Eilat
| Eilat | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hebrew transcription(s) | ||
| • Hebrew |
| |
| Arabic transcription(s) | ||
| • Arabic | ايلات | |
|
Eilat, its harbor, and the surrounding mountains | ||
| ||
 Eilat | ||
| Coordinates: 29°33′N 34°57′E / 29.550°N 34.950°ECoordinates: 29°33′N 34°57′E / 29.550°N 34.950°E | ||
| District | Southern | |
| Founded | 1951 | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | City (from 1959) | |
| • Mayor | Meir Yitzhak Halevi | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 84,789 dunams (84.789 km2 or 32.737 sq mi) | |
| Population (2012)[1] | ||
| • Total | 47,719 | |
Eilat (Hebrew: ![]() אֵילַת ; Arabic: ايلات) is Israel's southernmost city, a busy port and popular resort located at the northern tip of the Red Sea, on the Gulf of Aqaba.
אֵילַת ; Arabic: ايلات) is Israel's southernmost city, a busy port and popular resort located at the northern tip of the Red Sea, on the Gulf of Aqaba.
Home to about 47,700 people,[1] Eilat is part of the Southern Negev Desert, at the southern end of the Arava, adjacent to the Egyptian village of Taba to the south, the Jordanian port city of Aqaba to the east, and within sight of Saudi Arabia to the south-east, across the gulf.
Eilat's arid desert climate and low humidity are moderated by proximity to a warm sea. Temperatures often exceed 40 °C (104 °F) in summer, and 21 °C (70 °F) in winter, while water temperatures range between 20 and 26 °C (68 and 79 °F). Eilat averages 360 sunny days a year.[2]
The city's beaches, coral reef, nightlife and desert landscapes make it a popular destination for domestic and international tourism.
Geography

The geology and landscape are varied: igneous and metamorphic rocks, sandstone and limestone; mountains up to 892 metres (2,927 ft) above sea level; broad valleys such as the Arava, and seashore on the Gulf of Aqaba. With an annual average rainfall of 28 millimetres (1.1 in) and summer temperatures of 40 °C (104 °F) and higher, water resources and vegetation are limited. "The main elements that influenced the region's history were the copper resources and other minerals, the ancient international roads that crossed the area, and its geopolitical and strategic position. These resulted in a settlement density that defies the environmental conditions."[3]
History
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1955 | 500 | — |
| 1961 | 5,300 | +960.0% |
| 1972 | 13,100 | +147.2% |
| 1983 | 18,900 | +44.3% |
| 1995 | 32,500 | +72.0% |
| 2008 | 47,300 | +45.5% |
| 2010 | 47,800 | +1.1% |
| 2011 | 46,700 | −2.3% |
| Source: | ||
Etymology
The origin of the name Eilat is not definitively known, but likely comes from the Hebrew root A–Y–L (Hebrew: א. י. ל.), which is also the root for the word Elah (Hebrew: אלה), meaning Pistacia tree. Like numerous other localities, Eilat is mentioned in the Bible both in singular (possibly construct state) and plural form (Eilot).[4]
Antiquity
The original settlement was probably at the northern tip of the Gulf of Eilat.[5] Archaeological excavations uncovered impressive prehistoric tombs dating to the 7th millennium BC at the western edge of Eilat, while nearby copper workings and mining operations at Timna Valley are the oldest on earth. Ancient Egyptian records also document the extensive and lucrative mining operations and trade across the Red Sea with Egypt starting as early as the Fourth dynasty of Egypt. Eilat is mentioned in antiquity as a major trading partner with Elim, Thebes' Red Sea Port, as early as the Twelfth dynasty of Egypt.[6] Trade between Elim and Eilat furnished frankincense and myrrh, brought up from Ethiopia and Punt; bitumen and natron, from the Dead Sea; finely woven linen, from Byblos; and copper amulets, from Timna; all mentioned in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea. In antiquity Eilat bordered the states of Edom, Midian and the tribal territory of the Rephidim, the indigenous inhabitants of the Sinai Peninsula.
