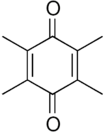
Duroquinone
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,3,5,6-Tetramethyl-1,4-benzoquinone | |||
| Other names
Tetramethyl-p-benzoquinone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 527-17-3 | |||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:42023 | ||
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL151604 | ||
| ChemSpider | 61539 | ||
| DrugBank | DB01927 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| |||
| UNII | X0Q8791R69 | ||
| Properties | |||
| C10H12O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 164.20408 g/mol | ||
| Melting point | 109 to 114 °C (228 to 237 °F; 382 to 387 K) | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Duroquinone is the organic compound with the formula C4(CH3)4O2. It is related to 1,4-benzoquinone by replacement of four H centres with methyl (Me) groups. The C10O2 core of this molecule is planar with two pairs of C=O and C=C bonds.[1]
The compound is produced via nitration of durene (1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene) followed reduction to the diamine and then oxidation.[2]
A derived organoiron compound (η2,η2-C4(CH3)4O2)Fe(CO)3 is obtained by the carbonylation of 2-butyne in the presence of iron pentacarbonyl.[3]
The molecule has been mentioned in the popular press as a component of a "nano brain".[4]
References
- ↑ J.-M. Lü, S. V. Rosokha, I. S. Neretin and J. K. Kochi, "Quinones as Electron Acceptors. X-Ray Structures, Spectral (EPR, UV-vis) Characteristics and Electron-Transfer Reactivities of Their Reduced Anion Radicals as Separated vs Contact Ion Pairs" Journal of the American Chemical Society 2006 128, 16708-16719.doi:10.1021/ja066471o
- ↑ Lee Irvin Smith. (1943). "Duronquinone". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 2, p. 254
- ↑ H. W. Sternberg, R. Markby and I. Wender, "A Quinone Iron Tricarbonyl Complex and its Significance in Organic Synthesis", Journal of the American Chemical Society 1958 volume 80, pp. 1009-1010. doi:10.1021/ja01537a075
- ↑
- Fildes, Jonathan (2008-03-11). "Chemical brain controls nanobots". British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2008-03-11.