Dominica
| Commonwealth of Dominica |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: "Après Bondie, C'est La Ter" (Kwéyòl) "Post deum terra est " (Latin) ("After God is the earth") | ||||||
| Anthem: Isle of Beauty, Isle of Splendour |
||||||
.svg.png) |
||||||
_-_DMA_-_UNOCHA.svg.png) |
||||||
| Capital and largest city | Roseau 15°18′N 61°23′W / 15.300°N 61.383°W | |||||
| Official languages | English | |||||
| Vernacular languages |
Kwéyòl Island Carib |
|||||
| Ethnic groups (2014[1]) |
|
|||||
| Demonym | Dominican (stress on the "ni") | |||||
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic | |||||
| - | President | Charles Savarin | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | Roosevelt Skerrit | ||||
| Legislature | House of Assembly | |||||
| Independence | ||||||
| - | Associated State | 1 March 1967 | ||||
| - | from the United Kingdom | 3 November 1978 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 750 km2 (184th) 290 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 1.6 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | July 2009 estimate | 72,660 (195th) | ||||
| - | 2014 census | 72,337 | ||||
| - | Density | 105/km2 (95th) 272/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2012 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $1.002 billion[2] | ||||
| - | Per capita | $14,166[2] | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2012 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $497 million[2] | ||||
| - | Per capita | $7,022[2] | ||||
| HDI (2013) | high · 93rd |
|||||
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar (XCD) | |||||
| Time zone | Eastern Caribbean (UTC–4) | |||||
| Drives on the | left | |||||
| Calling code | +1-767 | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | DM | |||||
| Internet TLD | .dm | |||||
Dominica (/ˌdɒmɪˈniːkə/ DOM-i-NEE-kə;[4][5] French: Dominique; Island Carib: Wai‘tu kubuli), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island nation in the Lesser Antilles region of the Caribbean Sea, south-southeast of Guadeloupe and northwest of Martinique. Its size is 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi) and the highest point in the country is Morne Diablotins, which has an elevation of 1,447 metres (4,747 ft). The Commonwealth of Dominica had a population of 72,301 at the 2014 Census. The capital is Roseau which is located on the leeward side of the island.
Dominica was first discovered by the Spanish, then colonized by the French and British before finally obtaining independence in 1978. Dominica has been nicknamed the "Nature Isle of the Caribbean"[6] for its unspoiled natural beauty. It is the youngest island in the Lesser Antilles, still being formed by geothermal-volcanic activity, as evidenced by the world's second-largest hot spring, Boiling Lake. The island features lush mountainous rainforests, home of many rare plant, animal, and bird species. There are xeric areas in some of the western coastal regions, but heavy rainfall occurs inland. The island has 365 rivers. The Sisserou parrot (also known as the imperial amazon), is found only on Dominica and is the island's national bird. It is featured on the national flag. Dominica's economy is heavily dependent on tourism and agriculture.
Christopher Columbus named the island after the day of the week on which he spotted it, a Sunday (dies Dominica in Latin), 3 November 1493. In the hundred years after Columbus's landing, Dominica remained isolated. At the time it was inhabited by the Island Caribs, or Kalinago people, and over time more settled there after being driven from surrounding islands, as European powers entered the region. The people of Spain left the island due to isolation and the fierce Island Carib warriors that inhabited the island at the moment. France had a colony for several years, importing African slaves to work on its plantations. In this period, the Antillean Creole language developed. France formally ceded possession of Dominica to Great Britain in 1763. Great Britain established a small colony on the island in 1805.
Britain abolished slavery throughout the British Empire in 1834. By 1838, Dominica became the first British Caribbean colony to have a legislature controlled by an ethnic African majority. In 1896, the United Kingdom took governmental control of Dominica, turning it into a Crown colony. Half a century later, from 1958 to 1962, Dominica became a province of the short-lived West Indies Federation. On 3 November 1978, Dominica became an independent nation.
Etymology and languages
The name Dominica comes from the Latin word for Sunday, which was the day on which it was spotted by Christopher Columbus. Its pre-Columbian name by the Caribs was Wai‘tu kubuli, which means "Tall is her body".[7] The indigenous people of the island were the Island Caribs or Kalinago.
The island became multi-ethnic due to European colonization, which included the importation of numerous African slaves. The French had the longest influence prior to ceding the island to the British in 1763 after losing the Seven Years' War. An Antillean Creole, based on the French language, West African and Carib influences, is still spoken by many residents, especially people of older generations.
