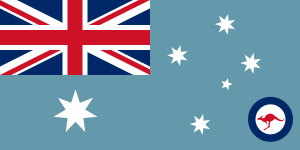
National civil ensign of New Zealand flown from the stern of
HikitiaAn ensign is a national flag when used at sea as a country's maritime flag. It serves as a distinguishing token, emblem, or badge, such as a symbol of office in heraldry. The military rank of ensign, a junior officer[1] once responsible for bearing the ship's ensign, derives from it.
Large versions of naval ensigns called battle ensigns are used when a warship goes into battle.
National ensigns
In nautical use, the ensign is flown on a ship or boat to indicate its nationality.[1]
Ensigns are usually at the stern flagstaff when in port, and may be shifted to a gaff (if available) when the ship is under way, becoming known as a steaming ensign.
Vexillologists distinguish three varieties of a national flag when used as an ensign:
- A civil ensign (usage symbol
 ) is worn by merchant and pleasure vessels. In some countries the yacht ensign, used on recreational boats or ships instead of merchant vessels, differs from the civil ensign.
) is worn by merchant and pleasure vessels. In some countries the yacht ensign, used on recreational boats or ships instead of merchant vessels, differs from the civil ensign.
- A state ensign or government ensign (usage symbol
 ) is worn by government vessels, such as coast guard ships.
) is worn by government vessels, such as coast guard ships.
- A naval ensign (usage symbol
 ) is used by a country's navy.[2]
) is used by a country's navy.[2]
Many countries do not distinguish between these uses, and employ only one national flag and ensign in all cases. Others (like the United Kingdom, Ukraine, Italy, Russia, South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, and Japan) use different ensigns. Such ensigns are strictly regulated and indicate if the boat is a warship, a merchant vessel or a yacht, for example.
Several Commonwealth countries' national flags had their origin in the ensigns of their original colonising power, the United Kingdom. Most notable of these national flags are those of Australia, New Zealand, and several smaller island nations. It is also very likely that the original design from which the flag of the United States developed was strongly influenced by the British Red Ensign or the flag of the (British controlled) East India Company. In countries such as Australia and New Zealand which have national flags based on the design of British ensigns, the national flag is often (erroneously) referred to as the national ensign.
Heraldic ensigns
In heraldry, an ensign is the ornament or sign, such as the crown, coronet, or mitre, borne above the charge or arms.[3]
Air ensigns
With the creation of independent air forces and the growth in civil aviation in the first half of the 20th century, a range of distinguishing flags and ensigns were adopted. These may be divided into air force ensigns (often light blue in colour,[4] such as the Royal Air Force Ensign) and civil air ensigns.
Gallery
| The Red Ensign as currently used for British civilian vessels |
|
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Znamierowski. "Types of flags". The world encyclopedia of flags. p. 31.
- ↑ Znamierowski. "Naval ensigns and flags". The world encyclopedia of flags. p. 88.
- ↑ Snell, Melissa. "Pimbley's Dictionary of Heraldry".
- ↑ Znamierowski. "Air force flags". The world encyclopedia of flags. p. 85.
References
- Znamierowski, Alfred (2002). The world encyclopedia of flags : The definitive guide to international flags, banners, standards and ensigns. London: Hermes House. ISBN 1-84309-042-2.
 ) is worn by merchant and pleasure vessels. In some countries the yacht ensign, used on recreational boats or ships instead of merchant vessels, differs from the civil ensign.
) is worn by merchant and pleasure vessels. In some countries the yacht ensign, used on recreational boats or ships instead of merchant vessels, differs from the civil ensign. ) is worn by government vessels, such as coast guard ships.
) is worn by government vessels, such as coast guard ships. ) is used by a country's navy.[2]
) is used by a country's navy.[2]