Eiffel Tower
| Eiffel Tower | |
|---|---|
| La tour Eiffel | |
 The Eiffel Tower as seen from the Champ de Mars | |
 Location within Paris | |
| Record height | |
| Tallest in the world from 1889 to 1930[I] | |
| General information | |
| Type |
Observation tower, radio broadcasting tower |
| Location | 7th arrondissement, Paris, France |
| Coordinates | 48°51′29.6″N 2°17′40.2″E / 48.858222°N 2.294500°ECoordinates: 48°51′29.6″N 2°17′40.2″E / 48.858222°N 2.294500°E |
| Construction started | 28 January 1887 |
| Completed | 15 March 1889 |
| Opening | 31 March 1889 |
| Owner | City of Paris, France |
| Management | Société d'Exploitation de la Tour Eiffel (SETE) |
| Height | |
| Roof | 300.65 m (986 ft) |
| Top floor | 273.00 m (896 ft) |
| Technical details | |
| Floor count | 3 |
| Lifts/elevators | 9 |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect | Stephen Sauvestre |
| Structural engineer |
Maurice Koechlin, Émile Nouguier |
| Main contractor | Compagnie des Etablissements Eiffel |
The Eiffel Tower (French: La tour Eiffel, [tuʁ ɛfɛl]) is an iron lattice tower located on the Champ de Mars in Paris, France. It was named after the engineer Alexandre Gustave Eiffel, whose company designed and built the tower. Erected in 1889 as the entrance arch to the 1889 World's Fair, it was initially criticised by some of France's leading artists and intellectuals for its design, but has become both a global cultural icon of France and one of the most recognizable structures in the world.[1] The tower is the tallest structure in Paris and the most-visited paid monument in the world; 6.98 million people ascended it in 2011.[2] The tower received its 250 millionth visitor in 2010.[2]
The tower is 324 metres (1,063 ft) tall,[2] about the same height as an 81-storey building. Its base is square, 125 metres (410 ft) on a side. During its construction, the Eiffel Tower surpassed the Washington Monument to assume the title of the tallest man-made structure in the world, a title it held for 41 years, until the Chrysler Building in New York City was built in 1930. Because of the addition of the aerial atop the Eiffel Tower in 1957, it is now taller than the Chrysler Building by 5.2 metres (17 ft). Not including broadcast aerials, it is the second-tallest structure in France, after the Millau Viaduct.
The tower has three levels for visitors, with restaurants on the first and second. The third level observatory's upper platform is 276 m (906 ft) above the ground,[2] the highest accessible to the public in the European Union. Tickets can be purchased to ascend by stairs or lift (elevator) to the first and second levels. The climb from ground level to the first level is over 300 steps, as is the walk from the first to the second level. Although there are stairs to the third and highest level, these are usually closed to the public and it is generally only accessible by lift.
History
Origin
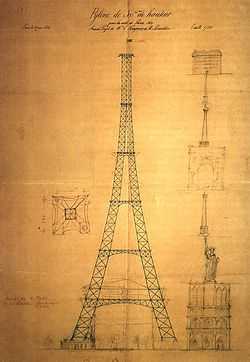
The design of the Eiffel Tower was originated by Maurice Koechlin and Émile Nouguier, two senior engineers who worked for the Compagnie des Établissements Eiffel, after discussion about a suitable centrepiece for the proposed 1889 Exposition Universelle, a World's Fair which would celebrate the centennial of the French Revolution. In May 1884 Koechlin, working at home, made an outline drawing of their scheme, described by him as "a great pylon, consisting of four lattice girders standing apart at the base and coming together at the top, joined together by metal trusses at regular intervals".[3] Initially Eiffel himself showed little enthusiasm, but he did sanction further study of the project, and the two engineers then asked Stephen Sauvestre, the head of company's architectural department, to contribute to the design. Sauvestre added decorative arches to the base, a glass pavilion to the first level, and other embellishments. This enhanced version gained Eiffel's support: he bought the rights to the patent on the design which Koechlin, Nougier, and Sauvestre had taken out, and the design was exhibited at the Exhibition of Decorative Arts in the autumn of 1884 under the company name. On 30 March 1885 Eiffel presented a paper on the project to the Société des Ingénieurs Civils; after discussing the technical problems and emphasising the practical uses of the tower, he finished his talk by saying that the tower would symbolise[4]
"not only the art of the modern engineer, but also the century of Industry and Science in which we are living, and for which the way was prepared by the great scientific movement of the eighteenth century and by the Revolution of 1789, to which this monument will be built as an expression of France's gratitude."
