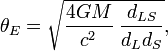Einstein ring
| Gravitational lensing |
|---|
|
Introduction Formalism Strong lensing Microlensing Weak lensing |
|
Strong lens systems Abell 1689 · Abell 2218 CL0024+17 · Bullet Cluster QSO2237+0305 · SDSSJ0946+1006 B1359+154 · QSO 0957+561 |
|
Surveys Strong: CLASS · SLACS (SDSS) Micro: OGLE Weak: DLS · Pan-STARRS · CFHTLS . DES · LSST · SNAP · DESTINY |
In observational astronomy an Einstein ring is the deformation of the light from a source (such as a galaxy or star) into a ring through gravitational lensing of the source's light by an object with an extremely large mass (such as another galaxy or a black hole).[1] This occurs when the source, lens, and observer are all aligned. The first complete Einstein ring, designated B1938+666, was discovered by collaboration between astronomers at the University of Manchester and NASA's Hubble Space Telescope in 1998.[2]
Introduction
Gravitational lensing is predicted by Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. Instead of light from a source traveling in a straight line (in three dimensions), it is bent by the presence of a massive body, which distorts spacetime. An Einstein Ring is a special case of gravitational lensing, caused by the exact alignment of the source, lens, and observer. This results in a symmetry around the lens, causing a ring-like structure.

The size of an Einstein ring is given by the Einstein radius. In radians, it is
where
-
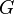 is the gravitational constant,
is the gravitational constant, -
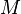 is the mass of the lens,
is the mass of the lens, -
 is the speed of light,
is the speed of light, -
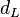 is the angular diameter distance to the lens,
is the angular diameter distance to the lens, -
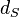 is the angular diameter distance to the source, and
is the angular diameter distance to the source, and -
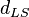 is the angular diameter distance between the lens and the source.
is the angular diameter distance between the lens and the source.
Note that, over cosmological distances 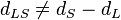 in general.
in general.
History
The bending of light by a gravitational body was predicted by Albert Einstein in 1912, a few years before the publication of General Relativity in 1916 (see Renn et al. 1997). The ring effect was first mentioned in academic literature by Orest Chwolson in 1924. Einstein remarked upon this effect in 1936 in a paper prompted by a letter by a Czech engineer, R W Mandl , but stated
Of course, there is no hope of observing this phenomenon directly. First, we shall scarcely ever approach closely enough to such a central line. Second, the angle β will defy the resolving power of our instruments.—Science vol 84 p 506 1936
In this statement, β is the Einstein Radius currently denoted by 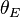 (see above). However, Einstein was only considering the chance of observing Einstein rings produced by stars, which is low; however, the chance of observing those produced by larger lenses such as galaxies or black holes is higher since the angular size of an Einstein ring increases with the mass of the lens.
(see above). However, Einstein was only considering the chance of observing Einstein rings produced by stars, which is low; however, the chance of observing those produced by larger lenses such as galaxies or black holes is higher since the angular size of an Einstein ring increases with the mass of the lens.
Known Einstein rings

Hundreds of gravitational lenses are currently known. About half a dozen of them are partial Einstein rings with diameters up to an arcsecond, although as either the mass distribution of the lenses is not perfectly axially symmetrical, or the source, lens, and observer are not perfectly aligned, we have yet to see a perfect Einstein ring. Most rings have been discovered in the radio range. The degree of completeness needed for an image seen through a gravitational lens to qualify as an Einstein ring is yet to be defined.
The first Einstein ring was discovered by Hewitt et al. (1988), who observed the radio source MG1131+0456 using the Very Large Array. This observation saw a quasar lensed by a nearer galaxy into two separate but very similar images of the same object, the images stretched round the lens into an almost complete ring.[5] These dual images are another possible effect of the source, lens, and observer not being perfectly aligned.
