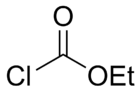
Ethyl chloroformate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
chloroformic acid ethyl ester | |
| Other names
Cathyl chloride; Ethyl chlorocarbonate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 541-41-3 | |
| ChemSpider | 10465 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 10928 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5ClO2 | |
| Molar mass | 108.52 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear liquid |
| Density | 1.1403 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 95 °C (203 °F; 368 K) |
| Decomposes | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive Flammable |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 61 °C (142 °F; 334 K) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl chloroformate is the ethyl ester of chloroformic acid. It is a reagent used in organic synthesis for the introduction of the ethyl carbamate protecting group[2] and for the formation of carboxylic anhydrides. It is capable of producing GABAergic anxiolytic/sedative/anesthetic effects (in order of increasing dose-effect threshold) in sufficient doses but produces potent hemotoxic and neurotoxic effects doses below the anesthetic threshold (roughly equivalent to the anxiolytic threshold) and was therefore never used for medical applications.
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 3742.
- ↑ Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, Third Edition, Theodora W. Greene and Peter G. M. Wuts, pages 504-506, ISBN 0-471-16019-9