Little happened until the beginning of 1886, when Jules Grévy was re-elected as President and Édouard Lockroy was appointed as Minister for Trade. A budget for the Exposition was passed and on 1 May Lockroy announced an alteration to the terms of the open competition which was being held for a centerpiece for the exposition, which effectively made the choice of Eiffel's design a foregone conclusion: all entries had to include a study for a 300 m (980 ft) four-sided metal tower on the Champ de Mars.[4] On 12 May a commission was set up to examine Eiffel's scheme and its rivals and on 12 June it presented its decision, which was that all the proposals except Eiffel's were either impractical or insufficiently worked out. After some debate about the exact site for the tower, a contract was finally signed on 8 January 1887. This was signed by Eiffel acting in his own capacity rather than as the representative of his company, and granted him 1.5 million francs toward the construction costs: less than a quarter of the estimated 6.5 million francs. Eiffel was to receive all income from the commercial exploitation of the tower during the exhibition and for the following twenty years. Eiffel later established a separate company to manage the tower, putting up half the necessary capital himself.[5]
The "Artists Protest"

The projected tower had been a subject of some controversy, attracting criticism from both those who did not believe that it was feasible and those who objected on artistic grounds, whose objections were an expression of a longstanding debate about the relationship between architecture and engineering. This came to a head as work began at the Champ de Mars: A "Committee of Three Hundred" (one member for each metre of the tower's height) was formed, led by the prominent architect Charles Garnier and including some of the most important figures of the French arts establishment, including Adolphe Bouguereau, Guy de Maupassant, Charles Gounod and Jules Massenet: a petition was sent to Charles Alphand, the Minister of Works and Commissioner for the Exposition, and was published by Le Temps on 14 February 1887.[6]
We, writers, painters, sculptors, architects and passionate devotees of the hitherto untouched beauty of Paris, protest with all our strength, with all our indignation in the name of slighted French taste, against the erection ... of this useless and monstrous Eiffel Tower ... To bring our arguments home, imagine for a moment a giddy, ridiculous tower dominating Paris like a gigantic black smokestack, crushing under its barbaric bulk Notre Dame, the Tour Saint-Jacques, the Louvre, the Dome of les Invalides, the Arc de Triomphe, all of our humiliated monuments will disappear in this ghastly dream. And for twenty years ... we shall see stretching like a blot of ink the hateful shadow of the hateful column of bolted sheet metal.
Gustave Eiffel responded to these criticisms by comparing his tower to the Egyptian Pyramids: "My tower will be the tallest edifice ever erected by man. Will it not also be grandiose in its way? And why would something admirable in Egypt become hideous and ridiculous in Paris?"[7] These criticisms were also masterfully dealt with by Édouard Lockroy in a letter of support written to Alphand, ironically[8] saying "Judging by the stately swell of the rhythms, the beauty of the metaphors, the elegance of its delicate and precise style, one can tell that...this protest is the result of collaboration of the most famous writers and poets of our time", and going on to point out that the protest was irrelevant since the project had been decided upon months before and was already under construction. Indeed, Garnier had been a member of the Tower Commission that had assessed the various proposals, and had raised no objection. Eiffel was similarly unworried, pointing out to a journalist that it was premature to judge the effect of the tower solely on the basis of the drawings, that the Champ de Mars was distant enough from the monuments mentioned in the protest for there to be little risk of the tower overwhelming them, and putting the aesthetic argument for the Tower: "Do not the laws of natural forces always conform to the secret laws of harmony?"[9]
Some of the protestors were to change their minds when the tower was built: others remained unconvinced.[10] Guy de Maupassant supposedly ate lunch in the tower's restaurant every day because it was the one place in Paris where the tower was not visible.[11]
Before 1918 it had become a symbol for Paris and for France, when Guillaume Apollinaire made a nationalist poem in the shape of the tower (a calligram) to express his feelings about the war against Germany.[12] It is widely considered now to be a striking piece of structural art, and is often featured in films and literature.
Construction

Work on the foundations started on 28 January 1887.[13] Those for the east and south legs were straightforward, each leg resting on four 2 m (6.6 ft) concrete slabs, one for each of the principal girders of each leg but the other two, being closer to the river Seine, were more complicated: each slab needed two piles installed by using compressed-air caissons 15 m (49 ft) long and 6 m (20 ft) in diameter driven to a depth of 22 m (72 ft)[14] to support the concrete slabs, which were 6 m (20 ft) thick. Each of these slabs supported a block built of limestone each with an inclined top to bear a supporting shoe for the ironwork.
Each shoe was anchored into the stonework by a pair of bolts 10 cm (4 in) in diameter and 7.5 m (25 ft) long. The foundations were complete by 30 June and the erection of the ironwork began. The very visible work on-site was complemented by the enormous amount of exacting preparatory work that was entailed: the drawing office produced 1,700 general drawings and 3,629 detailed drawings of the 18,038 different parts needed.[15] The task of drawing the components was complicated by the complex angles involved in the design and the degree of precision required: the position of rivet holes was specified to within 0.1 mm (0.004 in) and angles worked out to one second of arc. The finished components, some already riveted together into sub-assemblies, arrived on horse-drawn carts from the factory in the nearby Parisian suburb of Levallois-Perret and were first bolted together, the bolts being replaced by rivets as construction progressed. No drilling or shaping was done on site: if any part did not fit it was sent back to the factory for alteration. In all there were 18,038 pieces joined by two and a half million rivets.[13]
At first the legs were constructed as cantilevers but about halfway to the first level construction was paused in order to construct a substantial timber scaffold. This caused a renewal of the concerns about the structural soundness of the project, and sensational headlines such as "Eiffel Suicide!" and "Gustave Eiffel has gone mad: he has been confined in an Asylum" appeared in the popular press.[16] At this stage a small "creeper" crane was installed in each leg, designed to move up the tower as construction progressed and making use of the guides for the lifts which were to be fitted in each leg. The critical stage of joining the four legs at the first level was complete by the end of March 1888.[13] Although the metalwork had been prepared with the utmost precision, provision had been made to carry out small adjustments in order to precisely align the legs: hydraulic jacks were fitted to the shoes at the base of each leg, each capable of exerting a force of 800 tonnes, and in addition the legs had been intentionally constructed at a slightly steeper angle than necessary, being supported by sandboxes on the scaffold. Although construction involved 300[13] on-site employees, only one person died thanks to Eiffel's stringent safety precautions and use of movable stagings, guard-rails, and screens.
