Erythromycin
 | |
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
(3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-6- {[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}- 14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)- 5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]oxy}- 3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-1-oxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | E-mycin, Erythrocin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682381 |
| |
| oral, iv, im, topical, ophthalmic eye drops | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Depends on the ester type between 30% - 65% |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | liver (under 5% excreted unchanged) |
| Half-life | 1.5 hours |
| Excretion | bile |
| Identifiers | |
|
114-07-8 | |
| D10AF02 J01FA01 S01AA17 QJ51FA01 | |
| PubChem | CID 3255 |
| IUPHAR ligand | 1456 |
| DrugBank |
DB00199 |
| ChemSpider |
12041 |
| UNII |
63937KV33D |
| KEGG |
D00140 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:42355 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL532 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C37H67NO13 |
| 733.93 g/mol | |
|
SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Erythromycin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. It is in the macrolide class and has an antimicrobial spectrum similar to or slightly wider than that of penicillin, and is often prescribed for people who have an allergy to penicillins. For respiratory tract infections, it has better coverage of atypical organisms, including Mycoplasma and Legionella. It was first marketed by Eli Lilly and Company, and it is today commonly known as erythromycin ethylsuccinate (EES), a commonly administered ester prodrug. It is commonly applied after delivery to the eyes of newborns to prevent neonatal conjunctivitis. It is used as an alternative treatment to treat sexually transmitted diseases.
Erythromycin improves gastric emptying and symptoms from delayed gastric emptying, yet it is used in an off-label basis. Intravenous (IV) erythromycin Is sometimes administered when IV prokinetic therapy is needed in hospitalized patients. Oral treatment with erythromycin improves gastric emptying, but has limited long-term efficacy.[1]
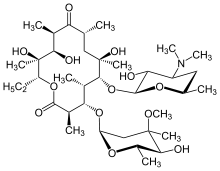
In structure, this macrocyclic compound contains a 14-membered lactone ring with 10 asymmetric centers and two sugars (L-cladinose and D-desosamine), making it a compound very difficult to produce by synthetic methods. Erythromycin is produced from a strain of the actinomycete Saccharopolyspora erythraea.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, a list of the most important medications needed in a basic health system.[2]
History
Dr. Abelardo B. Aguilar, a Filipino scientist, sent some soil samples to his employer Eli Lilly in 1949. Eli Lilly’s research team, led by J. M. McGuire, managed to isolate erythromycin from the metabolic products of a strain of Streptomyces erythreus (designation changed to "Saccharopolyspora erythraea") found in the samples.
Lilly filed for patent protection of the compound and U.S. patent 2,653,899 was granted in 1953. The product was launched commercially in 1952 under the brand name Ilosone (after the Philippine region of Iloilo where it was originally collected). Erythromycin was formerly also called Ilotycin.
In 1981, Nobel laureate (1965 in chemistry) and professor of chemistry at Harvard University (Cambridge, MA) Robert B. Woodward (posthumously), along with a large number of members from his research group, reported the first stereocontrolled asymmetric chemical synthesis of erythromycin A.
The antibiotic clarithromycin was invented by scientists at the Japanese drug company Taisho Pharmaceutical in the 1970s as a result of their efforts to overcome the acid instability of erythromycin.
Scientists at Chugai Pharmaceuticals discovered an erythromycin-derived motilin agonist called mitemcinal that is believed to have strong prokinetic properties (similar to erythromycin) but lacking antibiotic properties. Erythromycin is commonly used off-label for gastric motility indications such as gastroparesis. If mitemcinal can be shown to be an effective a prokinetic agent, it would represent a significant advance in the gastrointestinal field, as treatment with this drug would not carry the risk of unintentional selection for antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Adverse effects
Gastrointestinal disturbances, such as diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, and vomiting, are very common because erythromycin is a motilin agonist.[3] Because of this, erythromycin tends not to be prescribed as a first-line drug. However, it may be useful in treating gastroparesis due to this promotility effect. Intravenous erythromycin may also be used in endoscopy as an adjunct to clear gastric contents.
More serious side effects include arrhythmia with prolonged QT intervals including torsades de pointes, and reversible deafness. Allergic reactions range from urticaria to anaphylaxis. Cholestasis, Stevens–Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis are some other rare side effects that may occur.
