Erft Railway
| Bedburg–Horrem | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
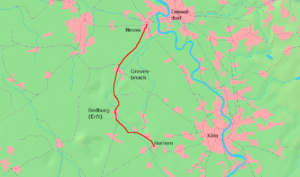 Current course of the Erft Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route number: | 481 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge: | 1435 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum speed: | 100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| German state: | North Rhine-Westphalia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating points and lines[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Erft Railway (German: Erftbahn is a line in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The non-electrified main line was originally built as a line of the Bergheim District Railway (Bergheimer Kreisbahn) and operated as a metre gauge railway. Later, the line was converted to standard gauge. The Erft Railway is now only served by a Regionalbahn service.
Operations and history
The Bedburg–Horrem–Mödrath line was opened in 1896 as part of the Bergheim District Railway.[2] In 1983, the Horrem–Quadrath-Ichendorf section was electrified because of its high freight traffic, but in 1996 its catenary was dismantled.[3] As of 2 June 1991, trains ran through from Neuss to Horrem, continuing in the peak hour to Cologne. From 15 December 2002, the rail service was extended throughout the day to Cologne.
On 1 November 2007, the rest of the line was also connected to the electronic signalling centre. At the same time, all older level crossings were upgraded to the state of the art with flashing lights. The crossing at Bahnhofstraße in Holzheim had been equipped with a full barrier and a gatekeeper who visually checked whether the tracks were free of vehicles; this is now done with a radar scanner.
Erft railway
The Regionalbahn service (Erft-Bahn) operates from Düsseldorf Central Station (Hauptbahnhof) to Cologne Messe/Deutz via Neuss, Grevenbroich, Bedburg, Bergheim without stopping in Horrem, although half the services terminate in Horrem instead of running to Cologne. The service has the line number of RB 38 and is operated every half hour (between Neuss and Grevenbroich and between Bedburg and Quad-Ichendorf) or hourly (elsewhere) by DB Regio NRW.[4] Between Düsseldorf and Neuss it runs along the Mönchengladbach–Düsseldorf line and between Horrem and Cologne it runs along the Cologne–Aachen high-speed line.
Rolling stock

Before the 1990s, class 150 accumulator cars were operated on the line. In the 1990s, class 212 diesel locomotives and later class 215 and 218 locomotives were used together with Silberling carriages. In the late 1990s, the locomotive-hauled trains were replaced with class 628 diesel multiple units. In 2003, two and three carriage class 643 (Bombardier Talent) diesel multiple units was added; two carriage sets were used until the 2010/2011 timetable.
Currently RB 38 services are operated exclusively with class 628 diesel multiple units, mostly as coupled sets with four carriages. Single class 628 sets (two carriages) are used on the short shuttles between Düsseldorf/Neuss and Grevenbroich and between Bedburg and Horrem.
Outlook

In the 1990s, it was planned (as part of a network targeted for 2015) to extend the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn network from Horrem via Bedburg to Düsseldorf as line S 18. This meant that the line would be upgraded and electrified. Two new stations were planned at Neuss Polizeidirektion and Neuss Insel Hombroich.[5]
The plans for the extension of the S-Bahn on the northern section of the line have not be pursued further by the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr (VRR). The Zweckverband Nahverkehr Rheinland (Rhineland Local Transport Association, NVR) still plans to upgrade the southern section of the line by around 2020, including electrication and a flying junction in Horrem to connect to the existing S-Bahn line to Cologne. The NVR is pursuing the goal of relieving the Hohenzollern Bridge in Cologne by eliminating the RB 38 services. This would involve running line S 12 services over the Erft Railway from Horrem to Bedburg; the section of the S 12 from Horrem to Düren would be taken over by the line S 13. Under this plan RB 38 would run between Neuss and Bedburg. Subject to an agreement with the VRR, the S-Bahn service would later replace the Regionalbahn service to Grevenbroich.[6]
Route
The Erft Railway runs next to the Erft from Bedburg to Bergheim. The line crosses the Erft shortly before Bergheim. Otherwise, the Erft is not in the immediate vicinity of the railway tracks. The railway is a single-track branch line.
Notes
- ↑ Eisenbahnatlas Deutschland (German railway atlas) (2009/10 ed.). Schweers + Wall. 2009. ISBN 978-3-89494-139-0.
- ↑ "Line 2581: Bedburg - Abzw Martinswerk". NRW Rail Archive (in German). André Joost. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- ↑ "Line 2601: Mödrath - Rommerskirchen". NRW Rail Archive (in German). André Joost. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- ↑ "B38: Erft-Bahn". NRW Rail Archive (in German). André Joost. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- ↑ "S-Bahn Rhein-Ruhr-Sieg - Zielnetz" (in German). Marco Wegener. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- ↑ "SPNV-Planungskonzept 2016 -2030 als Basis des zukünftigen SPNV-Nahverkehrsplans" (PDF) (in German). Nahverkehr Rheinland. pp. 15–17). Retrieved 14 June 2013.
External links
- Paul Ximmer. "Information on the Erft Railway" (in German). Retrieved 8 February 2012.
- Paul Ximmer. "Photographs of the Erft Railway" (in German). Retrieved 8 February 2012.