Today the Carib have some reserved land, known as the Carib Territory, an area similar to the Indian reserves of Canada or the US. The official language is English, following the island's history since the late 18th century as a British colony, territory, and state. The demonym or adjective is "Dominican" in English. It is pronounced with the syllable stress on the second "i," to distinguish it from the Dominican Republic, where the stress is on the first "i".[8]
History
Early European contacts
In 1632, the French Compagnie des Îles de l'Amérique claims Dominica and other "Petite Antilles" for France, but no physical occupation takes place. Between 1642 and 1650 a French missionary Raymond Breton became the first regular European visitor to the island. In 1660 the French and English agreed that both Dominica and St. Vincent should not be settled, but left to the Caribs as neutral territory. Dominica was officially neutral for the next century. Its natural resources attracted rival expeditions of English and French foresters, who began harvesting timber by the start of the 18th century.[9]
French colony
Spain had little to no success in colonizing Dominica, and in 1690 the French established their first permanent settlements. French woodcutters from Martinique and Guadeloupe begin to set up timber camps to supply the French islands with wood and gradually become permanent settlers. They brought the first enslaved people from West Africa to Dominica. In 1715, a revolt of "poor white" smallholders in the north of Martinique, known as La Gaoulé,[10] causes an exodus of them to southern Dominica. They set up smallholdings. Meanwhile, French families and others from Guadeloupe settled in the north. In 1727, the first French commander, M. Le Grand, took charge of the island with a basic French government; Dominica formally became a colony of France, and the island was divided into districts or "quarters".[11] Already installed in Martinique and Guadeloupe and cultivating sugar cane, the French gradually developed plantations in Dominica for coffee. They imported African slaves to fill the labor demands.
In 1761, during the Seven Years' War a British expedition against Dominica led by Lord Rollo was successful and the island was conquered along with several other Caribbean islands. After France was defeated by Britain in the Seven Years' War, it ceded the island to the British under the Treaty of Paris (1763). In 1778, during the American Revolutionary War, the French mounted a successful invasion with the active cooperation of the population. The 1783 Treaty of Paris, which ended the war, returned the island to Britain. French invasions in 1795 and 1805 ended in failure.[9]
British colony

In 1763, the British established a legislative assembly, representing only the white population. In 1831, reflecting a liberalization of official British racial attitudes, the Brown Privilege Bill[12] conferred political and social rights on free blacks (or people of color). Britain abolished slavery in Dominica and the rest of its empire in 1834. The next year, three men of African descent were elected to the legislative assembly. Many slaves fled the neighboring islands of Guadeloupe and Martinique during this period, trying to find refuge in Dominica.
In 1838, Dominica became the only British Caribbean colony to have a legislature with a majority of ethnic African members. (Most were of mixed race and had ancestors free before abolition). Most ethnic African legislators were smallholders or merchants, who held economic and social views diametrically opposed to the interests of the small, wealthy English planter class. Reacting to a perceived threat to their power, the planters lobbied for more direct British rule.[9]
In 1865, after much agitation and tension, the colonial office replaced the elective assembly with one that had one-half of members who were elected and one-half who were appointed. Planters allied with colonial administrators outmaneuvered the elected legislators on numerous occasions. In 1871, Dominica became part of the Leeward Island Federation. The power of the ethnic African population progressively eroded. Crown Colony government was re-established in 1896. All political rights for the vast majority of the population were effectively curtailed. Development aid, offered as compensation for disfranchisement, proved to have a negligible effect in improving conditions for most ethnic Africans.[9]
History post-1900
In 1914 -1918 World War I; many young Dominican men, mainly the sons of small farmers, volunteered to go to Europe and fight for the British Empire. Following World War I, an upsurge of political consciousness throughout the Caribbean led to the formation of the Representative Government Association. Marshaling public frustration with the lack of a voice in the governing of Dominica, this group won one-third of the popularly elected seats of the legislative assembly in 1924 and one-half in 1936. Shortly thereafter, Dominica was transferred from the Leeward Island Administration.[9] In 1940-1945 World War II, some Dominicans volunteered to serve in British and Caribbean forces. Thousands of Free French refugees from Martinique and Guadeloupe escaped to Dominica from the Vichy controlled French islands and stay in Roseau and villages.
It was governed as part of the Windwards until 1958, when it joined the short-lived West Indies Federation.[9] After the federation dissolved, Dominica became an associated state of the United Kingdom in 1967 and formally took responsibility for its internal affairs. On 3 November 1978, the Commonwealth of Dominica was granted independence from the United Kingdom.[9]
In mid-1979, political discontent led to the formation of an interim government. It was replaced after the 1980 elections by a government led by the Dominica Freedom Party under Prime Minister Eugenia Charles, the Caribbean's first female prime minister. Chronic economic problems were compounded by the severe impact of hurricanes in 1979 and in 1980.
