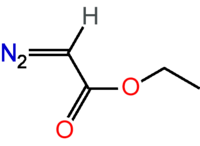
Ethyl diazoacetate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ethyl diazoacetate | |
| Other names
2-diazoacetic acid ethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| 623-73-4 | |
| ChemSpider | 11692 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 114.10 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow oil |
| Density | 1.085 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −22 °C (−8 °F; 251 K) |
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K) 720 mmHg |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
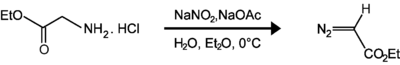
Ethyl diazoacetate (N=N=CHC(O)OC2H5) is a diazo compound and a reagent in organic chemistry. It was discovered by Theodor Curtius in 1883.[3] The compound can be prepared by reaction of the ethyl ester of glycine with sodium nitrite and sodium acetate in water.
It is used in the cyclopropanation of alkenes.
Although the compound is hazardous it is used in chemical industry.[4] Procedures for safe industrial handling have been published [5]
References
- ↑ Womack, E. B.; Nelson, A. B. (1944). "Ethyl Diazoacetate". Org. Synth. 24: 56.; Coll. Vol. 3, p. 392
- ↑ "Ethyl diazoacetate". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ Curtius, T. (1883). "Ueber die Einwirkung von salpetriger Säure auf salzsauren Glycocolläther". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft 16 (2): 2230–2231. doi:10.1002/cber.188301602136.
- ↑ Maas, G. (2009). "New Syntheses of Diazo Compounds". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 48 (44): 8186–8195. doi:10.1002/anie.200902785.
- ↑ Clark, J. D.; Shah, A. S.; Peterson, J. C. (2002). "Understanding the large-scale chemistry of ethyl diazoacetate via reaction calorimetry". Thermochimica Acta. 392–393: 177–186. doi:10.1016/S0040-6031(02)00100-4.