Equatorial Spanish
| Spanish language |
|---|
| Overview |
|
| Grammar |
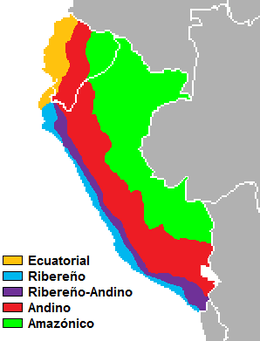
Equatorial Spanish, also called Coastal Colombian-Ecuadorian dialect or Chocoano is a dialect of Spanish spoken mainly in the Coastal region of Ecuador, as well as coastal bordering areas of northern Peru and southern Colombia. It is considered to be transitional between the Caribbean dialects and the Peruvian Coast accents. The major influential linguistic center is the city of Guayaquil, Quito, Buenaventura, and Bogota. There is an important subvariety of this dialect spoken by the majority of African-descent communities dwelling on the border between coastal Colombia (Choco department) and Ecuador (Esmeraldas province) which give a touch of "African" style to the dialect on this area.
The particular intonation which identifies the speakers of these regions has been subject of study. American hispanicist Peter Boyd Bowman quoted in 1953 "a phonetic continuity between the coasts of northern Peru, Ecuador and southern Colombia(...) opposite to the dialects of their Andean provinces." He believed that "the current borders of Ecuador with its neighboring countries are not natural, since they do not match cultural nor linguistic criteria (Spanish is spoken the same way on both sides), neither match old political boundaries (either Inca or colonial)." In a recent study, American John Lipski also considered the dialect of northern coastal Peru as a distinct Spanish variety based on phonetic features.
Notable phonological characteristics
It presents markedly attenuated Caribbean features:
- The /s/ in the end of the syllables is aspirated or elided, though the middle class tends to avoid it in the pre-vocalic context.
- As in the Caribbean dialects, the /x/ ("j") phoneme is pronounced [h] (as in English).
- The /n/ end of words is velar, sometimes bilabialized, especially among African descents.
- In rural areas, there is virtually no difference between of liquid /l/ and /r/, elision is rare.
- In the area of Choco intervocalic /d/ is realized as /r/. In this same region the aspirated/s/ and /k/ may result in a glottal stop.
- As in most American dialects, seseo is the widest spread, so both "z" (traditionally /θ/) and "s" merge into the sound /s/. However, there are rural areas in the coast of Ecuador, where ceceo is present, one of the very few cases in America to happen right the opposite, so both "s" and "z" are pronounced as /θ/). This is common to large areas of Andalusia, Spain.
- Yeismo is also the general rule just as it is in most of the American Spanish dialects, that means there is no differentiation between the sounds of "ll" and "y", and they both merge into j.
References
- Zamora Munné, Juan y Guitart, Jorge: Dialectología Hispanoamericana. Teoría-Descripción-Historia, Salamanca, Ediciones Almar, 1982.
- Instituto Caro y Cuervo: Atlas lingüístico-etnográfico de Colombia-ALEC-, Bogotá, 1981-1983.
- "Sobre la pronunciación del Español en el Ecuador". Peter Boyd Bowman. Nueva revista de filología hispánica, V.7, NO. 1-2 (ene.-jun. 1953), p. 221-233. http://codex.colmex.mx:8991/F/?func=service&doc_library=ECM01&doc_number=000570173&line_number=0001&func_code=WEB-BRIEF&service_type=MEDIA
- "Hacia la búsqueda de la realidad lingüística en el Departamento de Lambayeque" - Lucinda García Albújar. http://portal.fachse.edu.pe/sites/default/files/UN1-%20Garc%C3%ADa.pdf
- "Acerca del habla de los negros del Norte del Perú. Expresiones afronorteñas" - Luis Rocca Torres. http://portal.fachse.edu.pe/sites/default/files/UN1-%20Rocca.pdf
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Annex: Ecuadorian Spanish
- Annex: Colombian Spanish
- Annex: Peruvian Spanish