In 1981, Dominica was threatened with a takeover by mercenaries[13] led by Mike Perdue of Houston and Wolfgang Droege of Toronto, who tried to overthrow the government of Eugenia Charles. The North America mercenary group was to aid ex-Prime Minister Patrick John and his Dominica Defence Force in regaining control of the island in exchange for control over the island's future development. The entire plan failed. The ship hired to transport the men of Operation Red Dog never left the dock, as the United States FBI was tipped off. The self-titled mercenaries lacked any formal military experience or training, and the majority of the crew had been misled into joining the armed coup by Mike Perdue, considered a con-man ringleader. White nationalist Don Black was also jailed for his part in the attempt, which violated US neutrality laws.[14]
By the end of the 1980s, the economy recovered. It weakened again in the 1990s because of a decrease in banana prices and worldwide recession.[9]
In the January 2000 elections, the Edison James United Workers Party (UWP) was defeated by the Dominican Labour Party (DLP), led by Roosevelt P. "Rosie" Douglas. Douglas died after only a few months in office and was replaced by Pierre Charles, who died in office in January 2004. Roosevelt Skerrit, also of the DLP, replaced Charles as Prime Minister. Under Prime Minister Skerrit's leadership, the DLP won elections in May 2005 that gave the party 12 seats in the 21-member Parliament to the UWP's 8 seats. An independent candidate affiliated with the DLP won a seat as well. Later, the independent candidate joined the government and one UWP member crossed the aisle, making the total 14 seats for the DLP and 7 for the UWP.[9]
The DLP won a crushing victory in elections in December 2009, winning 18 of 21 seats. The UWP claimed campaign improprieties and boycotted Parliament; by-elections were conducted for two of its seats in July 2010, and the UWP once again won the seats.[15] On 17 September 2012 Eliud Thaddeus Williams was sworn in as President, replacing Dr Nicholas Liverpool who was reportedly removed from office due to ill health.
Geography and climate

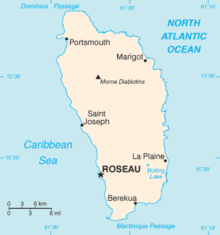
Dominica is an island nation in the Caribbean Sea, the northernmost of the Windward Islands (though it is sometimes considered the southernmost of the Leeward Islands). The size of the country is about 289.5 square miles (750 km2). The capital is Roseau.
Dominica is largely covered by rainforest and is home to the world's second-largest hot spring, Boiling Lake.[16] Dominica has many waterfalls, springs, and rivers. The Calibishie area in the country's northeast has sandy beaches.[17] Some plants and animals thought to be extinct on surrounding islands can still be found in Dominica's forests.[18] The volcanic nature of the island has attracted scuba divers. The island has several protected areas, including Cabrits National Park, as well as 365 rivers.
On his second voyage to the Caribbean, Dominica was the first New World country that Christopher Columbus discovered. It is said that when his royal sponsors asked Christopher Columbus to describe this island, he crumpled a piece of parchment roughly and threw it on the table. "This", Columbus explained, "is what Dominica looks like—completely covered with mountains with nary a flat spot."
Morne Trois Pitons National Park is a tropical forest blended with scenic volcanic features.[19] It was recognised as a World Heritage Site on 4 April 1995, a distinction it shares with four other Caribbean islands.[20]
.jpg)
The Commonwealth of Dominica is engaged in a long-running dispute with Venezuela over Venezuela's territorial claims to the sea surrounding Isla Aves (literally Bird Island, but in fact called Bird Rock by Dominica authorities),[21] a tiny islet located 140 miles (225 km) west of the island of Dominica.
There are two primary population centres: Roseau (with 14,725 inhabitants in 2011) and Portsmouth (with 4,167 inhabitants in 2011).
Dominica, known as "The Nature Island of the Caribbean" due to its spectacular, lush, and varied flora and fauna, which are protected by an extensive natural park system; the most mountainous of the Lesser Antilles, its volcanic peaks are cones of lava craters and include Boiling Lake, the second-largest, thermally active lake in the world possesses the most pristine wilderness in the Caribbean.[22] Originally, it was protected by sheer mountains which led the European powers to build ports and agricultural settlements on other islands. More recently, the citizens of this island have sought to preserve its spectacular natural beauty by discouraging the type of high-impact tourism which has damaged nature in most of the Caribbean.
Visitors can find large tropical forests, including one which is on the UNESCO list of World Heritage sites, hundreds of streams, coastlines and coral reefs.