Biblical period
Eilat is first mentioned in the Hebrew Bible in the Book of Exodus. The first six stations of the Exodus are in Egypt. The 7th is the crossing of the Red Sea and the 9th–13th are in and around Eilat, after the exodus from Egypt and crossing the Red Sea. Station 12 refers to a dozen campsites in and around Timna in Modern Israel near Eilat. When King David conquered Edom,[7] which up to then had been a common border of Edom and Midian, he took over Eilat, the border city shared by them as well. The commercial port city and copper based industrial center were maintained by Egypt until reportedly rebuilt by Solomon at a location known as Ezion-Geber (I Kings 9:26). In 2 Kings 14:21–22 "All the people of Judah took Uzziah, who was sixteen years old, and made him king in the room of his father Amaziah. He rebuilt Elath, and restored it to Judah, after his father's death." And again in 2 Kings 16:6: "At that time the king of Edom recovered Elath for Edom, and drove out the people of Judah and sent Edomites to live there, as they do to this day."

Roman and Muslim periods
During the Roman period a road was built to link the area with the Nabataean city of Petra (in modern-day Jordan). The remains of a large copper smelting and trading community which flourished during the Umayyad Period (700–900 CE) were also found between what is now Eilat's industrial zone and nearby Kibbutz Eilot.
In the writings of medieval Muslim scholars, such as Al-Waqidi, it is told that Muhammad made a treaty with Eilat's (Ayla) population, Jews and Christians. In the treaty, Muhammad offered protection to the Jews and the Christians, preserving their self-rule over the city, in exchange for an annual tax.[8] Another reference to the Eilat in Islamic texts is believed to appear in the Quran, sura 7:163–169. In these Ayats appears a story about "a town by the sea" where the Jewish residents were tested by God to check if they truly observe the Shabbat. Once they didn't, they were turned into apes.[9] The Darb el Hajj or "Pilgrim's Road", from Africa through Egypt to Mecca, passed out of Sinai from the west at Umm Al-Rashrash, the modern Arabic name for Eilat, before skirting the sea and continuing south into Arabia. A British police post was established in this area in 1906.[10]
An Islamic village of 250–400 residents flourished at the northern edge of modern Eilat during the 7th and 8th centuries. It was excavated in 1989 to make way for an industrial area.[11]
After the establishment of the State of Israel
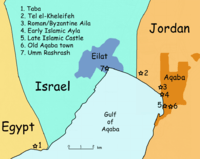
The area was designated as part of the Jewish state in the 1947 UN Partition Plan. The Arab village of Umm Al-Rashrash was taken without a fight on March 10, 1949, as part of Operation Uvda.
The Timna Copper Mines[12] near Timna valley were opened, a port was constructed, the Eilat Ashkelon Pipeline laid, and tourism began. Construction of the city and the Port of Eilat began shortly after the end of the war. The port became vital to the fledgling country's development. After the 1948 Arab–Israeli War Arab countries maintained a state of hostility with Israel, blocking all land routes; Israel's access to and trade with the rest of the world was by air and sea alone. Further, Egypt denied passage through the Suez Canal to Israeli-registered ships or to any ship carrying cargo to or from Israeli ports. This made Eilat and its sea port crucial to Israel's communications, commerce and trade with Africa and Asia, and for oil imports. Without recourse to a port on the Red Sea Israel would have been unable to develop its diplomatic, cultural and trade ties beyond the Mediterranean basin and Europe. This happened in 1956 and again in 1967, when Egypt's closure of the Straits of Tiran to Israeli shipping effectively blockaded the port of Eilat. In 1956, this led to Israel's participation alongside Britain and France in the war against Egypt sparked by the Suez Crisis, while in 1967 90% of Israeli oil passed through the Straits of Tiran.[13] Oil tankers that were due to pass through the straits were delayed.[14][15] The straits closure was cited by Israel as an additional casus belli leading to the outbreak of the Six-Day War. Following peace treaties signed with Egypt in 1979 and Jordan in 1994, Eilat's borders with its neighbors were finally opened.