-
7 December 1887: Construction of the legs with scaffolding.
-
20 March 1888: Completion of 1st level.
-
15 May 1888: Start of construction of second stage.
-
21 August 1888: Completion to 2nd level
-
26 December 1888: Construction of upper stage
-
15 March 1889: Construction of cupola
Lifts
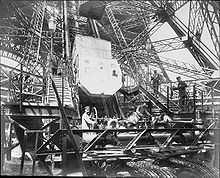
Equipping the Tower with adequate and safe passenger lifts was a major concern of the government commission overseeing the Exposition. Although some visitors could be expected to climb to the first or even the second stage, the main means of ascent clearly had to be lifts.[17]
Constructing lifts to reach the first platform was relatively straightforward: the legs of the lower section were wide enough and so nearly straight that they could contain a straight track, and a contract was given to the French company Roux, Combaluzier and Lepape for two lifts to be fitted in the east and west legs.[18] Roux, Combaluzier and Lepape used a pair of endless chains with rigid, articulated links to which the car was attached. Lead weights on some links of the chains’ upper or return sections counterbalanced most of the car’s weight. The car was pushed up by the links below, not drawn by those above: to prevent the chain buckling it was enclosed in a conduit. At the bottom of the run the chains passed around 3.9 m (12 ft 10 in) diameter sprockets. Smaller sprockets at the top guided the chains.[18]

The lifts to the second platform presented a more complex problem, because a straight track was not possible. No French company was willing to undertake the work. The European branch of Otis Brothers & Company submitted a proposal but this was rejected: the fair’s charter ruled out the use of any foreign material in the construction of the Tower. The deadline for bids was extended, but still no French companies put themselves forward, and eventually the contract was given to Otis in July 1887.[19] Otis had been confident that they would eventually be given the contract and had already started design studies. The car was divided into two superimposed compartments, each holding 25 passengers, with the lift operator occupying an exterior platform on the lower level. Motive power was provided by an inclined hydraulic ram, 12.67 m (36 ft) long 96.5 cm (38 in) diameter 10.83 m 35 ft 6 in stroke in the tower leg: this moved a carriage carrying six sheaves. Five fixed sheaves were mounted higher up the leg, producing an arrangement similar to a block and tackle but acting in reverse, multiplying the stroke of the piston rather than the force generated. The hydraulic pressure in the driving cylinder was produced by a large open reservoir on the second platform. After being exhausted from the cylinder, the water was pumped back up to the reservoir by two pumps in the machinery room at the base of the south leg. This reservoir also provided power to the lifts to the first level.
The original lifts from the second to the third floor were supplied by Léon Edoux. A pair of 81 m (266 ft) hydraulic rams were mounted on the second level, reaching nearly halfway up to the third level. One lift car was mounted on top of these rams: cables ran from the top of this car up to sheaves on the third level and then back down to a second car. Each car only travelled half the distance between the second and third levels and passengers were required to change lifts halfway by means of a short gangway. The ten-ton cars held 65 passengers each.[20]
Inauguration and the 1889 Exposition

The main structural work was completed at the end of March 1889 and on the 31st Eiffel celebrated this by leading a group of government officials, accompanied by representatives of the press, to the top of the tower.[10] Since the lifts were not yet in operation, the ascent was made by foot, and took over an hour, Eiffel frequently stopping to make explanations of various features. Most of the party chose to stop at the lower levels, but a few, including Nouguier, Compagnon, the President of the City Council and reporters from Le Figaro and Le Monde Illustré completed the climb. At 2:35 Eiffel hoisted a large French flag, to the accompaniment of a 25-gun salute fired from the lower level.[21] There was still work to be done, particularly on the lifts and the fitting out of the facilities for visitors, and the tower was not opened to the public until nine days after the opening of the Exposition on 6 May: even then the lifts had not been completed. The tower was an immediate success with the public, and nearly 30,000 visitors made the 1,710-step climb to the top using the stairs before the lifts entered service on 26 May.[22] Tickets cost 2 francs for the first level, 3 for the second, and 5 for the top, with half-price admission on Sundays,[23] and by the end of the exhibition there had been 1,896,987 visitors.[2]
After dark the tower was lit by hundreds of gas lamps and a beacon sending out three beams of red, white and blue light. Two searchlights were mounted on a circular rail, and were used to illuminate various features of the Exposition. The opening and closing of the Exposition were announced every day by a cannon fired from the top.

On the second level, the French newspaper Le Figaro had an office and a printing press, where a special souvenir edition, Le Figaro de la Tour, was produced. There was also a pâtisserie.
On the third level there was a post office, where visitors could send letters or postcards as a memento of their visit. Graffitists were also catered for: sheets of paper were mounted on the walls for visitors to record their impressions: these were replaced daily. Gustave Eiffel describes some of the responses as "vraiment curieuse".[24]
Famous visitors to the tower included The Prince of Wales, Sarah Bernhardt, "Buffalo Bill" Cody (his Wild West show was an attraction at the Exposition) and Thomas Edison.[22] Edison was invited by Eiffel to his private apartment at the top of the tower, where Edison presented him with one of his phonographs: this invention was one of the sensations of the Exposition.[25] Edison signed the guestbook with the following message—
To M Eiffel the Engineer the brave builder of so gigantic and original specimen of modern Engineering from one who has the greatest respect and admiration for all Engineers including the Great Engineer the Bon Dieu, Thomas Edison.
Eiffel had a permit for the tower to stand for 20 years; it was to be dismantled in 1909, when its ownership would revert to the City of Paris. The City had planned to tear it down (part of the original contest rules for designing a tower was that it should be easy to demolish) but as the tower proved valuable for communication purposes it was allowed to remain after the expiry of the permit. Eiffel made use of his apartment at the top level of the tower to carry out meteorological observations, and also made use of the tower to perform experiments on the action of air resistance on falling bodies.
