Dolichodial
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Methyl-5-(3-oxo-1-propen-2-yl)cyclopentanecarbaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| 5951-57-5 (A or A') 864826-30-2 (B, B', C or C') 913835-24-3 (C) 60478-52-6 (A) 3671-76-9 (B) 1198-22-7 (A') | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:4685 |
| ChemSpider | 390862 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 534263 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C10H14O2 |
| Molar mass | 166.22 g·mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Dolichodial is a natural chemical compound with two aldehyde groups, which belongs to the group of iridoids.
Chemistry
It has in its five-membered ring three asymmetric carbon atoms and accordingly exists in four diastereomeric pairs of enantiomers. The pairs with a different stereochemistry of dolichodial are called anisomorphal and peruphasmal.
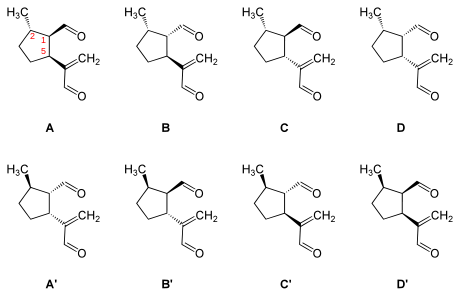
- (1R,2S,5S) = (−)-Dolichodial (A)
- (1S,2S,5S) = (+)-Anisomorphal (B)
- (1S,2S,5R) = Peruphasmal (C)
- (1S,2S,5R) = D
- (1S,2R,5R) = (+)-Dolichodial (A’)
- (1R,2R,5R) = (−)-Anisomorphal (B’)
- (1S,2R,5S) = Peruphasmal (C’)
- (1R,2R,5S) = D’
Occurrence
Dolichodial and its stereoisomers can be found in the essential oils of certain plants, and also in the defensive secretions of some insect species.[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ Tschuch G, Lindemann P, Moritz G (2008). "An unexpected mixture of substances in the defensive secretion of the Tubuliferan thrips, Callococcus fuscipennis". Journal of Chemical Ecology 34: 742–747. doi:10.1007/s10886-008-9494-3.
- ↑ Boevé JL, Braekman JC, Daloze D, Houart M, Pasteels JM (1984). "Defensive secretions of Nematinae larvae (Symphyta - Tenthredinidae)". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 40: 546–547. doi:10.1007/BF01982322.
- ↑ Dossey AT, Walse S, Edison AS (2008). "Developmental and geographical variation in the chemical defense of the walkingstick insect Anisomorpha buprestoides". Journal of Chemical Ecology 34 (5): 584–590. doi:10.1007/s10886-008-9457-8. PMID 18401661.