Enalapril
 | |
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
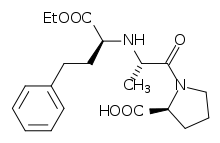
| (2S)-1-[(2S)-2-{[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino}propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Vasotec |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a686022 |
| |
| |
| intravenous and by mouth | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60% (oral) |
| Metabolism | hepatic (to enalaprilat) |
| Half-life | 11 hours (enalaprilat) |
| Excretion | renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
75847-73-3 | |
| C09AA02 | |
| PubChem | CID 5388962 |
| DrugBank |
DB00584 |
| ChemSpider |
4534998 |
| UNII |
69PN84IO1A |
| KEGG |
D07892 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:4784 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL578 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C20H28N2O5 |
| 376.447 g/mol | |
|
SMILES
| |
| |
| Physical data | |
| Melting point | 143 to 144.5 °C (289.4 to 292.1 °F) |
| | |
Enalapril (marketed as Vasotec in the USA, Enaladex in some other countries, and Enacard for veterinary use[1]:142-143) is an angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used in the treatment of hypertension, diabetic nephropathy, and some types of chronic heart failure. ACE converts the peptide hormone angiotensin I to angiotensin II. One of the actions of angiotensin II is the vasoconstriction of blood vessels, resulting in an increase in blood pressure. ACE inhibitors such as enalapril prevent this effect. Enalapril has been shown to lower the death rate in systolic heart failure. Enalapril was the first member of the group known as the dicarboxylate-containing ACE inhibitors.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system.[2]
Medical uses
Enalapril is used to treat hypertension, symptomatic heart failure, and asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction.[3] It has been proven to protect the function of the kidneys in hypertension, heart failure, and diabetes, and may be used in the absence of hypertension for its kidney protective effects.[4] It is widely used in chronic kidney failure.[5]
Cautions and contraindications
Enalapril is pregnancy category D. Some evidence suggests it will cause injury and death to a developing fetus. Patients are advised not to become pregnant while taking enalapril and to notify their doctors immediately if they become pregnant. In pregnancy, enalapril may result in damage to the fetus’s kidneys and resulting oligohydramnios (not enough amniotic fluid). Enalapril is secreted in breast milk and is not recommended for use while breastfeeding.[6]
Side effects
The most common side effects of enalapril include increased serum creatinine (20%), dizziness (2–8%), low blood pressure (1–7%), syncope (2%), and dry cough (1–2%). The most serious common adverse event is angioedema (swelling) (0.68%) which often affects the face and lips, endangering the patient’s airway. Angioedema can occur at any point during treatment with enalapril but is most common after the first few doses.[6] Angioedema and fatality there from is reportedly higher among black people.[6]
Mechanism of action
Normally, angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II constricts blood vessels, increasing blood pressure. By inhibiting ACE, enalapril decreases levels of angiotensin II leading to less vasoconstriction and decreased blood pressure.[6]
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
Pk and Pd are as follows:[6]
- Onset of action: about 1 hour
- Peak effect: 4–6 hours
- Duration: 12–24 hours
- Absorption: ~60%
- Metabolism: Prodrug, undergoes biotransformation to enalaprilat
History
Squibb developed the first inhibitor, captopril, but it had adverse effects such as a metallic taste (which, as it turned out, was due to the sulfhydryl group). Merck & Co. developed enalapril as a competing prodrug.[7][8]:12-13
Enalaprilat, the first dicarboxylate-containing ACE inhibitor, was developed partly to overcome these limitations of captopril. The sulfhydryl moiety was replaced by a carboxylate moiety, but additional modifications were required in its structure-based design to achieve a similar potency to captopril. Enalaprilat, however, had a problem of its own in that it had poor oral availability. This was overcome by the researchers at Merck by the esterification of enalaprilat with ethanol to produce enalapril.[8]:13
Merck introduced Enalapril to market in 1981; it became Merck's first billion-dollar selling drug in 1988.[8]:13
References
- ↑ Boyce P. Wanamaker, Kathy Massey Applied Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians, 5th Edition. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2014 ISBN 9780323291705
- ↑ "WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines". World Health Organization. October 2013. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
- ↑ U.S. National Library of Medicine. Last Revised October 1, 2010 MedlinePlus: Enalapril
- ↑ John J.V. McMurray (January 21, 2010). "Clinical Practice: Systolic Heart Failure". N Engl J Med 362 (3): 228–238. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp0909392. PMID 20089973.
Two large trials showed that when patients with NYHA class II, III, or IV heart failure were treated with enalapril, as compared with placebo, in addition to diuretics and digoxin, the rates of admission to the hospital were reduced, and there was a relative risk reduction for death of 16 to 40%.
- ↑ He YM et al. Enalapril versus losartan for adults with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrology (Carlton). 2013 Sep;18(9):605-14. doi: 10.1111/nep.12134. PMID 23869492
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 FDA Label: Enalapril Maleate Tablet Last updated April 2011
- ↑ Jenny Bryan for The Pharmaceutical Journal, 17 Apr 2009 From snake venom to ACE inhibitor — the discovery and rise of captopril
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Jie Jack Li, History of Drug Discovery. Chapter 1 in Drug Discovery: Practices, Processes, and Perspectives. Eds. Jie Jack Li, E. J. Corey. John Wiley & Sons, Apr 3, 2013 ISBN 9781118354469
External links
Package insert at DailyMed: http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=08f90170-f53c-4272-92ae-951cf115e271
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||