Studies have shown evidence both for and against the association of pyloric stenosis and exposure to erythromycin prenatally and postnatally.[4][5] Exposure to erythromycin (especially long courses at antimicrobial doses, and also through breastfeeding) has been linked to an increased probability of pyloric stenosis in young infants.[6][7] Erythromycin used for feeding intolerance in young infants has not been associated with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.[6]
Erythromycin estolate has been associated with reversible hepatotoxicity in pregnant women in the form of elevated serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase and is not recommended during pregnancy. Some evidence suggests similar hepatotoxicity in other populations.[8]
It can also affect the central nervous system, causing psychotic reactions, nightmares and night sweats.[9]
It may also alter the effectiveness of combined oral contraceptive pills because of its effect on the gut flora. Erythromycin is an inhibitor of the cytochrome P450 system, which means it can have a rapid effect on levels of other drugs metabolised by this system, e.g., warfarin.
Synthesis
Over the three decades after the discovery of erythromycin A and its activity as an antimicrobial, many attempts were made to synthesize it in the laboratory. However, the presence of 10 stereospecific carbons and several points of distinct substitution has made the total synthesis of erythromycin A a formidable task.[10] Complete syntheses of erythromycins’ related structures and precursors such as 6-deoxyerythronolide B have been accomplished, giving way to possible syntheses of different erythromycins and other macrolide antimicrobials.[11] However, Woodward did successfully complete the synthesis of erythromycin A.[12][13][14] This total synthesis begins with (7) and (8). After being coupled, the resulting structure is subjected to a series of reactions, including hydrolysis and stereospecific aldolization. The resulting pure enone is then converted to the desired (9) through a series of reduction and oxidation reactions. The dithiadecalin product (9) is then converted to both a ketone (10) and an aldehyde (11).
Available forms
Erythromycin is available in enteric-coated tablets, slow-release capsules, oral suspensions, ophthalmic solutions, ointments, gels, Enteric-coated Capsules Non Enteric-coated tablets Non Enteric-coated capsules and injections.

The following erythromycin combinations are available for oral dosage:[15]
- erythromycin base (capsules, tablets)
- erythromycin estolate (capsules, oral suspension, tablets), contraindicated during pregnancy[16]
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate (oral suspension, tablets)
- erythromycin stearate (oral suspension, tablets)
For injection the available combinations are:[15]
- erythromycin gluceptate
- erythromycin lactobionate
Brand names include Robimycin, E-Mycin, E.E.S. Granules, E.E.S.-200, E.E.S.-400, E.E.S.-400 Filmtab, Erymax, Ery-Tab, Eryc, Ranbaxy, Erypar, EryPed, Eryped 200, Eryped 400, Erythrocin Stearate Filmtab, Erythrocot, E-Base, Erythroped, Ilosone, MY-E, Pediamycin, Zineryt, Abboticin, Abboticin-ES, Erycin, PCE Dispertab, Stiemycine, Acnasol, and Tiloryth.
Composition
Standard-grade erythromycin is primarily composed of four related compounds known as erythromycins A, B, C, and D. Each of these compounds can be present in varying amounts and can differ by lot. Erythromycin A has been found to have the most antibacterial activity, followed by erythromycin B. Erythromycins C and D are about half as active as erythromycin A.[17][18] Some of these related compounds have been purified and can be studied and researched individually.
Spectrum of susceptibility
Erythromycin can be used to treat bacteria responsible for causing infections of the skin and upper respiratory tract, including Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Haemophilus genera. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant bacteria:[19]
- Haemophilus influenzae: 0.015 to 256 μg/ml
- Staphylococcus aureus: 0.023 to 1024 μg/ml
- Streptococcus pyogenes: 0.004 to 256 μg/ml
Mechanism of action
Erythromycin displays bacteriostatic activity or inhibits growth of bacteria, especially at higher concentrations,[20] but the mechanism is not fully understood. By binding to the 50s subunit of the bacterial 70s rRNA complex, protein synthesis and subsequent structure and function processes critical for life or replication are inhibited.[20] Erythromycin interferes with aminoacyl translocation, preventing the transfer of the tRNA bound at the A site of the rRNA complex to the P site of the rRNA complex. Without this translocation, the A site remains occupied, thus the addition of an incoming tRNA and its attached amino acid to the nascent polypeptide chain is inhibited. This interferes with the production of functionally useful proteins, which is the basis of this antimicrobial action.