Subsequent events
.ogv.jpg)

- 1900
- For the 1900 Exposition Universelle the lifts in the east and west legs were replaced by lifts running as far as the second level constructed by the French firm Fives-Lille. These had a compensating mechanism to keep the floor level as the angle of ascent changed at the first level, and were driven by a similar hydraulic mechanism to the Otis lifts, although this was situated at the base of the tower. Hydraulic pressure was provided by pressurised accumulators located near this mechanism.[19] At the same time the lift in the north pillar was removed, and replaced by a staircase to the first level. The layout of both first and second levels was modified, with the space available for visitors on the second level.
- 19 October 1901
- Alberto Santos-Dumont flying his No.6 airship won a 100,000-franc prize offered by Henri Deutsch de la Meurthe for the first person to make a flight from St. Cloud to the Eiffel tower and back in less than half an hour.[26]
- 1910
- Father Theodor Wulf measured radiant energy at the top and bottom of the tower. He found more at the top than expected, incidentally discovering what are today known as cosmic rays.[27]
- 4 February 1912
- Austrian tailor Franz Reichelt died after jumping from the first level of the tower (a height of 57 metres) to demonstrate his parachute design.[28]
- 1913
- The original lift in the south pillar was removed.
- 1914
- In the opening weeks of World War I a radio transmitter located in the tower jammed German radio communications. This seriously hindered their advance on Paris, and contributed to the Allied victory at the First Battle of the Marne.[29]
- 1925
- The con artist Victor Lustig "sold" the tower for scrap metal on two separate, but related occasions.[30]
- February 1926
- Pilot Leon Collet was killed after flying beneath the arch of the tower. His aircraft was entangled in an aerial belonging to the wireless station.[31]
- 1930
- The tower lost the title of the world's tallest structure when the Chrysler Building was completed in New York City.
- 1925 to 1934
- Illuminated signs for Citroën adorned three of the tower's four sides, making it the tallest advertising space in the world at the time.

- 2 May 1929
- A bust of Gustave Eiffel by Antoine Bourdelle, situated at the base of the north leg, is unveiled.[32]
- 1935
- In April the tower was used to make experimental low-resolution television transmissions, using a short wave transmitter of only 200 watts power. On 17 November an improved 180-line transmitter was installed.[33]
- 1938
- The decorative arcade around the first level was removed.[34]
- 1940 to 1944
- Upon the German occupation of Paris in 1940 the lift cables were cut by the French. The Tower was closed to the public during the Occupation and the lifts were not repaired until 1946.[35] In 1940 German soldiers had to climb to the top to hoist the swastika, but the flag was so large it blew away just a few hours later, and was replaced by a smaller one. When visiting Paris, Hitler chose to stay on the ground. In August 1944, when the Allies were nearing Paris, Hitler ordered General Dietrich von Choltitz, the military governor of Paris, to demolish the tower along with the rest of the city. Von Choltitz disobeyed the order.[36] On 25 June, before the Germans had been driven out of Paris, the Nazi flag was replaced with a French Tricolore by two men from the French Naval Museum, who narrowly beat three men led by Lucien Sarniguet, who had lowered the Tricolore on 13 June 1940 when Paris fell to the Germans.[35]
- 3 January 1956
- A fire which started in the television transmitter damaged the top of the tower: repairs took a year.[37]
- 1957
- The present radio aerial was added to the top.
- 1965
- Due to increasing visitor numbers an additional lift system was installed in the north pillar.
- 1964
- The Tower was officially declared to be an historical monument by Minister of Cultural Affairs André Malraux.[38]
- 1967
- According to interviews, Montreal Mayor Jean Drapeau negotiated a secret agreement with Charles de Gaulle for the tower to be dismantled and temporarily relocated to Montreal to serve as a landmark and tourist attraction during Expo 67. The plan was allegedly vetoed by the company which operated the tower out of fear that the French government could refuse permission for the tower to be restored to its original location.[39]
- 1982
- The original lifts between the second and third levels were replaced after 97 years' service. These had been closed to the public between November and March because the water in the hydraulic drive tended to freeze. The new cars operate in pairs, with one counterbalancing the other, and perform the journey in one stage, reducing the time taken from eight minutes to less than two minutes. At the same time two new emergency staircases were installed, replacing the original spiral staircases.
- 1983
- The south pillar was fitted with an electrically driven lift in 1983 to serve the Jules Verne restaurant. This was supplied by Otis.
- 31 March 1984
- Robert Moriarty flew a Beechcraft Bonanza through the arches of the tower.[40]
- 1986
- The Fives-Lille lifts in the east and west legs in 1899 were extensively refurbished: the cars were replaced, a computer-controlled system which completely automated the operation was installed. The motive power was moved from the water hydraulic system to a new electrically driven oil-filled hydraulic system. The original water hydraulics were retained but only as a counterbalance system.[41]
- 1987
- A.J. Hackett made one of his first bungee jumps from the top of the Eiffel Tower, using a special cord he had helped develop. Hackett was arrested by the Paris police upon reaching the ground.[42]
- 1989
- A service lift was added to the south pillar for moving small loads or maintenance personnel.
