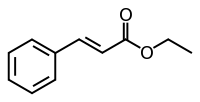
Ethyl cinnamate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ethyl 3-phenylprop-2-enoate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 103-36-6 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL318196 |
| ChemSpider | 553344 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 637758 |
| |
| UNII | C023P3M5JJ |
| Properties | |
| C11H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 176.21 g/mol |
| Density | 1.046 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 6.5 °C (43.7 °F; 279.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 271 °C (520 °F; 544 K) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl cinnamate is the ester of cinnamic acid and ethanol. It is present in the essential oil of cinnamon. Pure ethyl cinnamate has a "fruity and balsamic odor, reminiscent of cinnamon with an amber note".[1]
The p-methoxy derivative is reported to be a monoamine oxidase inhibitor.[2]
List of plants that contain the chemical
References
- ↑ Budavari, Susan (2001). "Merck Index 13th Ed.". Merck & co., Inc.
- ↑ Noro T, Miyase T, Kuroyanagi M, Ueno A, Fukushima S. (1983). "Monoamine oxidase inhibitor from the rhizomes of Kaempferia galanga L". Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 31 (8): 2708–11. PMID 6652816.
- ↑ Wong, K. C. et al. (2006). "Composition of the essential oil of rhizomes of kaempferia galanga L". Flavour and Fragrance Journal 7 (5): 263–266. doi:10.1002/ffj.2730070506.
- ↑ Othman, R. et al. (2006). "Bioassay-guided isolation of a vasorelaxant active compound from Kaempferia galanga L". Phytomedicine 13 (1 – 2): 61–66. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2004.07.004. PMID 16360934.