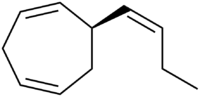
Ectocarpene
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(R,Z)-6-(But-1-en-1-yl)cyclohepta-1,4-diene | |
| Other names
(−)-Dictyopterene D' | |
| Identifiers | |
| 33156-93-3 | |
| ChemSpider | 28290131 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C11H16 |
| Molar mass | 148.24 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.908 g/mL |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ectocarpene is a sexual attractant, or pheromone, found with several species of brown algae (Phaeophyceae). The substance has a fruity scent and can be sensed by humans when millions of algae gametes swarm the seawater and the females start emitting the substance to attract the male gametes.
Ectocarpene was the first isolated algal pheromone. It was isolated from algae Ectocarpus (order Ectocarpales) by Müller and col. in 1971.[1] More recent studies have shown that a pre-ectocarpene compound may be responsible for actual attraction of the male gametes.[2]
All the double bonds are cis and the absolute configuration of the stereocenter is (R).[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Mueller, D. G.; Jaenickel, L.; Donike, M.; Akintobi, T. (1971). "Sex attractant in a brown alga: chemical structure". Science 171 (3973): 815–817. doi:10.1126/science.171.3973.815. PMID 17812027.
- ↑ Wilhelm Boland (1995). "The Chemistry of Gamete Attraction: Chemical Structures, Biosynthesis, and (a)biotic Degradation of Algal Pheromones". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 92 (1): 37–43. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.1.37. JSTOR 2366495. PMC 42813. PMID 7816845.
- ↑ SciFinder Scholar, version 2004.2; Chemical Abstracts Service: Columbus, OH, 2004; RN 133876-92-3