The Sisserou parrot (Amazona imperialis) is Dominica's national bird and is endemic to its mountain forests. A related species, the Jaco or red-necked parrot (A. arausiaca),. is also a Dominican endemic. Both birds are rare and protected, though some forest is still threatened by logging in addition to the long-standing threat of hurricanes.
The Caribbean Sea offshore of the island of Dominica is home to many cetaceans. Most notably a group of sperm whales live in this area year round. Other cetaceans commonly seen in the area include spinner dolphins, pantropical spotted dolphins and bottlenose dolphins. Less commonly seen animals include killer whales, false killer whales, pygmy sperm whales, dwarf sperm whales, Risso's dolphins, common dolphins, Atlantic spotted dolphins, humpback whales and Bryde's whales. This makes Dominica a destination for tourists interested in whale-watching.
Dominica is especially vulnerable to hurricanes as the island is located in what is referred to as the hurricane region. In 1979, Dominica was hit directly by category 5 Hurricane David, causing widespread and extreme damage. On 17 August 2007, Hurricane Dean, a category 1 at the time, hit the island. A mother and her seven-year-old son died when a landslide caused by the heavy rains crushed their house.[23] In another incident two people were injured when a tree fell on their house.[24] Prime Minister Roosevelt Skerrit estimated that 100 to 125 homes were damaged, and that the agricultural sector was extensively damaged, in particular the banana crop.[25]



Government and administrative divisions
Dominica is a parliamentary democracy within the Commonwealth of Nations and, since 1979, a member of La Francophonie. The Commonwealth of Dominica is one of the Caribbean's few republics. The president is the head of state, while executive power rests with the cabinet, headed by the prime minister. The unicameral parliament consists of the thirty-member House of Assembly, which consists of twenty-one directly elected members and nine senators, who may either be appointed by the president or elected by the other members of the House of Assembly.
Unlike other former British colonies in the region, Dominica was never a Commonwealth realm, instead becoming a republic on independence. Dominica is a full and participating member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS).
Dominica is also a member of the International Criminal Court with a Bilateral Immunity Agreement of protection for the US military, as covered under Article 98. In January 2008 Dominica joined the Bolivarian Alternative for the Americas.
Dominica is divided into ten parishes, given below with their 2011 Census populations:
|
|
Economy


In 2008, Dominica had one of the lowest per capita gross domestic product (GDP) rates of Eastern Caribbean states.[26][27] The country nearly had a financial crisis in 2003 and 2004, but Dominica's economy grew by 3.5% in 2005 and 4.0% in 2006, following a decade of poor performance. Growth in 2006 was attributed to gains in tourism, construction, offshore and other services, and some sub-sectors of the banana industry. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) recently praised the Government of Dominica for its successful macroeconomic reforms. The IMF also pointed out remaining challenges, including the need for further reductions in public debt, increased financial sector regulation, and market diversification.[9]
Bananas and other agriculture dominate Dominica's economy, and nearly one-third of the labour force works in agriculture. This sector, however, is highly vulnerable to weather conditions and to external events affecting commodity prices. In 2007, Hurricane Dean caused significant damage to the agricultural sector as well as the country's infrastructure, especially roads. In response to reduced European Union (EU) banana trade preferences, the government has diversified the agricultural sector by promoting the production of coffee, patchouli, aloe vera, cut flowers, and exotic fruits such as mango, guava, and papaya. Dominica has also had some success in increasing its manufactured exports, primarily soap.[9]
Dominica is mostly volcanic and has few beaches; therefore, tourism has developed more slowly than on neighboring islands. Nevertheless, Dominica's mountains, rainforests, freshwater lakes, hot springs, waterfalls, and diving spots make it an attractive eco-tourism destination. Cruise ship stopovers have increased following the development of modern docking and waterfront facilities in Roseau, the capital.[9] Out of 22 Caribbean islands tracked, Dominica had the fewest visitors in 2008 (55,800 or 0.3% of the total). This was about half as many as visited Haiti.[28]
Dominica's currency is the East Caribbean Dollar.
Dominica is a beneficiary of the Caribbean Basin Initiative (CBI) that grants duty-free entry into the United States for many goods. Dominica also belongs to the predominantly English-speaking Caribbean Community (CARICOM), the CARICOM Single Market and Economy (CSME), and the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS).[9]
Dominica supposedly offers tax-free status to companies locating from abroad. It is not known how many companies benefit from the tax-free status because of the strict confidentiality the government enforces, although it is known many Internet businesses utilise Dominica for this reason. However, on 12 July 2012 Dominica signed an agreement with Poland to exchange tax information.[29]
The Commonwealth of Dominica offers an official and legally mandated economic citizenship to those seeking a valid second passport. The nationality law of Dominica authorizes the government to waive the normal requirement of seven years of legal residence to acquire citizenship in exchange for a cash contribution. Total costs including all fees for a single applicant come to about $105,000, with an additional $25,000 specified for a spouse and up to two children under 18. The Dominican passport holders can travel without a visa, or obtain a visa upon entry, to nearly 90 countries and territories. Applying for Dominica citizenship requires interacting with official Government Approved Economic Citizenship Agents.