Future development plans
In July 2012, Israel signed an agreement with China to cooperate in building the high-speed railway to Eilat, a railway line which will serve both passenger and freight trains. It will link Eilat with Beersheba and Tel Aviv, and will run through the Arava Valley and Nahal Zin.[16]
Currently, there are plans to vacate and dismantle Eilat Airport due to the plans for Timna Airport, and develop the area. Hotels and apartment buildings, containing a total of 2,080 hotel rooms and 1,000 apartments will be constructed on the site, as well as 275 dunams of public space and pedestrian paths. The plans also set aside space for the railway line and an underground railway station. The plan's goal is to create an urban continuum between the city center and North Beach, as well as tighten the links between the city's neighborhoods, which are currently separated by the airport.[17]
In addition, there are plans to move the Port of Eilat and the Eilat-Ashkelon pipeline terminal to the northern part of the city, as well as to turn it into a university town of science and research, and brand it an international sports city. All these projects are part of a plan to turn Eilat into a metropolitan area of 150,000 people and 35,000 hotel rooms.[18]
Climate
| Eilat | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Eilat has a hot desert climate (BWh[20] with hot, dry summers and warm and almost rainless winters in Köppen climate classification). Winters are usually between 11–23 °C (52–73 °F). Summers are usually between 26–40 °C (79–104 °F). There are relatively small coral reefs near Eilat; however, 50 years ago they were much larger: the corals have been dying as a result of water pollution.
| Climate data for Eilat | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 30.2 (86.4) |
31.6 (88.9) |
36.2 (97.2) |
40.6 (105.1) |
44.8 (112.6) |
45.6 (114.1) |
47.4 (117.3) |
47.4 (117.3) |
45 (113) |
41.5 (106.7) |
36.4 (97.5) |
31.4 (88.5) |
47.4 (117.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.8 (69.4) |
22.1 (71.8) |
25.5 (77.9) |
31.1 (88) |
35.4 (95.7) |
38.7 (101.7) |
40.9 (105.6) |
40.8 (105.4) |
37.3 (99.1) |
33 (91) |
27.2 (81) |
22.3 (72.1) |
31.3 (88.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 15 (59) |
17 (63) |
20 (68) |
24 (75) |
28 (82) |
31 (88) |
32 (90) |
32 (90) |
30 (86) |
27 (81) |
21 (70) |
16 (61) |
25 (77) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 9.6 (49.3) |
10.6 (51.1) |
13.6 (56.5) |
17.8 (64) |
21.5 (70.7) |
24.2 (75.6) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
24.5 (76.1) |
21 (70) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.2 (52.2) |
18.5 (65.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 2.2 (36) |
0.9 (33.6) |
6.4 (43.5) |
8.4 (47.1) |
14.6 (58.3) |
19.1 (66.4) |
20 (68) |
20.4 (68.7) |
19.2 (66.6) |
13.7 (56.7) |
7 (45) |
2.5 (36.5) |
0.9 (33.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 3.5 (0.138) |
5.8 (0.228) |
3.7 (0.146) |
1.7 (0.067) |
1 (0.04) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
3.5 (0.138) |
3.5 (0.138) |
6 (0.24) |
28.7 (1.13) |
| Avg. precipitation days | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 10.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 32 | 28 | 25 | 19 | 16 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 23 | 27 | 29 | 33 | 23.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 229.4 | 237.3 | 251.1 | 273 | 319.3 | 324 | 347.2 | 347.2 | 291 | 282.1 | 246 | 217 | 3,364.6 |
| Source #1: Israel Meteorological Service[21][22] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Climatemps.com for mean temperatures[23] | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 °C (72 °F) | 21 °C (70 °F) | 21 °C (70 °F) | 23 °C (73 °F) | 25 °C (77 °F) | 26 °C (79 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 27 °C (81 °F) | 25 °C (77 °F) | 23 °C (73 °F) |
Demographics
In 2007, over 200 Sudanese refugees from Egypt who arrived in Israel illegally on foot were given work and allowed to stay in Eilat.[24][25][26] Eilat's population includes a large number of foreign workers, estimated at over 10,000 working as caregivers, hotel workers and in the construction trades. Eilat also has a growing Israeli Arab population, as well as many affluent Jordanians and Egyptians who visit Eilat in the summer months.
