairy sedge Carex lacustris in the north (particularly in shaded wetlands, including coastal swamps and ditches), shoreline sedge Carex hyalinolepis in the south (Mississippi River basin), falsehope sedge Carex lupuliformis, Carex walteriana, Walter's sedge Carex striata in the southeast, narrowfruit horned beaksedge Ryncospora inundata, and millet beaksedge Rynchospora miliacea in Florida.[3]
Adults feed on flower nectar of various plants including buttonbush Cephalanthus occidentalis, common milkweed Asclepias syriaca, swamp milkweed Asclepias incarnata, joe-pye weed Eupatorium maculatum, blue mistflower Eupatorium coelestinum, pickerelweed Pontederia cordata, hibiscus species Hibiscus, sneezeweed Helenium autumnale, alfalfa Medicago sativa, and red clover Trifolium pratense.[3]
Subspecies
There are two subspecies of Euphyes dukesi: the nominate subspecies discovered in 1922, and a swamp-dwelling Florida subspecies discovered in 1995.[6][7][10]
- Euphyes dukesi dukesi Lindsey, 1923: "Occurs from the Lake Erie region south mostly through the Ohio and Mississippi drainages to Louisiana, and disjunctly on the Atlantic coastal plain from Virginia to Georgia."[3]
- Euphyes dukesi calhouni Shuey, 1996: Allopatric with E. dukesi dukesi, this subspecies occurs in the southern US coastal plain, and is endemic to Florida. It lives in swamp habitats with large stands of sedge host plants (primarily Rhynchospora inundata).[3]
The divergence of two subspecies may have occurred due to isolation of Florida and other populations during the Wisconsinian glaciation or an earlier glacier event, with boreal forests acting as barriers.[4]
E. d. calhouni is named after its discoverer John Calhoun, and Shuey proposed the common name Florida swamp skipper to emphasize its endemic range and habitat, but which has also been proposed for the species Euphyes berryi.[10]
Distinguishing characteristics between the subspecies:[10]
- The ground color of E. d. calhouni is darker, nearing black, compared to the dark brown ground color of E. d. dukesi, which contrasts with a black stigma in males.
- Dorsal wings of E. d. calhouni have overscaling of olive-brown hairs, while E. d. dukesi have overscaling of orange-brown hairs.
- On the ventral forewing of E. d. calhouni, overscaling is olive-brown, while on E. d. dukesi overscaling is heavier and is orange-brown, in strong contrast with the ground color.
- On the ventral hindwing of E. d. calhouni, the yellow dash between veins M1 and M2 is diffuse and often does not reach the edge of the wing, and there is usually no yellow dash between veins Cu2 and 2A. On E. d. dukesi, both yellow dashes are typically heavily scaled and extend boldly to the edge of the wing in fresh specimens.
- Wing fringes of E. d. calhouni are mostly dark and match the dorsal ground color, except a lightening in the anal region of the hindwing. In E. d. dukesi the fringes are lighter than the ground color.
Conservation Status
Dukes' skipper threat status has not been assessed by the IUCN Red List, nor is it covered by the US Endangered Species Act or Canadian Species at Risk Act.[11] The state of Michigan lists it as a threatened species protected by state law,[12][13] the Xerces Society Red List of Butterflies and Moths lists it as Vulnerable,[9][11] and NatureServe lists the species' national conservation status as N3 (Vulnerable) in the United States and N2 (Imperiled) in Canada, with a global status of G3 (Vulnerable), last reviewed in 2008 as of 2013.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Schweitzer, DF (2008). "Comprehensive Report Species – Euphyes dukesi". NatureServe Explorer. NatureServe Inc. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Dukes' skipper – Euphyes dukesi – Overview". Encyclopedia of Life. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 "Facts about Dukes' skipper (Euphyes dukesi)". Encyclopedia of Life. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Calhoun, John V. (1995). "The Biogeography and Ecology of Euphyes Dukesi (Hesperiidae) in Florida". Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 49 (1): 6–23. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
- ↑ "Butterflies of Canada: Dukes' skipper". Government of Canada – Canadian Biodiversity Information Facility. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Skinner, Henry; Williams, Jr, RC (1924). "On the male genitalia of the hesperiidae of North America: paper IV". Transactions of the American Entomological Society (Philadelphia: American Entomological Society) 50 (1): 57–74.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Lindsey, A. W. (1923). "New North American Hesperiidae (Lepid.)". Entomological news, and proceedings of the Entomological Section of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 34: 209–210.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Butterflies and Moths of North America collecting and sharing data about Lepidoptera "Attributes of Euphyes dukesi". Butterflies and Moths of North America: Collecting and sharing data about Lepidoptera. Butterfly and Moth Information Network. 14 December 2013.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Red List of Butterflies and Moths". The Xerces Society. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Shuey, John A. (1996). "Another new Euphyes from the southern United States coastal plain (Hesperiidae)". Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 50: 46–53.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Skippers: Dukes' skipper (Euphyes dukesi)". The Xerces Society. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
- ↑ "Endangered and Threatened Species". State of Michigan official website. State of Michigan Department of Natural Resources, Wildlife Division. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
- ↑ "Michigan's Special Animals". Michigan Natural Features Inventory. Michigan State University. 15 December 2013.
External links
- Butterflies of America: Euphyes dukesi Many detailed photographs of the two subspecies of Dukes' skipper.
- State-by-state dates and locations of specimens collected as of 1963 are detailed in:
- Mather, Bryant (1963). "Euphyes dukesi – a review of knowledge of its distribution in time and space and its habitat" (PDF). Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 2 (2): 161–169.
| Wikispecies has information related to: Euphyes dukesi |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Euphyes dukesi. |