Infrastructure
Air
There are two small airports on the island. The primary airport, Melville Hall Airport (DOM), is on the northeast coast and is about a 45-minute drive from Portsmouth. The second is Canefield Airport (DCF), about 15 minutes from Roseau on the southwest coast. Melville Hall Airport is suitable for limited use of commercial jets because of runway length. Melville Hall currently has regular service by BVI Airways, Winair, Seaborne Airlines and LIAT using twin turboprop aircraft like the De Havilland Dash 8, as well as Conviasa and Amerijet, which, using Boeing 727 Freighters, is the only airline with jet service to the republic. A runway extension and service upgrade project began at Melville Hall around 2006 and was finished in 2010. In March 2013, airline American Eagle halted flights to the island citing high labor costs.[30]
Roads
The only major highway on the island is the road between Portsmouth and Roseau. It takes about 45 minutes to drive from Portsmouth to Roseau. Private minibuses form the major public transport system. However, this "highway" was under major reconstruction via help from the Chinese and was completed in April 2012.[31]
Demographics
The vast majority of Dominicans are of African descent. There is a growing mixed population, along with a significant Indo-Caribbean or East Indian groups, a small European origin minority (descendants of French, British, and Irish colonists) and there are small numbers of Lebanese, Syrians and Asians. Dominica is also the only Eastern Caribbean island that still has a population of pre-Columbian native Caribs, who were exterminated or driven from neighbouring islands. As of 2014 there are more than 3,000 Caribs remaining. They live in eight villages on the east coast of Dominica. This special Carib Territory was granted by the British Crown in 1903.[32] There are also about 1,000 medical students from the United States and Canada who study at the Ross University School of Medicine in Portsmouth.
The population growth rate of Dominica is very low, due primarily to emigration to other countries. In the early 21st century, emigrant numbers for the most popular countries are as follows: the United States (8,560), the United Kingdom (6,739), Canada (605) and France (394).
It has recently been noted that Dominica has a relatively large number of centenarians. As of March 2007, there are 22 centenarians out of the island's 70,000 inhabitants—three times the average incidence of centenarianism in developed countries.[33] The reasons for this are the subject of current research being undertaken at Ross University School of Medicine.
Dominica was partially integrated into the federal colony of the Leeward Islands in 1832. Later, in 1871, it became a full part of the Federation of the Leeward Islands. From the start it was a peculiar relationship for previously Dominica had played no part in the political or cultural traditions of the other more Anglophone islands of the federation. Now, as a Leeward Island, this much larger territory, with thousands of acres of forested unclaimed land, was open to the people of Montserrat and Antigua. At the beginning of the twentieth century the Rose's Company, which produced Rose's lime juice, saw demand for its product outgrow its ability to supply the product from Montserrat. Their response to the situation was to buy land on Dominica and encourage Montserrat farm labourers to relocate. As a result there came to be two linguistic communities in Dominica, Wesley and Marigot.
In 1902, 8 May, the Mount Pelée volcano on Martinique erupted destroying the city of Saint-Pierre. Refugees from Martinique arrived in boats to the southern villages of Dominica and some remained permanently on the island.
Languages
English is the official language of Dominica and is universally spoken and understood. However, because of historic French occupation during different times in history, and the island's location (it lies between the two French-speaking departments of Martinique and Guadeloupe), Antillean Creole, based on French, is spoken by many people on the island. The French creole language is particularly used among the older generation, which also speaks a language known as "patois". Because of a decline in its usage by the younger generation, initiatives have been set up in an effort to increase usage and promote this unique part of the nation's history and culture.
The dialect of Dominica also includes Kokoy, along with Creole—French-based patois. Cocoy, or Kokoy,[34] is a mix of Leeward Island English Creole and Dominican Creole.[35] It is mainly spoken in the north-eastern villages of Marigot and Wesley by immigrants from Montserrat and Antigua. Over time there has been much intermarrying, but there are still traces of difference in origin.[36] As a result of this mixture of languages and heritage, Dominica is a member of both the English-speaking Commonwealth of Nations and the French-speaking La Francophonie.