The first complete Einstein ring to be discovered was B1938+666, which was found by King et al. (1998) via optical follow-up with the Hubble Space Telescope of a gravitational lens imaged with MERLIN.[2][6] The galaxy causing the lens at B1938+666 is an ancient elliptical galaxy, and the image we see through the lens is a dark dwarf satellite galaxy, which we would otherwise not be able to see with current technology.[7]
.jpg)
In 2005, the combined power of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey(SDSS) with the Hubble Space Telescope was used in the Sloan lens Advanced camera for surveys (SLACS) to find 19 new gravitational lenses, 8 of which showed Einstein rings,[8] these are the 8 shown in the image to the right. As of 2009 this survey has found 85 confirmed gravitational lenses, there is not yet a number for how many show Einstein rings.[9] This survey is responsible for most of the recent discoveries of Einstein rings in the optical range, following are some examples which were found:
- FOR J0332-3557, discovered by Remi Cabanac et al. in 2005,[10] notable for its high redshift which allows us to use it to make observations about the early universe.
- The "Cosmic Horseshoe" is a partial Einstein ring which was observed through the gravitational lens of LRG 3-757, a distinctively large Luminous Red Galaxy. It was discovered in 2007 by N.W.Evans et al.[11]
- SDSSJ0946+1006, the "double Einstein ring" was discovered by Raphael Gavazzi and Tomasso Treu[12] in 2008, notable for the presence of multiple rings observed through the same gravitational lens, the significance of which is explained in the next section on extra rings.
Another example is the radio/X-Ray Einstein ring around PKS 1830-211, which is unusually strong in radio.[13] It was discovered in X-Ray by Varsha Gupta et al. at the Chandra X-Ray observatory[14] It is also notable for being the first case of a quasar being lensed by an almost face-on spiral galaxy.[15]
There is also a radio ring around galaxy MG1654+1346, the image in the ring is that of a quasar radio lobe, discovered in 1989 by G.Langston et al.[16]
Extra rings
Using the Hubble Space Telescope, a double ring has been found by Raphael Gavazzi of the STScI and Tommaso Treu of the University of California, Santa Barbara. This arises from the light from three galaxies at distances of 3, 6, and 11 billion light years. Such rings help in understanding the distribution of dark matter, dark energy, the nature of distant galaxies, and the curvature of the universe. The odds of finding such a double ring are 1 in 10,000. Sampling 50 suitable double rings would provide astronomers with a more accurate measurement of the dark matter content of the universe and the equation of state of the dark energy to within 10 percent precision.[17]
A simulation

To the right is a simulation depicting a zoom on a Schwarzschild black hole in front of the Milky Way. The first Einstein ring corresponds to the most distorted region of the picture and is clearly depicted by the galactic disc. The zoom then reveals a series of 4 extra rings, increasingly thinner and closer to the black hole shadow. They are easily seen through the multiple images of the galactic disk. The odd-numbered rings correspond to points which are behind the black hole (from the observer's position) and correspond here to the bright yellow region of the galactic disc (close to the galactic center), whereas the even-numbered rings correspond to images of objects which are behind the observer, which appear bluer since the corresponding part of the galactic disc is thinner and hence dimmer here.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Einstein Rings. |
References
- ↑ Overbye, Dennis (March 5, 2015). "Astronomers Observe Supernova and Find They’re Watching Reruns". New York Times. Retrieved March 5, 2015.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "A Bull's Eye for MERLIN and the Hubble". University of Manchester. 27 March 1998.
- ↑ "ALMA at Full Stretch Yields Spectacular Images". ESO Announcement. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ↑ Loff, Sarah; Dunbar, Brian (10 February 2015). "Hubble Sees A Smiling Lens". NASA. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ↑ "Discovery of the First "Einstein Ring" Gravitational Lens". NRAO. 2000. Retrieved 2012-02-08.
- ↑ Browne, Malcolm W. (1998-03-31). "'Einstein Ring' Caused by Space Warping Is Found". The New York Times. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ↑ Vegetti, Simona et al. (January 2012). "Gravitational detection of a low-mass dark satellite at cosmological distance". Nature 481 (7381): 341–343. arXiv:1201.3643. Bibcode:2012Natur.481..341V. doi:10.1038/nature10669. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ↑ Bolton, A et al. "Hubble, Sloan Quadruple Number of Known Optical Einstein Rings". Hubblesite. Retrieved 2014-07-16.
- ↑ Auger, Matt et al. (November 2009). "The Sloan Lens ACS Survey. IX. Colors, Lensing and Stellar Masses of Early-type Galaxies". The Astrophysical Journal 705 (2): 1099–1115. arXiv:0911.2471. Bibcode:2009ApJ...705.1099A. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/705/2/1099. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ↑ Cabanac, Remi et al. (2005-04-27). "Discovery of a high-redshift Einstein ring". Astronomy and Astrophysics 436 (2): L21–L25. arXiv:astro-ph/0504585. Bibcode:2005A&A...436L..21C. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200500115. Retrieved 2014-07-15.
