Emissions & Generation Resource Integrated Database
| Stable release |
eGRID Ninth Edition Version 1.0 / February 2014 (Data years 2010) |
|---|---|
| Website | eGRIDweb version 1.0 (Data years 2005 and 2004) |
The Emissions & Generation Resource Integrated Database (eGRID) is a comprehensive source of data on the environmental characteristics of almost all electric power generated in the United States. eGRID is issued by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
As of January 2015, the available editions of eGRID contain data for years 2010, 2009, 2007, 2005, 2004, and 1996 through 2000. eGRID is unique in that it links air emissions data with electric generation data for United States power plants.[1]
eGRIDweb version 1.0 was released on April 27, 2009 by the U.S. EPA. This user friendly web application allows users to select, view, and export eGRID2007 electric generation and emissions data for years 2005 and 2004. The application includes downloadable eGRID subregion GHG total and non-baseload output emission rates for calculating indirect CO2 emissions, summary tables, representational maps, and a 2012 paper, “How to use eGRID for Carbon Footprinting Electricity Purchases in Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventories”.
History
The Ninth Edition of eGRID was released by EPA on February 24, 2014. It contains the complete release year 2010 data.
eGRID2012 Version 1.0, the Eighth Edition of eGRID, was released by EPA on May 10, 2012. It contains the complete release of year 2009 data.
eGRID2010 Version 1.1, the Seventh Edition of eGRID, was released by EPA on May 20, 2011. It contains the complete release of year 2007 data, as well as data files for years 2005 and 2004 data. Data for year 2007 were configured to reflect the electric power industry’s current structure as of December 31, 2010, including plant ownership and operators, parent company affiliations, company mergers, and grid configurations.
eGRID2007 Version 1.1, the Sixth Edition of eGRID, was released by EPA on January 28, 2009 and the Fifth Edition of eGRID, eGRID2006 Version 2.1, was released in April 2007; both years of data are included in eGRID2010 Version 1.1. The Fourth Edition of eGRID, eGRID2002 Version 2.01, was released in May 2003 and contains data for years 1996 through 2000. The First through Third Editions of eGRID contained data years 1996 through 1998. These editions are obsolete and have been replaced by the Fourth Edition.
Data summary
eGRID data include emissions, different types of emission rates, electricity generation, resource mix, and heat input. eGRID data also include plant identification, location, and structural information. The emissions information in eGRID2010 includes carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e), and mercury (Hg). CO2, CH4, and N2O are greenhouse gases (GHG) that contribute to global warming or climate change. NOx and SO2 contribute to unhealthy air quality and acid rain in many parts of the country. Hg is a toxic pollutant that can adversely affect exposed nervous systems. eGRID's resource mix information includes the following fossil fuel resources: coal, oil, gas, other fossil; nuclear resources; and the following renewable resources: hydroelectric (water), biomass (including biogas, landfill gas and digester gas), wind, solar, and geothermal.
The Ninth Edition of eGRID with year 2010 data is presented in three Excel workbooks. The eGRID workbook contains data at the boiler, generator, and plant levels and aggregated data by state, power control area, eGRID subregion, NERC region, and U.S. The workbook also includes a ninth file that displays the grid gross loss (%). The 2010 Technical Support Document, File Structure, Summary Tables (with regional map), and GHG Annual Output Emission Rates for CO2, CH4, and N2O (for GHG inventory and registry work) are included in Adobe PDF files. These files are contained in a ZIP file, "All year 2010 files," that can be downloaded from EPA’s eGRID website.
eGRID2007 data are also available at eGRIDweb version 1.0, the user friendly web application, which can be accessed directly from its own website or from EPA’s eGRID website, along with the eGRIDweb Users Manual.
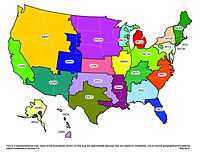 |
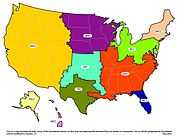 | |
| Ninth Edition eGRID subregion Representational Map | Ninth Edition eGRID NERC Region Representational Map |
The primary data sources used for eGRID include data reported by electric generators to EPA’s Clean Air Markets Division (pursuant to 40 CFR Part 70) and to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA).
Data use
eGRID data are used for carbon footprinting; emission reduction calculations; calculating indirect greenhouse gas emissions for The Climate Registry, the California Climate Action Registry, California’s Mandatory GHG emissions reporting program (Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006, AB 32), and other GHG protocols; were used as the starting point for the new international carbon emissions database, CARMA. EPA tools and programs such as Power Profiler (which has been updated with eGRID year 2010 data), Portfolio Manager, the WasteWise Office Carbon Footprint Tool, the Green Power Equivalency Calculator, the Personal Greenhouse Gas Emissions Calculator, and the Greenhouse Gas Equivalencies Calculator use eGRID. Other tools such as labeling/environmental disclosure, Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) and Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) attributes are supported by eGRID data. States also rely on eGRID data for electricity labeling (environmental disclosure programs), emissions inventories, and for policy decisions such as output based standards. eGRID is additionally used by nongovernmental organizations for tools and analysis by the International Council for Local Environmental Initiatives (ICLEI), the Northeast States for Coordinated Air Use Management (NESCAUM), the Rocky Mountain Institute, the National Resource Defense Council (NRDC), the Ozone Transport Commission (OTC), Powerscorecard.org, and the Greenhouse Gas Protocol Initiative.
In 2010, Executive Order 13514 was issued, requiring Federal agencies to “measure, report, and reduce their greenhouse gas emissions from direct and indirect activities.” The Federal GHG Accounting and Reporting Guidance accompanied this order and recommended using eGRID non-baseload emission rates to estimate the Scope 2 (indirect) emission reductions from renewable energy.
See also
- Air pollution
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
- Combined cycle
- Electric power
- Electric utility
- Electrical power industry
- Electricity generation
- External combustion engine
- Gas turbine
- Power station
- Renewable energy
- Steam turbine
References
External links
- EIA’s Electricity Database Files
- EPA’s Clean Air Markets - Data and Maps
- EPA’s Clean Energy Homepage
- EPA’s Climate Change Homepage
- EPA's eGRID paper “How to use eGRID for Carbon Footprinting Electricity Purchases in Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventories”
- EPA’s eGRID website (Data years 2010, 2009, 2007, 2005, and 2004)
- EPA's eGRIDweb Version 1.0
- EPA’s Energy Star Portfolio Manager
- EPA's Acid Rain Program
- EPA's Combined Heat and Power Partnership Homepage
- Executive Order 13514
- Federal GHG Accounting and Reporting Guidance
- Greenhouse Gas Equivalencies Calculator
- Northeast States for Coordinated Air Use Management (NESCAUM)
- Ozone Transport Commission (OTC)
- Personal Greenhouse Gas Emissions Calculator
- Powerscorecard.org
- World Business Council for Sustainable Development
- World Resources Institute Homepage