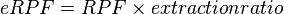Effective renal plasma flow
| Sodium |
Inulin |
Creatinine |
PAH |
| SNa=150 mEq/L |
SIn=1 mg/mL |
SCr=0.01 mg/ml |
SPAH= |
| UNa=710 mEq/L |
UIn=150 mg/mL |
UCr=1.25 mg/mL |
UPAH= |
| CNa=5 mL/min |
CIn=150 ml/min |
CCr=125 mL/min |
CPAH=420 ml/min |
| |
|
|
ER=90% |
| |
|
|
ERPF=540 ml/min |
Effective renal plasma flow (eRPF) is a measure used in renal physiology[1] to calculate renal plasma flow (RPF) and hence estimate renal function.
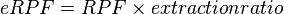
Where extraction ratio is the ratio of compound entering the kidney that is excreted into the final urine.
When using a compound with an extraction ratio near 1, such as para-aminohippurate (PAH), eRPF approximates RPF. Therefore, PAH clearance can be used to estimate RPF.
References
External links
|
|---|
| | Filtration | |
|---|
| Hormones affecting
filtration | |
|---|
| Secretion /
clearance | |
|---|
| | Reabsorption | |
|---|
| | Endocrine | |
|---|
| Assessing
renal function/
measures of dialysis | |
|---|
| Acid-base
physiology | |
|---|
| Buffering/
compensation | |
|---|
| | Other | |
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Development
- Cells
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Electrolyte and acid-base
- Congenital
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Other
- Symptoms and signs
- Urine tests
- Blood tests
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Drugs
- Intravenous fluids
|
|---|
|
|