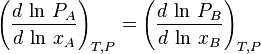Duhem–Margules equation
The Duhem–Margules equation, named for Pierre Duhem and Max Margules, is a thermodynamic statement of the relationship between the two components of a single liquid where the vapour mixture is regarded as an ideal gas:
where PA and PB are the partial vapour pressures of the two constituents and xA and xB are the mole fractions of the liquid.
Sources
- Atkins, Peter and Julio de Paula. 2002. Physical Chemistry, 7th ed. New York: W. H. Freeman and Co.
- Carter, Ashley H. 2001. Classical and Statistical Thermodynamics. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.