Dissociative substitution
Dissociative substitution describes a pathway by which compounds interchange ligands. The term is typically applied to coordination and organometallic complexes, but resembles the Sn1 mechanism in organic chemistry. This pathway can be well described by the cis effect, or the labilization of CO ligands in the cis position. The opposite pathway is associative substitution, being analogous to Sn2 pathway. Intermediate pathways exist between the pure dissociative and pure associative pathways, these are called interchange mechanisms.[1][2]
Complexes that undergo dissociative substitution are often coordinatively saturated and often have octahedral molecular geometry. The entropy of activation is characteristically positive for these reactions, which indicates that the disorder of the reacting system increases in the rate determining step.
Kinetics
Dissociative pathways are characterized by a rate determining step that involves release of a ligand from the coordination sphere of the metal undergoing substitution. The concentration of the substituting nucleophile has no influence on this rate, and an intermediate of reduced coordination number can be detected. The reaction can be described with k1, k-1 and k2, which are the rate constants of their corresponding intermediate reaction steps:
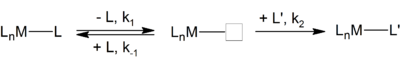
Normally the rate determining step is the dissociation of L from the complex, and [L'] does not affect the rate of reaction, leading to the simple rate equation:
However, in some cases, the back reaction (k-1) becomes important, and [L'] can exert an effect on the overall rate of reaction. The backward reaction k-1 therefore competes with the second forward reaction (k2), thus the fraction of intermediate (denoted as "Int") that can react with L' to form the product is given by the expression ![\frac{k_2[L'][Int]}{k_-1[L][Int]+k_2[L'][Int]}](../I/m/6dfa515a3d09c0368d4ce839b8613219.png) , which leads us to the overall rate equation:
, which leads us to the overall rate equation:
When [L] is small and negligible, the above complex equation reduces to the simple rate equation that depends on k1 and [LnM-L] only.
Dissociative interchange pathway
Interchange pathways apply to substitution reactions where intermediates are not observed, which is more common than pure dissociative pathways. If the reaction rate is insensitive to the nature of the attacking nucleophile, the process is called dissociative interchange, abbreviated Id. An illustrative process comes from the "anation" (reaction with an anion) of cobalt(III) complexes:[3]
- [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]3+ + SCN−
 {[Co(NH3)5(H2O)], NCS}2+
{[Co(NH3)5(H2O)], NCS}2+ - {[Co(NH3)5(H2O)], NCS}2+
 [Co(NH3)5NCS]2+ + H2O
[Co(NH3)5NCS]2+ + H2O
- [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]3+ + SCN−
Water exchange
The exchange between bulk and coordinated water is of fundamental interest as a measure of the intrinsic kinetic lability of metal ions. This rate is relevant to toxicity, catalysis, magnetic resonance imaging, and other effects. For octahedral mono- and dicationic aquo complexes, these exchange processes occur via an interchange pathway that has more or less dissociative character.[4] Rates vary by a factor of 1018, [Ir(H2O)6]3+ being the slowest and [Na(H2O)6]+ being one of the fastest for octahedral complexes. Charge has a significant influence on these rates but non-electrostatic effects are also important.
Sn1CB mechanism
The rate for the hydrolysis of cobalt(III) ammine (NH3-containing) halide complexes are deceptive, appearing to be associative but proceeding by a pathway that is dissociative in character. The hydrolysis of [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+ follows second order kinetics: the rate increases linearly with concentration of hydroxide as well as the starting complex. Studies show, however, that in the hydroxide deprotonates one NH3 ligand to give the conjugate base of the starting complex, i.e., [Co(NH3)4(NH2)Cl]+. In this monocation, the chloride spontaneously dissociates from this conjugate base of the starting complex. This pathway is called the Sn1CB mechanism.
References
- ↑ Basolo, F.; Pearson, R. G. "Mechanisms of Inorganic Reactions." John Wiley: New York: 1967. ISBN 0-471-05545-X
- ↑ R. G. Wilkins "Kinetics and Mechanism of Reactions of Transition Metal Complexes," 2nd Edition, VCH, Weinheim, 1991. ISBN 1-56081-125-0
- ↑ G. L. Miessler and D. A. Tarr “Inorganic Chemistry” 3rd Ed, Pearson/Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-035471-6.
- ↑ Helm, Lothar; Merbach, André E. (2005). "Inorganic and Bioinorganic Solvent Exchange Mechanisms". Chemical Reviews 105: 1923–1959. doi:10.1021/cr030726o.
![Rate = {k_1 [L_nM-L]}](../I/m/db8e7b2cb6237078c0ccfd6ba80d71be.png)
![Rate_{overall} = (\frac{k_2[L'][Int]}{k_{-1}[L][Int]+k_2[L'][Int]})({k_1 [L_nM-L]}) = \frac{k_1k_2[L'][L_nM-L]}{k_{-1}[L]+k_2[L']}](../I/m/9659dc8af1d871e641c85bdf6484ffa3.png)