- 27 October 1991
- Thierry Devaux, along with mountain guide Hervé Calvayrac, performed a series of acrobatic figures of bungee jumping (not allowed) from the second floor of the Tower. Facing the Champ de Mars, Thierry Devaux was using an electric winch between each figure to go back up. When firemen arrived, he stopped after the sixth jump.[43]
- 31 December 1999
- For the tower's "Countdown to the Year 2000" celebration, flashing lights and high-power searchlights were installed on the tower. Fireworks were set off all over it. An exhibition above a cafeteria on the first floor now commemorates this event. The searchlights on top of the tower made it a beacon in Paris's night sky, and the 20,000 flashing bulbs gave the tower a sparkly appearance for five minutes every hour on the hour.[44] On 31 December 2000 the lights glittered blue for several nights to welcome the new millennium. The glittery lighting continued for 18 months until July 2001.[45]
- 28 November 2002
- The tower received its 200,000,000th guest.[46][47]
- 21 June 2003
- The glittering lights are turned on again and the display is planned to continue for ten years.[45]
- 2004
- The Eiffel Tower began hosting an ice skating rink on the first floor each winter.[48]
- 2014
- During refurbishment of the tower a glass floor was installed on the first floor.[49]
Design
Material

The puddled iron (wrought iron) structure of the Eiffel Tower weighs 7,300 tonnes, while the entire structure, including non-metal components, is approximately 10,000 tonnes. As a demonstration of the economy of design, if the 7,300 tonnes of the metal structure were melted down it would fill the 125-metre-square base to a depth of only 6.25 cm (2.5 in), assuming the density of the metal to be 7.8 tonnes per cubic metre.[50] Additionally, a cubic box surrounding the tower (324m x 125m x 125m) would contain 6,200 tonnes of air, almost as much as the iron itself. Depending on the ambient temperature, the top of the tower may shift away from the sun by up to 18 cm (7.1 in) because of thermal expansion of the metal on the side facing the sun.[51]
Wind considerations

At the time the tower was built many people were shocked by its daring shape. Eiffel was accused of trying to create something artistic without regard to engineering. However, Eiffel and his engineers, as experienced bridge builders, understood the importance of wind forces and knew that if they were going to build the tallest structure in the world they had to be certain it would withstand them. In an interview with the newspaper Le Temps (Paris) of 14 February 1887, Eiffel said:[52]
Now to what phenomenon did I give primary concern in designing the Tower? It was wind resistance. Well then! I hold that the curvature of the monument's four outer edges, which is as mathematical calculation dictated it should be ... will give a great impression of strength and beauty, for it will reveal to the eyes of the observer the boldness of the design as a whole.
Eiffel used empirical and graphical methods accounting for the effects of wind rather than a specific mathematical formula. Careful examination of the tower shows a basically exponential shape (actually two different exponentials, the lower section overdesigned to ensure resistance to wind forces. Several mathematical explanations have been proposed over the years for the success of the design; the most recent is described as a nonlinear integral equation based on counterbalancing the wind pressure on any point on the tower with the tension between the construction elements at that point.[53] As proof of the tower's effectiveness in wind resistance, it sways only 6–7 cm (2–3 in) in the wind.
Accommodations
When built, the first level contained three restaurants (one French, one Russian and one Flemish) and an "Anglo-American Bar". After the exposition closed the Flemish restaurant was converted to a 250-seat theatre. A 2.6 m (8 ft 6 in) promenade ran around the outside. On the third level there were laboratories for various experiments and a small apartment reserved for Gustave Eiffel to entertain guests. This is now visible to the public, complete with period decorations and lifelike models of Gustave and some guests.
Passenger lifts
The arrangement of the lifts has been changed several times during the course of the Tower's history.
Owing to the elasticity of the cables and the time taken to get the cars level with the landings, each lift in normal service takes an average of 8 minutes and 50 seconds to do the round trip, spending an average of 1 minute and 15 seconds at each floor. The average journey time between floors is just 1 minute. The 1899 east and west hydraulic mechanism works are on display to the public in a small museum in the base of the east and west towers, which is somewhat hidden from public view. Because the massive mechanism requires frequent lubrication and attention, public access is often restricted. The rope mechanism of the north tower is visible to visitors as they exit from the lift.
Engraved names

Gustave Eiffel engraved on the tower seventy-two names of French scientists, engineers, and mathematicians in recognition of their contributions. Eiffel chose this "invocation of science" because of his concern over the artists' protests against the tower. This engraving was painted over at the beginning of the twentieth century but restored in 1986–1987 by the Société Nouvelle d'exploitation de la Tour Eiffel, a company contracted to operate business related to the Tower.
Aesthetics
In order to give the appearance of uniform colour the paint used is graduated in tone to counteract the effect of atmospheric perspective, and is lighter at the bottom, getting darker toward the top. Periodically the colour of the paint is changed; as of 2013 it is bronze coloured.[54] On the first floor there are interactive consoles hosting a poll for the colour to use for the next repaint.
The only non-structural elements are the four decorative grillwork arches, added in Sauvestre's sketches, which served to make the structure look more substantial, and to make a more impressive entrance to the Exposition.[55]
One of the great Hollywood movie clichés is that the view from a Parisian window always includes the tower. In reality, since zoning restrictions limit the height of most buildings in Paris to seven storeys high, only a small number of taller buildings have a clear view of the tower.
Maintenance
Maintenance of the tower includes applying 50 to 60 tonnes (49 to 59 long tons; 55 to 66 short tons) of paint every seven years to protect it from rust. The height of the Eiffel Tower varies by 15 cm (5.9 in) due to temperature.

Tourism
Transport
The nearest Paris Métro station is Bir-Hakeim and the nearest RER station is Champ de Mars-Tour Eiffel.[56] The tower itself is located at the intersection of the quai Branly and the Pont d'Iéna.
Popularity
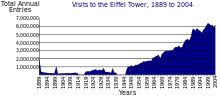
More than 250 million people have visited the tower since its construction in 1889: in 2012 there were 6,180,000 visitors.[2] The tower is the most-visited paid monument in the world.[57] An average of 25,000 people ascend the tower every day which can cause long queues.[58] Tickets can be purchased online to avoid long queues.[59]
Restaurants
The tower has two restaurants: Le 58 tour Eiffel, on the first floors and the Le Jules Verne, a gourmet restaurant on the second floor, with a private lift. This restaurant has one star in the Michelin Red Guide. It is run by the multi-Michelin star chef Alain Ducasse[60] and owes its name to the famous science-fiction writer Jules Verne.