Education
The educational system of Eilat accommodates more than 9,000 youngsters in eight day-care centers, 67 pre-kindergartens and kindergartens, 10 elementary schools, and four high schools.[27] Ben Gurion University of the Negev maintains a campus in Eilat. The Eilat branch has 1,100 students, about 75 percent from outside the city. In 2010, a new student dormitory was funded and built by the Jewish Federation of Toronto, the Rashi Foundation, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev and the municipality of Eilat.[28] The Eilat Field School on the outskirts of Eilat offers special hiking tours that focus on desert ecology, the Red Sea, bird migration and other aspects of Eilat's flora and fauna.[29]
Healthcare
Yoseftal Medical Center, established in 1968, is Israel’s southernmost hospital, and the only hospital covering the southern Negev. With 65 beds, the hospital is Israel's smallest. Special services geared to the Red Sea region are a hyperbaric chamber to treat victims of diving accidents and kidney dialysis facilities open to vacationing tourists.[30]
Transportation
Eilat is connected to the rest of Israel and internationally by air, road and sea.
- Eilat Airport is located in the city centre and is used largely for domestic flights[31] (IATA: ETH, ICAO: LLET).
- International flights often use Ovda International Airport some 50 kilometres (31 mi) northwest of the city[32] (IATA: VDA, ICAO: LLOV).
Eilat has two main roads connecting it with the center of Israel.
- Egged, the national bus company, provides regular service to points north on an almost hourly basis as well as in-city on a half-hourly basis during daylight hours.
- There are two main border crossings: the Taba Border Crossing to Taba, Egypt and Wadi Araba Crossing to Aqaba, Jordan, renamed the Yitzhak Rabin Border Crossing on the Israeli side. The Port of Eilat and Eilat Marina allow travel by sea. Near-term plans also call for a rail link (Med-Red)[33] to decrease travel times substantially from Eilat to Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, via the existing line at Beer Sheba; planning is underway.
Economy
In the 1970s tourism became increasingly important to the city's economy as other industries shut down or were drastically reduced. Today tourism is the city's major source of income, although Eilat became a free trade zone in 1985.[34]
Tourism



Eilat offers a wide range of accommodations, from hostels and luxury hotels to Bedouin hospitality. In recent years Eilat has been the target of millitants from Egypt and Gaza causing a reduced tourist inflow to the region. Attractions include:
- Birdwatching and ringing station: Eilat is located on the main migration route between Africa and Europe. International Birding & Research Center in Eilat.[35]
- Camel tours.
- Coral Beach Nature Reserve, an underwater marine reserve of tropical marine flora and fauna.
- Coral World Underwater Observatory – Located at the southern tip of Coral Beach, the observatory has aquaria, a museum, simulation rides, and shark, turtle and stingray tanks. The observatory is the biggest public aquarium in the middle east.[36]
- Dolphin Reef – A marine biology and research station where visitors can swim and interact with dolphins.[37]
- Freefall parachuting.
- Yotvata Hai-Bar Nature Reserve, established in the 1960s to conserve endangered species, including Biblical animals, from this and similar regions. The reserve has a Visitors Center, care and treatment enclosures, and large open area where desert animals are acclimated before re-introduction into the wild. Hai-Bar efforts have successfully re-introduced the Asian Wild Ass, or Onager, into the Negev.[38] The Hai-Bar Nature Reserve and animal re-introduction program were described in Bill Clark's book "High Hills and Wild Goats: Life Among the Animals of the Hai-Bar Wildlife Refuge". The book also describes life in Eilat and the surrounding area.[38]
- IMAX, Three-dimensional graphics films
- Kings City, a biblical theme park located in the hotel area next to the Stella Maris Lagoon.[39]
- Marina with some 250 yacht berths.