Island Carib, also known as Igneri (Iñeri, Igñeri, Inyeri), was an Arawakan language historically spoken by the Island Caribs of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. The Island Caribs lived throughout the southern Lesser Antilles such as Dominica, St Vincent and Trinidad, supposedly having conquered them from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. It went extinct about 1920, but an offshoot survives as Garifuna, primarily in Central America.
Religion
About 80% of the population is Roman Catholic, though in recent years a number of Protestant churches have been established. There is also a small Muslim community in Dominica, and the nation's first mosque was built recently near Ross University.[37]
Largest cities
| | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Parish | Pop. | ||||||
| Roseau .jpg) Portsmouth |
1 | Roseau | Saint George | 16,571 | |||||
| 2 | Portsmouth | Saint John | 3,633 | ||||||
| 3 | Marigot | Saint John | 2,669 | ||||||
| 4 | Berekua | Saint Patrick | 2,608 | ||||||
| 5 | Mahaut | Saint Paul | 2,369 | ||||||
| 6 | Saint Joseph | Saint Joseph | 2,184 | ||||||
| 7 | Wesley | Saint Andrew | 1,933 | ||||||
| 8 | Salisbury | Saint Joseph | 1,413 | ||||||
| 9 | Castle Bruce | Saint David | 1,387 | ||||||
| 10 | La Plaine | Saint Patrick | 1,332 | ||||||
Culture
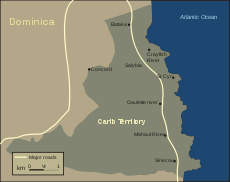
Dominica is home to a wide range of people. Although it was historically occupied by several native tribes, the Arawaks and Carib (Kalinago) tribes occupied it at the time European settlers reached the island. "Massacre" is a name of a river dedicated to the murders of the Native villagers by French and British settlers, because the river ran red with blood for days. Both the French and British tried to claim the island and imported slaves from Africa for labor. The remaining Caribs now live on a 3,700-acre (15 km2) territory on the east coast of the island. They elect their own chief. This mix of cultures has produced the current culture.
Music and dance are important facets of Dominica's culture. The annual independence celebrations display a variety of traditional song and dance. Since 1997, there have also been weeks of Creole festivals, such as "Creole in the Park" and the "World Creole Music Festival".
Dominica gained prominence on the international music stage when in 1973, Gordon Henderson founded the group Exile One and an original musical genre, which he coined "Cadence-lypso." This paved the way for modern Creole music. Other musical genres include "Jing ping" and "Cadence". Jing ping features the accordion and is native to the island. Dominica's music is a melange of Haitian, Afro-Cuban, African and European traditions. Popular artists over the years include Chubby and the Midnight Groovers, Bells Combo, the Gaylords, WCK, and Triple Kay.
The 11th annual World Creole Music Festival was held in 2007, part of the island's celebration of independence from Great Britain on 3 November. A year-long reunion celebration began in January 2008, marking 30 years of independence.
Dominica is often seen as a society that is migrating from collectivism to that of individualism. The economy is a developing one that previously depended on agriculture. Signs of collectivism are evident in the small towns and villages which are spread across the island.
The famed novelist Jean Rhys was born and raised in Dominica. The island is obliquely depicted in her best-known book, Wide Sargasso Sea. Rhys's friend, the political activist and writer Phyllis Shand Allfrey, set her 1954 novel, The Orchid House (ISBN 0-8135-2332-X), in Dominica.
Much of the Walt Disney film Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Man's Chest (the second in the series, starring Johnny Depp, Keira Knightley and Orlando Bloom, and released on July 7, 2006), was shot on location on Dominica (though in the film it was known as "Pelegosto," a fictional island), along with some shooting for the 3rd film in the series, At World's End (released on 2 May 2007).
Cuisine
Dominica's cuisine is similar to that of other Caribbean islands, particularly Trinidad and St Lucia. Like other Commonwealth Caribbean islands, Dominicans have developed a distinct twist to their cuisine. Breakfast is an important daily meal, typically including saltfish, dried and salted codfish, and "bakes," fried dough. Saltfish and bakes are combined for a fast food snack that can be eaten throughout the day; vendors on Dominica's streets sell these snacks to passersby, together with fried chicken, fish and fruit and yogurt "smoothies". Other breakfast meals include cornmeal porridge, which is made with fine cornmeal or polenta, milk and condensed milk and sugar to sweeten. Traditional British-influenced dishes, such as eggs, bacon and toast, are also popular, as are fried fish and plantains.