Replicas



As one of the most iconic structures in the world, the Eiffel Tower has been the inspiration for the creation of at least 12 replicas of a quarter scale or larger as itemized here and there are more than 40 duplicates and similar towers of various scales around the world. An early example is the Blackpool Tower in England. Mayor Sir John Bickerstaffe was so impressed on seeing the Eiffel Tower at the 1889 Exhibition that he invested in a similar tower for his own city.[61] Two full size replicas exist: Tokyo Tower in Japan and the Long Ta communications tower in northern China.
Communications
The tower has been used for radio transmission since the beginning of the 20th century. Until the 1950s, sets of aerial wires ran from the summit to anchors on the Avenue de Suffren and Champ de Mars. These were connected to long-wave transmitters in small bunkers; in 1909 a permanent underground radio centre was built near the south pillar, which still exists today. On 20 November 1913 the Paris Observatory, using the Eiffel Tower as an aerial, exchanged sustained wireless signals with the United States Naval Observatory which used an aerial in Arlington, Virginia. The object of the transmissions was to measure the difference in longitude between Paris and Washington, D.C.[62] Today, both radio and television stations broadcast their signals from the top of the Eiffel Tower.
FM-radio
| Frequency | kW | Service |
|---|---|---|
| 87.8 MHz | 10 | France Inter |
| 89.0 MHz | 10 | RFI Paris |
| 89.9 MHz | 6 | TSF Jazz |
| 90.4 MHz | 10 | Nostalgie |
| 90.9 MHz | 4 | Chante France |
Television
Analogue
Analogue television signals ceased from the Eiffel Tower on 8 March 2011.
| Frequency | VHF | UHF | kW | Service |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 182.25 MHz | 6 | — | 100 | Canal+ |
| 479.25 MHz | — | 22 | 500 | France 2 |
| 503.25 MHz | — | 25 | 500 | TF1 |
| 527.25 MHz | — | 28 | 500 | France 3 |
| 543.25 MHz | — | 30 | 100 | France 5 |
| 567.25 MHz | — | 33 | 100 | M6 |
Image copyright claims

The tower and its representations have long been in the public domain. However, in June 1990 a French court ruled that a special lighting display on the tower in 1989 (the tower's 100th anniversary) was an "original visual creation" protected by copyright. The Court of Cassation, France's judicial court of last resort, upheld the ruling in March 1992.[63] The Société d'Exploitation de la Tour Eiffel (SETE) now considers any illumination of the tower to be under copyright.[64] As a result, it is no longer legal to publish contemporary photographs of the tower at night without permission in France and some other countries.
The imposition of copyright has been controversial. The Director of Documentation for what was then the Société nouvelle d'exploitation de la tour Eiffel (SNTE), Stéphane Dieu, commented in January 2005, "It is really just a way to manage commercial use of the image, so that it isn't used in ways we don't approve." However, it also could be used to prohibit tourist photographs of the tower at night from being published, as well as hindering non-profit and semi-commercial publication of images of the tower. French doctrine and jurisprudence traditionally allow pictures incorporating a copyrighted work as long as their presence is incidental or accessory to the main represented subject,[65] a reasoning akin to the de minimis rule. Thus, SETE could not claim copyright on, for example, photographs or panoramas of Paris including the lit tower.
In popular culture
As a global landmark, the Eiffel Tower is featured in media including films, video games, and television shows.
In a commitment ceremony in 2007, Erika Eiffel, an American woman, "married" the Eiffel Tower. Her relationship with the tower has been the subject of extensive global publicity.[66]
Taller structures
Although it was the world's tallest structure when completed in 1889, the Eiffel Tower has since lost its standing both as the tallest lattice tower and as the tallest structure in France.
Lattice towers taller than the Eiffel Tower
| Name | Pinnacle height | Year | Country | Town | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tokyo Skytree | 2,080 ft (634 m) | 2011 | Japan | Tokyo | |
| Kiev TV Tower | 1,263 ft (385 m) | 1973 | Ukraine | Kiev | Tallest lattice tower of the world |
| Tashkent Tower | 1,230 ft (375 m) | 1985 | Uzbekistan | Tashkent | |
| Pylons of Zhoushan Island Overhead Powerline Tie | 1,214 ft (370 m) | 2009 | People's Republic of China | Jiangyin | 2 towers, tallest pylons in the world |
| Pylons of Yangtze River Crossing | 1,137 ft (347 m) | 2003 | People's Republic of China | Jiangyin | 2 towers |
| Dragon Tower | 1,102 ft (336 m) | 2000 | People's Republic of China | Harbin | |
| Tokyo Tower | 1,091 ft (333 m) | 1958 | Japan | Tokyo | |
| WITI TV Tower | 1,078 ft (329 m) | 1962 | U.S. | Shorewood, Wisconsin | |
| WSB TV Tower | 1,075 ft (328 m) | 1957 | U.S. | Atlanta, Georgia |
Architectural structures in France taller than the Eiffel Tower
| Name | Pinnacle height | Year | Structure type | Town | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longwave transmitter Allouis | 350 m (1,150 ft) | 1974 | Guyed Mast | Allouis | |
| HWU transmitter | 350 m (1,150 ft) | ? | Guyed Mast | Rosnay | Military VLF-Transmitter, multiple masts |
| Viaduc de Millau | 343 m (1,125 ft) | 2004 | Bridge Pillar | Millau | |
| TV Mast Niort-Maisonnay | 330 m (1,080 ft) | ? | Guyed Mast | Niort | |
| Transmitter Le Mans-Mayet | 342 m (1,122 ft) | 1993 | Guyed Mast | Mayet | |
| La Regine transmitter | 330 m (1,080 ft) | 1973 | Guyed Mast | Saissac | Military VLF transmitter |
| Transmitter Roumoules | 330 m (1,080 ft) | 1974 | Guyed Mast | Roumoules | spare transmission mast for long wave, insulated against ground |
See also
- List of tallest buildings and structures in the Paris region
- List of tallest buildings and structures in the world
- List of tallest freestanding structures in the world
- List of tallest towers in the world
Notes
- ↑ "The Eiffel Tower at a glance-Things to Remember". SETE (Official Tour Eiffel website). Retrieved 1 January 2014.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "The Eiffel Tower at a glance-Key Figures". SETE (Official Tour Eiffel website). Retrieved 1 January 2014.