- Timna Valley Park – the oldest copper mines in the world. Egyptian temple of Hathor, King Solomon's Pillars sandstone formation, ancient pit mines and rock art.[40]
- "What's Up" the Observatory in Eilat, a portable Astronomical Observatory with programs in the desert and on the promenade.[41]
- Ice Park, Park of ice and snow.
Dive tourism
Skin and Scuba diving, with equipment for hire on or near all major beaches. Scuba diving equipment rental and compressed air are available from diving clubs and schools all year round. Eilat is located in the Gulf of Aqaba, one of the most popular diving destinations in the world. The coral reefs along Eilat's coast remain relatively pristine and the area is recognized as one of the prime diving locations in the world.[42] About 250,000 dives are performed annually in Eilat's 11 km (6.84 mi) coastline, and diving represents 10% of the tourism income of this area.[43] In addition, given the proximity of many of these reefs to the shore, non-divers can encounter the Red Sea's reefs with relative ease.[42] Water conditions for SCUBA divers are good all year round, with water temperatures around 21–25 °C (70–77 °F), with little or no currents and clear waters with an average of 20–30 metres (66–98 feet) visibility.
Museums
- Eilat City Museum
- Eilat Art Gallery
- Eilat Erotic Museum (Sex museum) first erotic museum in Israel and Middle East
Film
Eilat has been utilized as a location by many films and television production teams, most notably in the early 90s as a tropical locale for season 2 of the Canadian production Tropical Heat. It was also used in Rambo III.
Archaeology
Despite harsh conditions, the region has supported large populations as far back as 8,000 BCE. Exploration of ancient sites began in 1861, but only 7% of the area has undergone serious archaeological excavation. Some 1,500 ancient sites are located in a 1,200-square-kilometre (460 sq mi) area. In contrast to the gaps found in settlement periods in the neighbouring Negev Highlands and Sinai, these sites show continuous settlement for the past 10,000 years.
Notable persons
- Amit Ivry, Olympic swimmer and national record holder
- Shahar Tzuberi, Israeli Olympic bronze-medal-winning windsurfer, 2008 Olympic Games in Beijing
- Raviv Ullman, Israeli-American actor and musician
Israeli–Arab conflict
In 2007, a suicide bomber attacked a bakery, in the Eilat bakery bombing, which killed three civilian employees.[44][45] This was the first suicide bombing to take place in Eilat,[46] although other terror attacks have been carried out.[47]
In 2011, terrorists infiltrated Israel across the Sinai border, attacking an Israeli civilian bus and an Israeli civilian car on Highway 12, a few miles from Eilat. The attack became known as the 2011 southern Israel cross-border attacks.[48][49] In order to prevent terrorist infiltration of Israel from the Sinai, Israel built the Israel-Egypt barrier, which is a steel barrier backed by cameras, radar and motion detectors at the country's southern border.[50] The fence was completed in January 2013.[51]
Neighborhoods
Eilat neighborhoods are Arava, Ganim A, Ganim B, Hadekel, Ha'eshel, Mizpe Yam, Maar'av Sheva also known as West7, Midbar, Ophir, Shahamon, Tse'elim, Urim, Ye'elim, Zofit Elite, and Zofit Tachtit.
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Eilat is twinned with:
Eilat has streets named after Antibes, Durban, Kamen, Kampen and Los Angeles as well as a Canada Park.
See also
- Bnei Eilat F.C.
- Eilat International Film Festival
- Eilat Pride
- Eilat Sports Center
- Eilat stone
- Hapoel Eilat B.C.
- Operation Ovda
- Red Sea Jazz Festival
- Yotvata Airfield
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Locality File" (XLS). Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. 2012. Retrieved November 3, 2013.