Pharmacokinetics
Erythromycin is easily inactivated by gastric acid; therefore, all orally administered formulations are given as either enteric-coated or more-stable salts or esters, such as erythromycin ethylsuccinate. Erythromycin is very rapidly absorbed, and diffuses into most tissues and phagocytes. Due to the high concentration in phagocytes, erythromycin is actively transported to the site of infection, where, during active phagocytosis, large concentrations of erythromycin are released.
Metabolism
Most of erythromycin is metabolised by demethylation in the liver by the hepatic enzyme CYP3A4. Its main elimination route is in the bile with little renal excretion, 2%-15% unchanged drug. Erythromycin's elimination half-life ranges between 1.5 and 2.0 hours and is between 5 and 6 hours in patients with end-stage renal disease. Erythromycin levels peak in the serum 4 hours after dosing; ethylsuccinate peaks 0.5-2.5 hours after dosing, but can be delayed if digested with food.[21]
Erythromycin crosses the placenta and enters breast milk. The American Association of Pediatrics determined erythromycin is safe to take while breastfeeding.[22] Absorption in pregnant patients has been shown to be variable, frequently resulting in levels lower than in nonpregnant patients.[21]
Interactions
Erythromycin is metabolized by enzymes of the cytochrome P450 system, in particular, by isozymes of the CYP3A superfamily, CYP3A.[23] The activity of the CYP3A enzymes can be induced or inhibited by certain drugs (e.g. dexamethasone) which can cause it to affect the metabolism of many different drugs, e.g. erythromycin. If other CYP3A substrates — drugs that are broken down by CYP3A — such as simvastatin (Zocor), lovastatin (Mevacor), or atorvastatin (Lipitor)—are taken concomitantly with erythromycin, levels of the substrates increase, often causing adverse effects. A noted drug interaction involves erythromycin and simvastatin, resulting in increased simvastatin levels and the potential for rhabdomyolysis. Another group of CYP3A4 substrates are drugs used for migraine such as ergotamine and dihydroergotamine; their adverse effects may be more pronounced if erythromycin is associated.[9] Earlier case reports on sudden death prompted a study on a large cohort that confirmed a link between erythromycin, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden cardiac death in patients also taking drugs that prolong the metabolism of erythromycin (like verapamil or diltiazem) by interfering with CYP3A4.[24] Hence, erythromycin should not be administered to people using these drugs, or drugs that also prolong the QT interval. Other examples include terfenadine (Seldane, Seldane-D), astemizole (Hismanal), cisapride (Propulsid, withdrawn in many countries for prolonging the QT time) and pimozide (Orap). Theophylline, which is used mostly in asthma, is also contraindicated.
Erythromycin may affect neuromuscular transmission by acting presynaptically, so may produce or worsen symptoms of myasthenia gravis in patients with pre-existing postsynaptic defects. Exacerbations of myasthenia gravis have also been reported with the use of telithromycin and azithromycin.[25]
Erythromycin is not recommended when using clindamycin-containing products, even topical products such as Duac or BenzaClin. In general, the simultaneous use of two different erythromycin derivatives (such as clindamycin and Mitemcinal) should be avoided as drugs in this macrolide family possess a common mechanism of action.
Erythromycin and Doxycycline can have a synergistic effect when combined and kill bacteria (E. coli) with a higher potency than the sum of the two drugs together. However, this synergistic relationship is only temporary. After approximately 72 hours, the relationship shifts to become antagonistic, whereby a 50/50 combination of the two drugs kills less bacteria than if the two drugs were administered separately. [26]
Erythromycin-derived compounds
- Ansamycin
- Azithromycin / Zithromax / Zitromax / Sumamed
- Carbomycin
- Cethromycin
- Clarithromycin / Biaxin
- Dirithromycin / Dynabac
- Mitemcinal
- Oleandomycin
- Roxithromycin / Rulid / Surlid / Roxid
- Spiramycin
- Telithromycin
- Tylocine
References
- ↑ http://gi.org/guideline/management-of-gastroparesis/
- ↑ "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines" (PDF). World Health Organization. October 2013. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
- ↑ Weber FH Jr, et. al (April 1993). "Erythromycin: a motilin agonist and gastrointestinal prokinetic agent". American Journal of Gastroenterology 88 (4): 485–90. PMID 8470625.
- ↑ http://online.lexi.com/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/patch_f/1831759#f_pregnancy-and-lactation
- ↑ http://online.lexi.com/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/74/304361
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Maheshwai N (March 2007). "Are young infants treated with erythromycin at risk for developing hypertrophic pyloric stenosis?". Arch. Dis. Child. 92 (3): 271–3. doi:10.1136/adc.2006.110007. PMC 2083424. PMID 17337692.