- ↑ Harvie, David (2006). Eiffel: The Genius Who Reinvented Himself. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton. p. 78. ISBN 0-7509-3309-7.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Loyrette, Henri (1985). Gustave Eiffel. New York: Rizzoli. p. 116. ISBN 0-8478-0631-6.
- ↑ Loyrette, Henri (1985). Gustave Eiffel. New York: Rizzoli. p. 121. ISBN 0-8478-0631-6.
- ↑ Loyrette, Henri (1985). Gustave Eiffel. New York: Rizzoli. p. 174. ISBN 0-8478-0631-6.
- ↑ Souriau, Paul; Souriau, Manon. The Aesthetics of Movement. p. 100.
- ↑ Harvie, David (2006). Eiffel: The Genius Who Reinvented Himself. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton. p. 99. ISBN 0-7509-3309-7.
- ↑ Loyrette, Henri (1985). Gustave Eiffel. New York: Rizzoli. p. 176. ISBN 0-8478-0631-6.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "The Eiffel Tower" (News). The Times (London). Monday, 1 April 1889. (32661), col B, p. 5.
- ↑ Jonnes, Jill (2009). Eiffel's Tower: And the World's Fair Where Buffalo Bill Beguiled Paris, the Artists Quarreled, and Thomas Edison Became a Count. Viking Adult. pp. 163–64. ISBN 978-0-670-02060-7.
- ↑ Apollinaire, Guillaume (1980) [1918]. Calligrammes: Poems of Peace and War (1913–1916). Translated by Anne Hyde Greet. With an Introduction by S. I. Lockerbie and Commentary by Anne Hyde Greet and S. I. Lockerbie. University of California Press. pp. 411–414. ISBN 978-0-520-01968-3.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 "Origins and Construction of the Eiffel Tower". SETE (official Tour Eiffel website. Retrieved 1 January 2014.
- ↑ Loyrette, Henri (1985). Gustave Eiffel. New York: Rizzoli. p. 123. ISBN 0-8478-0631-6.
- ↑ Loyrette, Henri (1985). Gustave Eiffel. New York: Rizzoli. p. 148. ISBN 0-8478-0631-6.
- ↑ Harvie, David (2006). Eiffel: The Genius Who Reinvented Himself. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton. p. 110. ISBN 0-7509-3309-7.
- ↑ Vogel, Robert M (1961). "Elevator Systems of the Eiffel Tower, 1889". United States National Museum Bulletin 228 (Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution): 20–21. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Vogel, Robert M (1961). "Elevator Systems of the Eiffel Tower, 1889". United States National Museum Bulletin 228 (Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution): 28. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Vogel, Robert M (1961). "Elevator Systems of the Eiffel Tower, 1889". United States National Museum Bulletin 228 (Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution): 23–4. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- ↑ Eiffel, Gustave (1900). La Tour de Trois Cents Mètres (in French). Paris: Société des imprimeries Lemercier. pp. 171–3.
- ↑ Harvie, David (2006). Eiffel: The Genius Who Reinvented Himself. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton. pp. 122–3. ISBN 0-7509-3309-7.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "The Eiffel Tower during the 1889 Exposition Universelle". SETE (official website of the Tour Eiffel).
- ↑ Harvie, David (2006). Eiffel: The Genius Who Reinvented Himself. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton. pp. 144–5. ISBN 0-7509-3309-7.
- ↑ Eiffel, Gustave (1900). La Tour de Trois Cents Mètres. Paris: Lemercier. p. 335.
- ↑ Jonnes, Jill. "Thomas Edison at the Eiffel Tower". Wonders and Marvels. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ↑ "M. Santos Dumont's Balloon" (News). The Times (London). Monday, 21 October 1901. (36591), col A, p. 4.
- ↑ Wulf, Theodor. Physikalische Zeitschrift, contains results of the four-day long observation done by Theodor Wulf while at the top of the Eiffel Tower in 1910.
- ↑ "L'inventeur d'un parachute se lance de le tour Eiffel et s'écrase sur le sol". Le Petit Parisien (in French). 5 February 1912. p. 1. Retrieved 26 November 2009.
- ↑ Tuchman, Barbara (1980). August 1914. London: Macmillan. p. 236.
- ↑ Letcher, Piers (2003). Eccentric Franc. Bradt Travel Guides. p. 105. ISBN 978-1-84162-068-8.
- ↑ "An air tragedy". The Sunday Times (Perth, WA). 28 February 1926. Retrieved 2 January 2012.
- ↑ Harriss, Joseph (1975). The Eiffel Tower:Symbol of an Age. London: Paul Elek. p. 178. ISBN 0236400363.
- ↑ "180-line Transmission from the Eiffel Tower". Retrieved 5 January 2014.
- ↑ Harriss, Joseph (1975). The Eiffel Tower:Symbol of an Age. London: Paul Elek. p. 195. ISBN 0236400363.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 Harriss, Joseph (1975). The Eiffel Tower:Symbol of an Age. London: Paul Elek. pp. 180–4. ISBN 0236400363.