- ↑ Discovering the World of the Bible, LaMar C. Berrett, (Cedar Fort 1996), page 204
- ↑ Avner, U. 2008. Eilat Region. In, A. Stern (ed.). The New Encyclopedia of Archaeological Excavation in the Holy Land, Volume 5 (Supplementary). Jerusalem. 1704–1711.
- ↑ Grinzweig, Michael (1993). Cohen, Meir; Schiller, Eli, eds. "From the Items of the Name Eilat". Ariel (in Hebrew) (Ariel Publishing) (93–94: Eilat – Human, Sea and Desert): 110.
- ↑ Dr. Muhammed Abdul Nayeem, (1990). Prehistory and Protohistory of the Arabian Peninsula. Hyderabad. ISBN.
- ↑ Michael Rice(1990). Egypt's Making. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-06454-6.
- ↑ "ישראל המקדשית". Gideon.022.co.il. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ↑ Moshe Gil. "A History of Palestine, 634–1099". Cambridge University Press, 1997, pp.29–31
- ↑ The Quran, sura 7:163–167. http://quran.com/7/163-169
- ↑ Gabriel Warburg (1979). "The Sinai Peninsula borders 1906–1947". Journal of Contemporary History 14: 677–692. doi:10.1177/002200947901400406.
- ↑ Yehudah Rapuano (2013). "An Early Islamic Settlement and a Possible Open-Air Mosque at Eilat". 'Atiqot 75: 129–165.
- ↑ "Timna Copper Mines homepage".
- ↑ Avi Shlaim; William Roger Louis (13 February 2012). The 1967 Arab-Israeli War: Origins and Consequences. Cambridge University Press. p. 224. ISBN 978-1-107-00236-4.
90% of Israeli oil was imported through the Straits of Tiran
- ↑ Avi Shlaim; William Roger Louis (13 February 2012). The 1967 Arab-Israeli War: Origins and Consequences. Cambridge University Press. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-107-00236-4.
- ↑ "Daily brief to the U.S president on 27 May 1967" (PDF). 27 May 1967.
"diverted as was a sister ship yesterday
- ↑ "Israel, China agree to build Eilat railway". Globes. 2012-07-03. Retrieved 2013-03-12.
- ↑ "Hotels, 1,000 apartments planned for Eilat Airport site". Globes. 2012-04-03. Retrieved 2013-03-12.
- ↑ "Despite Japan, IEC chairman urges nuclear power". Globes. 2011-03-15. Retrieved 2013-03-12.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "Eilat Climate and Weather Averages, Israel". Weather2Travel. Retrieved 2014-01-20.
- ↑ "Climate: Eilat - Climate graph, Temperature graph, Climate table". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 5 November 2013.
- ↑ "Averages and Records for Eilat (Precipitation, Temperature and Records [Excluding February, July and August] written in the page)". Israel Meteorological Service.
- ↑ "Records Data for Israel (Data used only for February, July and August)". Israel Meteorological Service.
- ↑ "Eilat Weather Averages". Climatemps.com. Retrieved 5 November 2013.
- ↑ Jonathan Saul, Elana Ringler for Reuters (2007). "Sudanese refugees in Israel face uncertainty". Boston Globe. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
- ↑ Joshua Mitnick (2006). "Sudan's "Genocide" Lands at Israel's Door". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
- ↑ Neta Sela (2007). "Israel must reject Darfur refugees, rabbi says". Ynet News – Jewish World. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
- ↑ Daniel Horowitz. "UJA Federation of Greater Toronto". Jewishtoronto.net. Retrieved January 28, 2011.
- ↑ "New Student Dormitories Dedicated in Eilat Campus". Web.archive.org. 2010-05-15. Retrieved 2013-08-08.
- ↑ "SPNI field schools". Aspni.org. Retrieved 2013-08-08.
- ↑ "Clalit Health Services". Clalit.org.il. Retrieved January 28, 2011.