- ↑ Evans, N.W. et al. (December 2007). "The Cosmic Horseshoe: Discovery of an Einstein Ring around a Giant Luminous Red Galaxy". The Astrophysical Journal 671 (1): L9–L12. arXiv:0706.2326. Bibcode:2007ApJ...671L...9B. doi:10.1086/524948. Retrieved 2014-07-15.
- ↑ Gavazzi, Raphael et al. (April 2008). "The Sloan Lens ACS Survey. VI: Discovery and Analysis of a Double Einstein Ring". The Astrophysical Journal 677 (2): 1046–1059. arXiv:0801.1555. Bibcode:2008ApJ...677.1046G. doi:10.1086/529541. Retrieved 2014-04-15.
- ↑ Mathur, Smita; Nair, Sunita (20 July 1997). "X-Ray Absorption toward the Einstein Ring Source PKS 1830-211". The Astrophysical Journal 484: 140–144. arXiv:astro-ph/9703015. Bibcode:1997ApJ...484..140M. doi:10.1086/304327. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ↑ Gupta, Varsha. "Chandra Detection of AN X-Ray Einstein Ring in PKS 1830-211". ResearchGate.net. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ↑ Courbin, Frederic (August 2002). "Cosmic alignment towards the radio Einstein ring PKS 1830-211 ?". The Astrophysical Journal 575 (1): 95–102. arXiv:astro-ph/0202026. Bibcode:2002ApJ...575...95C. doi:10.1086/341261. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ↑ Langston, G.I. et al. (May 1989). "MG 1654+1346 - an Einstein Ring image of a quasar radio lobe". Astronomical Journal 97: 1283–1290. Bibcode:1989AJ.....97.1283L. doi:10.1086/115071. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ↑ "Hubble Finds Double Einstein Ring". http://hubblesite.org''. Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 2008-01-26.
Journals
- Cabanac, R. A. et al. (2005). "Discovery of a high-redshift Einstein ring". Astronomy and Astrophysics 436 (2): L21–L25. arXiv:astro-ph/0504585. Bibcode:2005A&A...436L..21C. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200500115. (refers to FOR J0332-3357)
- Chwolson, O (1924). "Über eine mögliche Form fiktiver Doppelsterne". Astronomische Nachrichten 221 (20): 329. Bibcode:1924AN....221..329C. doi:10.1002/asna.19242212003. (The first paper to propose rings)
- Einstein, Albert (1936). "Lens-like Action of a Star by the Deviation of Light in the Gravitational Field" (PDF). Science 84 (2188): 506–507. Bibcode:1936Sci....84..506E. doi:10.1126/science.84.2188.506. PMID 17769014. (The famous Einstein Ring paper)
- Hewitt, J (1988). "Unusual radio source MG1131+0456 - A possible Einstein ring". Nature 333: 537. Bibcode:1988Natur.333..537H. doi:10.1038/333537a0.
- Renn, Jurgen; Sauer, Tilman; Stachel, John (1997). "The Origin of Gravitational Lensing: A Postscript to Einstein's 1936 Science paper". Science 275 (5297): 184–186. Bibcode:1997Sci...275..184R. doi:10.1126/science.275.5297.184. PMID 8985006.
- King, L (1998). "A complete infrared Einstein ring in the gravitational lens system B1938 + 666". MNRAS 295: 41. arXiv:astro-ph/9710171. Bibcode:1998MNRAS.295L..41K. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.295241.x.
News
- Barbour, Jeff (2005-04-29). "Nearly perfect Einstein ring discovered". Universe Today. Retrieved 2006-06-15. (refers to FOR J0332-3357)
- "Hubble Finds Double Einstein Ring". Science Daily. 2008-01-12. Retrieved 2008-01-14.
Further reading
- Kochanek, C. S.; Keeton, C. R.; McLeod, B. A. (2001). "The Importance of Einstein Rings". The Astrophysical Journal 547 (1): 50–59. arXiv:astro-ph/0006116. Bibcode:2001ApJ...547...50K. doi:10.1086/318350.