- ↑ "Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life". google.com.
- ↑ "The major events". SETE. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
- ↑ Harriss, Joseph (1975). The Eiffel Tower:Symbol of an Age. London: Paul Elek. p. 215. ISBN 0236400363.
- ↑ Auf der Mar, Nick (15 September 1980). "How this city nearly got the Eiffel Tower". The Montreal Gazette. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ↑ "A Bonanza in Paris". Retrieved 4 April 2008.
- ↑ "SETE website See "A simple but brilliant mechanism!" tab". tour-eiffel.fr.
- ↑ "Extreme bid to stretch bungy record – World". Sydney Morning Herald. 27 February 2007. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ↑ "Eiffel Tower". 21 October 1991. Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- ↑ "The Eiffel Tower’s Illuminations". Société d’Exploitation de la Tour Eiffel. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 "Card 11: Illumintaions". All You Need To Know About the Eiffel Tower (PDF). Société d’Exploitation de la Tour Eiffel. 2008. pp. 17–18. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2009. Retrieved 9 January 2009.
- ↑ "The Eiffel Tower: Paris' Grande Dame". france.com. Retrieved 24 July 2007.
- ↑ "Soirée réussie le 28 novembre pour fêter l'année du 200 millionième visiteur". Official Site (in French). 2002. Retrieved 24 July 2007.
- ↑ Porter, Darwin; Prince, D; McDonald, G; Mastrini, H; Marker, S; Princz, A; Bánfalvy, C; Kutor, A; Lakos, N (2006). Frommer's Europe. 9th ed. Frommer's. p. 318. ISBN 978-0-471-92265-0.
- ↑ "Eiffel Tower gets glass floor in refurbishment project". BBC News. 6 October 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ↑ Harriss, Joseph (1975). The Eiffel Tower: Symbol of an Age. London: Paul Elek. p. 60. ISBN 0236400363.
- ↑ Harriss, Joseph (1975). The Eiffel Tower: Symbol of an Age. London: Paul Elek. p. 231. ISBN 0236400363.
- ↑ "Debate and Controversy Surrounding the Eiffel Tower". SETE (Official tour Eiffel website). Retrieved 2 January 2013.
- ↑ "Elegant Shape Of Eiffel Tower Solved Mathematically By University Of Colorado Professor". Science Daily. 7 January 2005. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ↑ "Painting the Eiffel Tower". SETE {Official tour Eiffel website}. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ↑ "Exhibition buildings". Tata Steel. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ http://www.toureiffel.paris/en/preparing-your-visit/getting-to-the-eiffel-tower.html
- ↑ "Tour Eiffel et souvenirs de Paris". Le Monde. France. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ↑ "Eiffel Tower reopens to tourists after rare closure for 2-day strike". Fox News.
- ↑ "La billetterie officielle de la Tour Eiffel". toureiffel.fr.
- ↑ Wiederhoft, Dali. "Eiffel Tower: Sightseeing, Restaurants, Links, Transit". Bonjourparis.com. Retrieved 5 January 2014.
- ↑ "The Blackpool Tower". History Extra. Retrieved 6 March 2014.
- ↑ "Paris Time By Wireless", New York Times, 22 November 1913, pg 1.
- ↑ "Cour de cassation 3 mars 1992, Jus Luminum n°J523975". Jus Luminum. Archived from the original on 16 November 2009.
- ↑ "Image rights/the Eiffel Tower brand". Société d’Exploitation de la Tour Eiffel. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ↑ E.g., "La représentation d'une œuvre située dans un lieu public n'est licite que lorsqu'elle est accessoire par rapport au sujet principal représenté ou traité"; Cass. 1re civ. 4 juillet 1995. Christophe Caron, Droit d'auteur et droits voisins, Litec, 2006, §365.
- ↑ "Inanimate attachment: Love objects". Globe and Mail (Canada). 21 August 2009. Retrieved 4 May 2010.
References
- 1889: La Tour Eiffel et L’Exposition Universelle Paris: Editions de la Reunion des Musees Nationaux, 1989 [exhibition catalog].
- Chanson, Hubert (2009). Hydraulic Engineering Legends Listed on the Eiffel Tower, Great Rivers History, ASCE-EWRI Publication, Proceedings of the History Symposium of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2009, Kansas City, USA, 17–19 May, J.R. ROGERS Ed., pp. 1–7 (ISBN 978-0-7844-1032-5)
- Frémy, Dominique, Quid de la Tour Eiffel, Robert Lafont, Paris (1989) – out of print
- The Engineer: The Paris Exhibition, 3 May 1889 (Vol. XLVII). London: Office for Advertisements and Publication.
- Jonnes, Jill. Eiffel's Tower Viking, 2009
- Harvie, David I Eiffel: The Genius Who Reinvented Himself Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton, 2006 ISBN 0-7509-3309-7
- Loyrette, Henri Gustave Eiffel New York: Rizzoli, 1985. ISBN 0-8478-0631-6
- Watson, William. Paris Universal Exposition: Civil Engineering, Public Works, and Architecture. Washington [DC]: Government Printing Office, 1892.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eiffel Tower. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Eiffel Tower. |
- Official website of the Eiffel Tower (French)
- Official website of the Eiffel Tower (English)
- 360° Panoramic view – Under the Eiffel Tower
- Eiffel Tower at Structurae
- Eiffel Tower Facts
- Sketches and plans of the tower's construction
- 3D render of the Eiffel Tower for use in Google Earth
- The first transmitters at Eiffel Tower
- Eiffel Tower: A French Beauty – slideshow by Life magazine
| Records | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Washington Monument |
World's tallest structure 1889—1931 300.24m |
Succeeded by Chrysler Building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||





