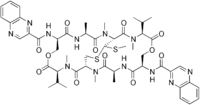
Echinomycin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Quinomycin A; Levomycin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 512-64-1 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 3197 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C51H64N12O12S2 | |
| Molar mass | 1101.26 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Echinomycin is a peptide antibiotic. It intercalates into DNA at two specific sites, thereby blocking the binding of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1alpha).
Biosynthesis
Echinomycin is a bis-intercalator peptide and is biosynthesized by a unique nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS).[1][2] Echinomycin is isolated from various bacteria such as Streptomyces lasalienis. It belongs to a family of quinoxaline antibiotics. There is great interest in this group of compounds because they have very potent antibacterial, anticancer, and antiviral activities.[3]
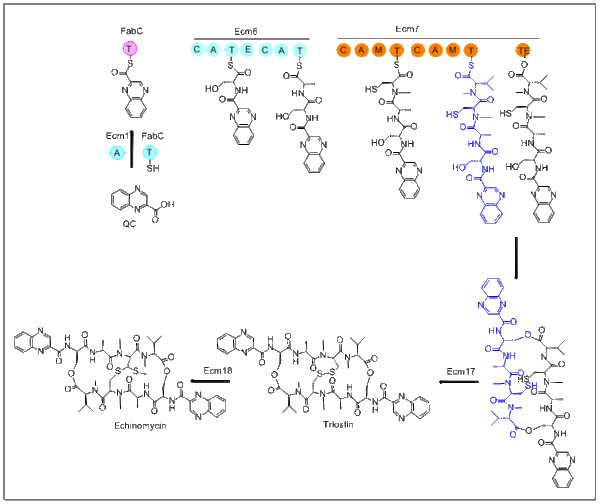
The biosynthesis of echinomycin starts with molecule QC. L-tryptophan is the precursor for QC and its biosynthesis parallels the first stage of nikkomycin biosynthesis. After QC is biosynthesized, the adenylation domain-containing Ecm1 activates and transfers QC to FabC using the fatty acid biosynthesis acyl carrier protein (ACP). The first module, Ecm6 accepts the QC-SFabC as the starter unit. Emc7 contains a terminal thioesterase domain which allows the peptide to dimerize and then release. This cyclized product then goes on to Ecm17, an oxioreductase, creating a disulfide bond. The last step in this biosynthesis transforms the disulfide bond into a thioacetal bridge. This transformation takes place with Ecm18, which is quite similar to S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM)-dependent methyltransferase.[3]
References
- ↑ Watanabe, K; Oguri, H; Oikawa, H (April 2009). "Diversification of echinomycin molecular structure by way of chemoenzymatic synthesis and heterologous expression of the engineered echinomycin biosynthetic pathway.". Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 13 (2): 189–96. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.02.012. PMID 19278894.
- ↑ Sato M, Nakazawa T, Tsunematsu Y, Hotta K, Watanabe K (2013). "Echinomycin biosynthesis". Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 17 (4): 537–45. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.06.022. PMID 23856054.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Watanabe, K et al. (August 2006). "Total biosynthesis of antitumor nonribosomal peptides in Escherichia coli.". Nature chemical biology 2 (8): 423–8. doi:10.1038/nchembio803. PMID 16799553.