- ↑ Israel Airports Authority (2007). "Eilat Airport". Israel Airports Authority. Retrieved November 16, 2007.
- ↑ Israel Airports Authority (2007). "Ovda Airport". Israel Airports Authority. Retrieved November 16, 2007.
- ↑ Moti Bassok, Cabinet examining plan for Med-Red railway Haaretz, January 30, 2012
- ↑ Maltz, Judy (January 12, 1989). "Eilat turns to industry to complement tourism trade". The Jerusalem Post. p. 9. Retrieved October 30, 2007.
- ↑ "birdsofeilat.com". birdsofeilat.com. Retrieved January 28, 2011.
- ↑ Coral World (2005). "The Underwater Observatory Marine Park, Eilat". Coral World. Retrieved November 16, 2007.
- ↑ The Dolphin Reef Eilat (2007). "The Freedom To Choose". The Dolphin Reef Eilat. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 The Red Sea Desert (2007). "Hai-Bar Yotvata Nature Reserve". The Red Sea Desert. Retrieved November 16, 2007.
- ↑ Kings City (2007). "Kings City, Eilat". Kings City. Retrieved November 16, 2007.
- ↑ BiblePlaces.com (2007). "Timna Valley". BiblePlaces.com. Retrieved November 16, 2007.
- ↑ ""What's Up" Observatory in Eilat". Whatsup.eilatnature.com. Retrieved January 28, 2011.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 "MFA, Gulf of Aqaba- Tourism, 30 Sep 1997". Mfa.gov.il. Retrieved January 28, 2011.
- ↑ Artificial Reefs and Dive Tourism in Eilat, Israel Dan Wilhelmsson, Marcus C. Öhman, Henrik Ståhl and Yechiam Shlesinger Ambio, Vol. 27, No. 8, Building Capacity for Coastal Management (Dec., 1998), pp. 764–766 Published by: Allen Press on behalf of Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
- ↑ Suicide Bomb Kills 3 in Bakery in Israel – The New York Times, Jan 29, 2007
- ↑ "Eilat driver warned police about terrorist minutes before attack". Haaretz. April 17, 2006.
- ↑ "Peretz orders IDF to prepare for operations in Gaza". The Jerusalem Post. January 29, 2007.
- ↑ "Past terror attacks in the Eilat area". Haaretz. January 29, 2007.
- ↑ Harel, Amos (September 2, 2011). "September songs". Haaretz.
- ↑ Wyre Davies (August 2, 2010). "'One killed' after rockets strike Jordan and Israel". BBC. Retrieved January 28, 2011.
- ↑ Joel Greenberg (2011-12-02). "On Israel’s uneasy border with Egypt, a fence rises". Washington Post. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
- ↑ Amos Harel (2011-11-13). "On Israel-Egypt border, best defense is a good fence". Haaretz. Retrieved 2012-01-07.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 52.2 52.3 52.4 52.5 "Sister Cities". Union of Local Authorities in Israel (ULAI). Retrieved August 23, 2012.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 53.2 53.3 "Eilat Sister Cities". Israel-Times.com. November 7, 2007. Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ "What we do: Humanitarian Aid". Israel MFA. Archived from the original on May 31, 2010. Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ "Facts about Durban". September 7, 2003. Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ "Municipal Smolyan". Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ "Weiterführende Informationen: Städtepartnerschaften". Israel MFA. Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ "Eilat, Israel – Sister Cities of Los Angeles". Retrieved October 16, 2011.
- ↑ "The anniversary of our sister city, Eilat". Retrieved October 16, 2011.
- ↑ "Sopron, Hungary, One Of Eilats Twin Cities". Eilat Today. Retrieved August 23, 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eilat. |
- Eilat + official tourism website of the city of Eilat
- Official city site (Hebrew)
- Crossing the Israel – Jordan Border
- Eilat Tourist directory
- A film about Eilat in 1960 commentary (Hebrew)
- Photos of Eilat
- Tourism city guide site
- Eilat Today, a magazine of current affairs
- Birding in Eilat
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||



