Droz-Farny line theorem

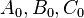 is Droz-Farny line
is Droz-Farny lineIn Euclidean geometry, the Droz-Farny line theorem is a property of two perpendicular lines through the orthocenter of an arbitrary triangle.
Let 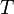 be a triangle with vertices
be a triangle with vertices 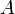 ,
, 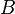 , and
, and 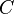 , and let
, and let 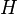 be its orthocenter (the common point of its three altitude lines. Let
be its orthocenter (the common point of its three altitude lines. Let 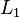 and
and 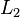 be any two mutually perpendicular lines through
be any two mutually perpendicular lines through 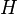 . Let
. Let 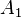 ,
, 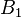 , and
, and 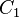 be the points where
be the points where 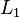 intersects the side lines
intersects the side lines 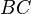 ,
, 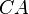 , and
, and 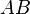 , respectively. Similarly, let Let
, respectively. Similarly, let Let 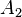 ,
, 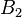 , and
, and 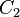 be the points where
be the points where 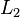 intersects those side lines. The Droz-Farny line theorem says that the midpoints three segments
intersects those side lines. The Droz-Farny line theorem says that the midpoints three segments 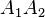 ,
, 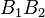 , and
, and 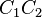 are collinear.[1][2][3]
are collinear.[1][2][3]
The theorem was stated by Arnold Droz-Farny in 1899,[1] but it is not clear whether he had a proof.[4]
Goormaghtigh's generalization
A generalization of the Droz-Farny line theorem was proved in 1930 by René Goormaghtigh.[5]
As above, let 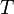 be a triangle with vertices
be a triangle with vertices 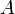 ,
, 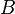 , and
, and 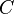 . Let
. Let 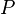 be any point distinct from
be any point distinct from 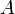 ,
, 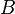 , and
, and 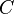 , and
, and 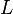 be any line through
be any line through 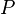 . Let
. Let 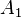 ,
, 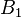 , and
, and 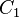 be points on the side lines
be points on the side lines 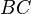 ,
, 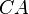 , and
, and 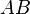 , respectively, such that the lines
, respectively, such that the lines 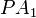 ,
, 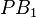 , and
, and 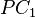 are the images of the lines
are the images of the lines 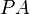 ,
, 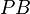 , and
, and 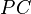 , respetively, by reflection against the line
, respetively, by reflection against the line 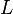 . Goormaghtigh's theorem then says that the points
. Goormaghtigh's theorem then says that the points 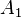 ,
, 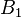 , and
, and 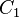 are collinear.
are collinear.
The Droz-Farny line theorem is a special case of this result, when 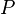 is the orthocenter of triangle
is the orthocenter of triangle 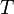 .
.
Dao's generalization
The theorem was further generalized by Dao Thanh Oai.[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 A. Droz-Farny (1899), "Question 14111". The Educational Times, volume 71, pages 89-90
- ↑ Jean-Louis Ayme (2004), "A Purely Synthetic Proof of the Droz-Farny Line Theorem". Forum Geometricorum, volume 14, pages 219–224, ISSN 1534-1178
- ↑ Floor van Lamoen and Eric W. Weisstein (), Droz-Farny Theorem at Mathworld
- ↑ J. J. O'Connor and E. F. Robertson (2006), Arnold Droz-Farny. The MacTutor History of Mathematics archive. Online document, accessed on 2014-10-05.
- ↑ René Goormaghtigh (1930), "Sur une généralisation du théoreme de Noyer, Droz-Farny et Neuberg". Mathesis, volume 44, page 25
- ↑ Son Tran Hoang (2014), "A synthetic proof of Dao's generalization of Goormaghtigh's theorem." Global Journal of Advanced Research on Classical and Modern Geometries, volume 3, pages 125–129, ISSN 2284-5569