Common vegetables include Plantain, Tania (a root vegetable), Yam, Potato, rice and peas. Meat and poultry typically eaten include chicken (which is very popular), beef, and fish. These are often prepared in stews with onions, carrots, garlic, ginger and herbs like thyme. The vegetables and meat are browned to create a rich dark sauce. Popular meals include rice and peas, brown stew chicken, stew beef, fried and stewed fish, and many different types of hearty fish broths and soups. These are filled with dumplings, carrots and ground provisions.
Education
Dominica boasts one of the most competitive education systems in the Caribbean and perhaps, the West. School is mandatory up to Secondary school. College is optional, but several millennials have and are pursuing a University education. After pre-school, pupils attend primary school for six, traditionally seven years, and were admitted into secondary school on the basis of a highly challenging Common Entrance Exam. After five years the students took Internationally competitive General Certificate of Education (GCE), widely replaced by the current Caribbean Secondary Education Certificate (CSEC or CXC) administered by the Caribbean Examination Council (a 15-member confederation of the Caribbean community (CARICOM). The more advance version of this examination CAPE) can be taken upon completion of two years of community college. The island has its own state college, formerly named Clifton Dupigny Community College. Some Dominicans attend universities in Cuba on scholarships offered by its government. Others go to the University of the West Indies or to universities in the United Kingdom, the United States, or other countries. Ross University,[38] a medical school, is located at Portsmouth. Ross has been operating in Dominica since the 1980s. Archbold Tropical Research and Education Center (ATREC),[39] a biological field station owned by Clemson University,[40] is located at Springfield Estate between Canefield and Pond Cassé. In 2006, All Saints University School of Medicine[41] opened in temporary facilities in Loubière, with a permanent campus being constructed in Grand Bay. Currently All Saints is located in Roseau, Dominica. A marine biology institute in Mahaut, I.T.M.E (Institute for Tropical Marine Ecology), closed in 2009.
Sports
Cricket is a popular sport on the island, and Dominica competes in test cricket as part of the West Indies cricket team. In West Indies domestic first-class cricket, Dominica participates as part of the Windward Islands cricket team, although they are often considered a part of the Leeward Islands geographically. This is due to being part of the British Windward Islands colony from 1940 until independence; its cricket federation remains a part of the Windward Islands Cricket Board of Control.
On 24 October 2007, the 8,000-seat Windsor cricket stadium was completed with a donation of EC$33 million (US$17 million, €12 million) from the government of the People's Republic of China.
During the 2014 Winter Olympics, a husband and wife team of Gary di Silvestri and Angela Morrone di Silvestri spent US$175,000 to register as Dominican citizens and enter the 15 km men's and 10 km women's cross-country skiing events, respectively. Angela did not start her race, and Gary pulled out several hundred meters into his race. To date, they are Dominica's only Olympic athletes.[42]
Media
Dominica has two major newspapers, The Sun and The Chronicle. There are two national television stations and a few radio stations, including Stations include: ZBC-AM 590, ZGBC-AM 740, ZGBC-FM 90.7 (Portsmouth), ZGBC-FM 102.1 (Roseau) and ZGBC-FM 106.1 (Marigot), Q95 FM,[43] the Dominica Broadcasting Corporation, and Kairi FM.[44] Before 2004, there was one telecommunication company Cable and Wireless. In 2005, Digicel and a UK-based company Orange started to offer service to the island. There are a number of mobile networks operating on the island; LIME and Digicel compete for most of Dominica's wireless customers. Orange shut down in 2010 and is no longer operating on the island of Dominica.
See also
- Index of Dominica-related articles
- Outline of Dominica
- Cricket in the West Indies
- Effects of Hurricane Dean in the Lesser Antilles
References
- ↑ "Dominica Ethnic groups 2001 Census". Cia.gov. Retrieved 2013-09-29.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Dominica". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2013-04-18.
- ↑ "2014 Human Development Report Summary" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2014. pp. 21–25. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ↑ "English Pronunciation Guide to the Names of People, Places, and Stuff – How to pronounce Dominica". inogolo.com. Retrieved 2010-09-09.
- ↑ http://www.theguardian.com/media/mediamonkeyblog/2014/nov/12/one-womans-fight-to-get-david-dimbleby-to-correctly-pronounce-dominica
- ↑ P.C. Evans & L. Honeychurch - Dominica: Nature Island of the Caribbean. Hansib (1989)
- ↑ "Discover Dominica: an introduction to our Caribbean island at www.dominica.dm". Dominica.dm. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ (Dominican = dOugh-mhn-KNEE-ken ) vs (Dominican Republic = dOugh-mIN-nAY-kun re-pub-lek )
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 9.8 9.9 9.10 9.11 9.12 "Background note: Dominica". U.S. Department of State (July 2008).
