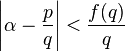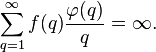Duffin–Schaeffer conjecture
The Duffin–Schaeffer conjecture is an important conjecture in metric number theory proposed by R. J. Duffin and A. C. Schaeffer in 1941.[1] It states that if 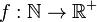 is a real-valued function taking on positive values, then for almost all
is a real-valued function taking on positive values, then for almost all 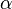 (with respect to Lebesgue measure), the inequality
(with respect to Lebesgue measure), the inequality
has infinitely many solutions in co-prime integers  with
with  if and only if the sum
if and only if the sum
Here 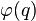 is the Euler totient function.
is the Euler totient function.
The full conjecture remains unsolved. However, a higher-dimensional analogue of this conjecture has been resolved.[2][3][4]
Progress
The implication from the existence of the rational approximations to the divergence of the series follows from the Borel–Cantelli lemma.[5] The converse implication is the crux of the conjecture.[2]
There have been many partial results of the Duffin–Schaeffer conjecture established to date. Paul Erdős established in 1970 that the conjecture holds if there exists a constant 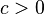 such that for every integer
such that for every integer 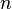 we have either
we have either 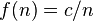 or
or 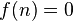 .[2][6] This was strengthened by Jeffrey Vaaler in 1978 to the case
.[2][6] This was strengthened by Jeffrey Vaaler in 1978 to the case 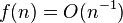 .[7][8] More recently, this was strengthened to the conjecture being true whenever there exists some
.[7][8] More recently, this was strengthened to the conjecture being true whenever there exists some 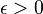 such that the series
such that the series 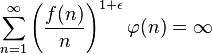 . This was done by Haynes, Pollington, and Velani.[9]
. This was done by Haynes, Pollington, and Velani.[9]
In 2006, Beresnevich and Velani proved that a Hausdorff measure analogue of the Duffin–Schaeffer conjecture is equivalent to the original Duffin–Schaeffer conjecture, which is a priori weaker. This result is published in the Annals of Mathematics.[10]
Notes
- ↑ Duffin, R. J.; Schaeffer, A. C. (1941). "Khintchine’s problem in metric diophantine approximation". Duke math. J. 8: 243–255. doi:10.1215/S0012-7094-41-00818-9. JFM 67.0145.03. Zbl 0025.11002.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Montgomery, Hugh L. (1994). Ten lectures on the interface between analytic number theory and harmonic analysis. Regional Conference Series in Mathematics 84. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society. p. 204. ISBN 0-8218-0737-4. Zbl 0814.11001.
- ↑ Pollington, A.D.; Vaughan, R.C. (1990). "The k dimensional Duffin–Schaeffer conjecture". Mathematika 37 (2): 190–200. doi:10.1112/s0025579300012900. ISSN 0025-5793. Zbl 0715.11036.
- ↑ Harman (2002) p.69
- ↑ Harman (2002) p.68
- ↑ Harman (1998) p.27
- ↑ http://www.math.osu.edu/files/duffin-schaeffer%20conjecture.pdf
- ↑ Harman (1998) p.28
- ↑ A. Haynes, A. Pollington, and S. Velani, The Duffin-Schaeffer Conjecture with extra divergence, arXiv, (2009), http://arxiv.org/abs/0811.1234
- ↑ Beresnevich, Victor; Velani, Sanju (2006). "A mass transference principle and the Duffin-Schaeffer conjecture for Hausdorff measures". Annals of Mathematics (2) 164 (3): 971–992. doi:10.4007/annals.2006.164.971. ISSN 0003-486X. Zbl 1148.11033.
References
- Harman, Glyn (1998). Metric number theory. London Mathematical Society Monographs. New Series 18. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-850083-1. Zbl 1081.11057.
- Harman, Glyn (2002). "One hundred years of normal numbers". In Bennett, M. A.; Berndt, B.C.; Boston, N.; Diamond, H.G.; Hildebrand, A.J.; Philipp, W. Surveys in number theory: Papers from the millennial conference on number theory. Natick, MA: A K Peters. pp. 57–74. ISBN 1-56881-162-4. Zbl 1062.11052.