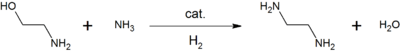Ethanolamine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Aminoethanol | |
| Other names
2-Amino-l-Ethanol, Ethanolamine, Monoethanolamine, β-Aminoethanol, β-hydroxyethylamine, β-Aminoethyl alcohol, Glycinol, Olamine, MEA, Ethylolamine, 2-Hydroxyethylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 141-43-5 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16000 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL104943 |
| ChemSpider | 13835336 |
| DrugBank | DB03994 |
| EC number | 205-483-3 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| KEGG | D05074 |
| PubChem | 700 |
| RTECS number | KJ5775000 |
| |
| UNII | 5KV86114PT |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C2H7NO |
| Molar mass | 61.08 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Viscous colourless liquid |
| Odor | unpleasant ammonia-like odour |
| Density | 1.012 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 10.3 °C (50.5 °F; 283.4 K) |
| Boiling point | 170 °C (338 °F; 443 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Vapor pressure | 64 Pa (20 °C)[1] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.50[2] |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.4539 (20 °C)[3] |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | JT Baker |
| R-phrases | R20, R34, R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26, S27, S36/37, S39, S45 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 85 °C (185 °F; 358 K) (closed cup) |
| 410 °C (770 °F; 683 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 5.5 - 17% |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 3 ppm (6 mg/m3)[4] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 3 ppm (8 mg/m3) ST 6 ppm (15 mg/m3)[4] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
30 ppm[4] |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
N-Methylethanolamine diethanolamine triethanolamine |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethanolamine, also called 2-aminoethanol or monoethanolamine (often abbreviated as ETA or MEA), is an organic chemical compound that is both a primary amine and a primary alcohol (due to a hydroxyl group). Like other amines, monoethanolamine acts as a weak base. Ethanolamine is a toxic, flammable, corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid with an odor similar to that of ammonia.
Ethanolamine is commonly called monoethanolamine or MEA in order to be distinguished from diethanolamine (DEA) and triethanolamine (TEA). Ethanolamine is the second-most-abundant head group for phospholipids, substances found in biological membranes (particularly those of procaryotes), and is also used in messenger molecules such as palmitoylethanolamide, which has an effect on CB1 receptors.[5]
The term ethanolamines (plural) is a group of amino alcohols. A class of antihistamines is identified as ethanolamines, which includes carbinoxamine, clemastine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, and doxylamine.[6]
Production
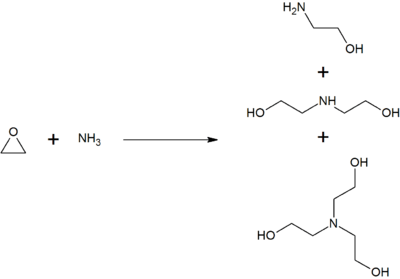
Monoethanolamine is produced by reacting ethylene oxide with aqueous ammonia; the reaction also produces diethanolamine and triethanolamine. The ratio of the products can be controlled by changing the stoichiometry of the reactants.[7]
Note that this reaction is exothermic and that controls are needed to prevent a runaway reaction.
Applications
MEA is used in aqueous solutions for scrubbing certain acidic gases. It is used as feedstock in the production of detergents, emulsifiers, polishes, pharmaceuticals, corrosion inhibitors, chemical intermediates.[7][8] For example, reacting ethanolamine with ammonia gives ethylenediamine, a precursor of the commonly used chelating agent, EDTA :[7]
In pharmaceutical formulations, MEA is used primarily for buffering or preparation of emulsions. MEA can be used as pH regulator in cosmetics.[9]
Gas stream scrubbing
Aqueous solutions of MEA (solutions of MEA in water) are used as a gas stream scrubbing liquid in amine treaters. For example, aqueous MEA is used to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from flue gas, as well as U.S. nuclear submarines for the same.[10] Aqueous solutions can weakly dissolve certain kinds of gases from a mixed gas stream. The MEA in such solutions, acting as a weak base, then neutralizes acidic compounds dissolved in the solution to turn the molecules into an ionic form, making them polar and considerably more soluble in a cold MEA solution, and thus keeping such acidic gases dissolved in this gas-scrubbing solution. Therefore, large surface area contact with such a cold scrubbing solution in a scrubber unit can selectively remove such acidic components as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and CO2 from some mixed gas streams. For example, basic solutions such as aqueous MEA or aqueous potassium carbonate can neutralize H2S into hydrosulfide ion (HS−) or CO2 into bicarbonate ion (HCO3−).
H2S and CO2 are only weakly acidic gases. An aqueous solution of a strong base such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) will not readily release these gases once they have dissolved. However, MEA is rather weak base and will re-release H2S or CO2 when the scrubbing solution is heated. Therefore, the MEA scrubbing solution is recycled through a regeneration unit, which heats the MEA solution from the scrubber unit to release these only slightly acidic gases into a purer form and returns the regenerated MEA solution to the scrubber unit again for reuse.
pH-control amine
Ethanolamine is often used for alkalinization of water in steam cycles of power plants, including nuclear power plants with pressurized water reactors. This alkalinization is performed to control corrosion of metal components. ETA (or sometimes a similar organic amine, e.g., morpholine) is selected because it does not accumulate in steam generators (boilers) and crevices due to its volatility, but rather distributes relatively uniformly throughout the entire steam cycle. In such application, ETA is a key ingredient of so-called "all-volatile treatment" of water (AVT).
References
- ↑ "Ethanolamine MSDS" (PDF). Acros Organics.
- ↑ Hall, H.K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1957, 79, 5441.
- ↑ R. E. Reitmeier; V. Sivertz; H. V. Tartar (1940). "Some Properties of Monoethanolamine and its Aqueous Solutions". Journal of the American Chemical Society 62 (8): 1943–1944. doi:10.1021/ja01865a009.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0256". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Calignano, A; La Rana, G; Piomelli, D (2001). "Antinociceptive activity of the endogenous fatty acid amide, palmitylethanolamide". European Journal of Pharmacology 419 (2–3): 191–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(01)00988-8. PMID 11426841.
- ↑ http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/812828-overview#showall
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Klaus Weissermel, Hans-Jürgen Arpe, Charlet R. Lindley, Stephen Hawkins (2003). "Chap. 7. Oxidation Products of Ethylene". Industrial Organic Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. pp. 159–161. ISBN 3-527-30578-5.
- ↑ "Ethanolamine". Occupational Safety & Health Administration.
- ↑ Carrasco, F. (2009). "Ingredientes Cosméticos". Diccionario de Ingredientes Cosméticos 4ª Ed. www.imagenpersonal.net. p. 306. ISBN 978-84-613-4979-1.
- ↑ http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=11170
External links
- Process technology to produce ethanolamines by reaction of ammonia and ethylene oxide
- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
| ||||||