- ↑ http://www.bmj.com/content/348/bmj.g1908
- ↑ McCormack WM, George H, Donner A, Kodgis LF, Albert S, Lowe EW, Kass EH (1997). "Hepatotoxicity of erythromycin estoate during pregnancy". Antimicrob Agents Chemother 12 (5): 630–5. doi:10.1128/AAC.12.5.630. PMC 429989. PMID 21610.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Erythromycin. Belgian Center for Pharmacotherapeutical Information. Retrieved July 20, 2008.
- ↑ Pal S (2006). "A journey across the sequential development of macrolides and ketolides related to erythromycin". Tetrahedron 62 (14): 3171–3200. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2005.11.064.
- ↑ Evans D. A., Kim A. S. (1997). "Synthesis of 6-Deoxyerythronolide B. Implementation of a General Strategy for the Synthesis of Macrolide Antibiotics". Tetrahedron Lett. 38: 53–56. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(96)02258-7.
- ↑ Woodward R. B., Logusch E., Nambiar K. P., Sakan K., Ward D. E., Au-Yeung , Balaram P., Browne L. J., Card P. J. et al. (1981). "Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Erythromycin. 1. Synthesis of an Erythronolide A Seco Acid Derivative via Asymmetric Induction". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 103 (11): 3210–3213. doi:10.1021/ja00401a049.
- ↑ Woodward R. B., Logusch E., Nambiar K. P., Sakan K., Ward D. E., Au-Yeung , Balaram P., Browne L. J., Card P. J. et al. (1981). "Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Erythromycin. 2. Synthesis of an Erythronolide A Lactone System". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 103 (11): 3213–3215. doi:10.1021/ja00401a050.
- ↑ Woodward R. B., Logusch E., Nambiar K. P., Sakan K., Ward D. E., Au-Yeung , Balaram P., Browne L. J., Card P. J. et al. (1981). "Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Erythromycin. 3. Total Synthesis of Erythromycin". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 103 (11): 3215–3217. doi:10.1021/ja00401a051.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 drugs.com > erythromycin (Oral route, Parenteral route) Retrieved on Jan 11, 2010
- ↑ Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines 2006 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. MMWR 2006;55
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC176346/
- ↑ http://www.toku-e.com/Assets/MIC/Erythromycin%20A%20EvoPure.pdf
- ↑ http://www.toku-e.com/Assets/MIC/Erythromycin.pdf
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Katzung PHARMACOLOGY, 9e Section VIII. Chemotherapeutic Drugs Chapter 44. Chloramphenicol, Tetracyclines, Macrolides, Clindamycin, & Streptogramins
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 http://online.lexi.com/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/74/304361#pkm
- ↑ http://www.breastfeedingmadesimple.com/AAPDrugsinMilk.pdf
- ↑ (Hunt et al., 1992).
- ↑ Ray WA, Murray KT, Meredith S, Narasimhulu SS, Hall K, Stein CM. Oral Erythromycin and the Risk of Sudden Death from Cardiac Causes. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1089-96.
- ↑ http://ispub.com/IJN/10/2/9809
- ↑ Pena-Miller A, P, H, Beardmore R., R; Laehnemann, D; Jansen, G; Fuentes-Hernandez, A; Rosenstiel, P; Schulenburg, H; Beardmore, R (April 23, 2013). "When the most potent combination of antibiotics selects for the greatest bacterial load: the smile-frown transition.". PLOS Biology 4 (11): e1001540. PMID 23630452.
Further reading
- British National Formulary "BNF 49" March 2005.
- Mims C, Dockrell HM, Goering RV, Roitt I, Wakelin D, Zuckerman M. Chapter 33: Attacking the Enemy: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy: Macrolides. In: Medical Microbiology (3rd Edition). London: Mosby Ltd; 2004. p 489
- Hunt,Ch.M., Watkins, P.B., Saenger, P., Stave, G.M., Barlascini, N., Watlington, Ch.O., Wright, J.T., Guzelian, P.S., (1992) Heterogeneity of CYP3A isoforms metabolizing erythromycin and cortisol. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 51: 18-23
External links
- Erythromycin bound to proteins in the PDB
- U.S. Patent 2,653,899
- E.E.S. (Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate) Drug Information: Uses, Side Effects, Drug Interactions and Warnings at RxList
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||