Eudorina
| Eudorina | |
|---|---|
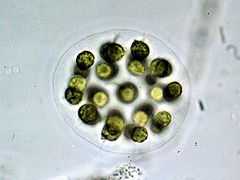 | |
| Eudorina elegans | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Viridiplantae |
| Phylum: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Chlorophyceae |
| Order: | Chlamydomonadales |
| Family: | Volvocaceae |
| Genus: | Eudorina |
| Species | |
| |
Eudorina is a genus of colonial green algae, specifically of the Volvocaceae.[1] Eudorina colonies consist of 16, 32 or 64 individual cells grouped together. Each individual cell contains flagella which allow the colony to move as a whole when the individual cells beat their flagella together. Description by GM Smith (1920, p 95):[2]
Eudorina Ehrenberg 1832.Colonies always motile, spherical or slightly elongate, of 16-32-64 cells lying some distance from one another and arranged to form a hollow sphere near the periphery of the homogeneous, hyaline, gelatinous envelope. Cells spherical, with or without a beak at the point of origin of the two cilia. Cilia parallel while passing through the colonial envelope and then widely divergent. Chloroplast single, cupshaped, filling practically the whole cell and generally with several pyrenoids. Cells with a firm wall, one or two anterior contractile vacuoles, and a single conspicuous eyespot near the base of the cilia.
Asexual reproduction by a simultaneous division of all cells to form autocolonies which are liberated by a rupture of the colonial envelope.
Sexual reproduction heterogamous, dioecious, with all cells of a colony developing into large immobile oospheres or plate-like masses of 32-64 fusiform antherozoids; or monoecious with four cells forming antherozoids and the remainder oospheres. Zygote smooth-walled.
Eudorina may be confused with young colonies of Pleodorina, which are very similar (Smith, 1920, p 97.)[2]
References
- ↑ See the NCBI webpage on Eudorina. Data extracted from the "NCBI taxonomy resources". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 2007-03-19.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Smith, GM. Phytoplankton of Inland Lakes of Wisconsin, Part I, Wisconsin Geological and Natural History Survey, Madison, WI. (1920).
Scientific journals
- Nozaki H, Onishi K, Morita E (2002). "Differences in pyrenoid morphology are correlated with differences in the rbcL genes of members of the Chloromonas lineage (Volvocales, Chlorophyceae)". J Mol Evol. 55 (4): 414–430. doi:10.1007/s00239-002-2338-9. PMID 12355262.
External links
- Eudorina - Description with pictures
Scientific references
- PubMed references for Eudorina
- PubMed Central references for Eudorina
- Google Scholar references for Eudorina
Scientific databases
- NCBI taxonomy page for Eudorina
- Search Tree of Life taxonomy pages for Eudorina
- Search Species2000 page for Eudorina
Further reading
Yamada, T.Y, Miyaja,K. and Nisayoshi, N. 2008. A taxonomic study of Eudorina unicocca (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyceae) and related species, based on morphology and molecular phylogeny. Eur. L.Phycol. 43: 317 - 326.