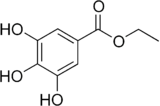
Ethyl gallate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ethyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate | |
| Other names
Phyllemblin gallic acid ethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| 831-61-8 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL453196 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 13250 |
| RTECS number | LW7700000 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 198.17 g/mol |
| Melting point | 149 to 153 °C (300 to 307 °F; 422 to 426 K) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl gallate is a food additive with E number E313. It is the ethyl ester of gallic acid. Ethyl gallate is added to food as an antioxidant.
Though found naturally in a variety of plant sources including walnuts[2] Terminalia myriocarpa[3] or chebulic myrobolan (Terminalia chebula).[4]
Ethyl gallate is produced from gallic acid and ethanol.[5] It can be found in wine.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ Ethyl gallate at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Zijia Zhanga, Liping Liaoc, Jeffrey Moored, Tao Wua, and Zhengtao Wanga (2009). "Antioxidant phenolic compounds from walnut kernels (Juglans regia L.)". Food Chemistry 113 (1): 160–165. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.07.061.
- ↑ Pharmacologically Active Ellagitannins from Terminalia myriocarpa. Mohamed S.A. Marzouk, Sayed A.A. El-Toumy, Fatma A. Moharram, Nagwa M.M. Shalaby and Amany A.E. Ahmed, Planta Med, 2002, 68(6), pages 523-527, doi:10.1055/s-2002-32549
- ↑ "Haritaki". Toddcaldecott.com. Retrieved 2014-05-18.
- ↑ Enzymic synthesis of gallic acid esters. Weetall, Howard Hayyim. Eur. Pat. 137601 (1985)
- ↑ "Simultaneous Determination of Nonanthocyanin Phenolic Compounds in Red Wines by HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS. María Monagas, Rafael Suárez, Carmen Gómez-Cordovés and Begoña Bartolomé, AJEV, June 2005, vol. 56, no. 2, pages 139-147". Ajevonline.org. 2005-06-01. Retrieved 2014-05-18.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||