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ P.C. Emmer & BW Highman, (1999) General History of the Caribbean: Methodology and historiography of the Caribbean, volume 6 pp 637
- ↑ "Important Dates in Dominica's History". Lennox Honychurch Article. 1990-07-05. Retrieved 2013-09-29.
- ↑ London Society for the Abolition of Slavery throughout the British Dominions. Anti-Slavery Monthly Reporter volume 3.
- ↑ "Caribbean Islands – Regional Security Threats, 1970–81". Country-data.com. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ Stewart Bell, Bayou of Pigs, presents the story of the planned coup.
- ↑ "U.S. Department of State Background Note on Dominica". State.gov. 2013-02-07. Retrieved 2013-09-29.
- ↑ "Between Two Reunions: Boiling Lake, 1988 to 2008 | dominica.gov.dm: The Government of the Commonwealth of Dominica's Official Website". dominica.gov.dm. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ "A Photo Tour of the Calibishie Coast". Calibishiecoast.com. Retrieved 2013-09-29.
- ↑ , Stephen Durand and Bertrand Jno. Baptiste (Forestry, Wildlife and Parks Division).
- ↑ "Morne Trois Pitons National Park by World Heritage Sites". Whc.unesco.org. 7 December 1997. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ St. Lucia (2004), Saint Kitts (1999), Hispaniola (Dominican Republic [1990]/Haiti [1982]) and Cuba (multiple)
- ↑ Carlyle L. Mitchell; Edgar Gold; Dalhousie Ocean Studies Programme (1983). Fisheries development in Dominica: an assessment of the New Law of the Sea Implications and Strategies. Dalhousie Ocean Studies Programme, Dalhousie University. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-7703-0280-1. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ↑ Thompson, Keith (2010). Life in the Caribbean. New Africa Press. p. 288. ISBN 978-9987160150. p.173.
- ↑ Jonathan Katz (18 August 2007). "Hurricane Dean Gains Caribbean Strength". Forbes. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2007-05-03. Retrieved 2007-08-18.
- ↑ "Hurricane claims one life in St. Lucia and possibly two in Dominica". CBC. 17 August 2007. Archived from the original on 28 August 2007. Retrieved 2007-08-17.
- ↑ "Dominica Badly Affected". CBC. 17 August 2007. Archived from the original on 28 August 2007. Retrieved 2007-08-17.
- ↑ "(Dominica 07/08, U.S. State Dept.)".
- ↑ "(World Bank 'At A Glance')" (PDF).
- ↑ DeLollis, Barbara and Hansen, Barbara (19 January 2009). Bookings started to fall along with stock market. USA Today.
- ↑ "Ministerstwo Finansów". Mf.gov.pl. Retrieved 2013-09-29.
- ↑ "American Eagle worries". Dominica News Online. Retrieved 2013-09-29.
- ↑ "Completion ceremony of Edward Oliver Leblanc Highway Friday". Dominica News Online. Retrieved 2013-09-29.
- ↑ "The Carib Indians". Avirtualdominica.com. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ Pickford, John From Our Own Correspondent BBC Radio 4. First broadcast 31 March 2007. Dominica report 17'49" – 22'55"
- ↑ Schreier, D et al. (2010). "Lesser-known varieties of English". Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ "Creole for Beginners". Avirtualdominica.com. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ "Migration from Montserrat to Dominica". Lennoxhonychurch.com. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ "Tropical Islam". Arabwashingtonian.org. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ "Ross University School of Medicine, Dominica". Rossu.edu. Retrieved 2013-09-29.
- ↑ "Clemson University ATREC". 2012. Retrieved 2012-10-07.
- ↑ "Clemson University". Clemson.edu. 8 January 2010. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ "All Saints University School of Medicine,Dominica". Retrieved 2012-10-07.
- ↑ McKenna, Dave (2014-02-24). "Dominica's Fake Ski Team Scammed The Olympics And The Press". Deadspin. Retrieved 2014-02-25.
- ↑ "Q95 FM". Wiceqfm.com. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ "Kairi FM". Kairi FM. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
External links
- Official website of the Government of the Commonwealth of Dominica.
- Dominica – Art, Articles, Culture, History & Resources (Lennox Honeychurch)
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- Dominica entry at The World Factbook
- Dominica at UCB Libraries GovPubs.
- Dominican creole or Kwéyòl (presentation, vocabulary and conversation guide)
- Dominica at DMOZ
-
 Wikimedia Atlas of Dominica
Wikimedia Atlas of Dominica - Discover Dominica: Nature Island of the Caribbean, official government tourism website by the Discover Dominica Authority.
- Official website of the Dominica Cricket Association.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.




Countries.png)