Discrete Hartley transform
A discrete Hartley transform (DHT) is a Fourier-related transform of discrete, periodic data similar to the discrete Fourier transform (DFT), with analogous applications in signal processing and related fields. Its main distinction from the DFT is that it transforms real inputs to real outputs, with no intrinsic involvement of complex numbers. Just as the DFT is the discrete analogue of the continuous Fourier transform, the DHT is the discrete analogue of the continuous Hartley transform, introduced by R. V. L. Hartley in 1942.
Because there are fast algorithms for the DHT analogous to the fast Fourier transform (FFT), the DHT was originally proposed by R. N. Bracewell in 1983 as a more efficient computational tool in the common case where the data are purely real. It was subsequently argued, however, that specialized FFT algorithms for real inputs or outputs can ordinarily be found with slightly fewer operations than any corresponding algorithm for the DHT (see below).
Definition
Formally, the discrete Hartley transform is a linear, invertible function H : Rn -> Rn (where R denotes the set of real numbers). The N real numbers x0, ...., xN-1 are transformed into the N real numbers H0, ..., HN-1 according to the formula
![H_k = \sum_{n=0}^{N-1} x_n \left[ \cos \left( \frac{2 \pi}{N} n k \right) + \sin \left( \frac{2 \pi}{N} n k \right) \right]
\quad \quad
k = 0, \dots, N-1](../I/m/2ea9b70bbeed22e03c660293bebb0d0b.png) .
.
The combination 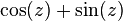
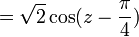 is sometimes denoted
is sometimes denoted 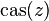 , and should be contrasted with the
, and should be contrasted with the 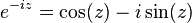 that appears in the DFT definition (where i is the imaginary unit).
that appears in the DFT definition (where i is the imaginary unit).
As with the DFT, the overall scale factor in front of the transform and the sign of the sine term are a matter of convention. Although these conventions occasionally vary between authors, they do not affect the essential properties of the transform.
Properties
The transform can be interpreted as the multiplication of the vector (x0, ...., xN-1) by an N-by-N matrix; therefore, the discrete Hartley transform is a linear operator. The matrix is invertible; the inverse transformation, which allows one to recover the xn from the Hk, is simply the DHT of Hk multiplied by 1/N. That is, the DHT is its own inverse (involutory), up to an overall scale factor.
The DHT can be used to compute the DFT, and vice versa. For real inputs xn, the DFT output Xk has a real part (Hk + HN-k)/2 and an imaginary part (HN-k - Hk)/2. Conversely, the DHT is equivalent to computing the DFT of xn multiplied by 1+i, then taking the real part of the result.
As with the DFT, a cyclic convolution z = x*y of two vectors x = (xn) and y = (yn) to produce a vector z = (zn), all of length N, becomes a simple operation after the DHT. In particular, suppose that the vectors X, Y, and Z denote the DHT of x, y, and z respectively. Then the elements of Z are given by:
where we take all of the vectors to be periodic in N (XN = X0, etcetera). Thus, just as the DFT transforms a convolution into a pointwise multiplication of complex numbers (pairs of real and imaginary parts), the DHT transforms a convolution into a simple combination of pairs of real frequency components. The inverse DHT then yields the desired vector z. In this way, a fast algorithm for the DHT (see below) yields a fast algorithm for convolution. (Note that this is slightly more expensive than the corresponding procedure for the DFT, not including the costs of the transforms below, because the pairwise operation above requires 8 real-arithmetic operations compared to the 6 of a complex multiplication. This count doesn't include the division by 2, which can be absorbed e.g. into the 1/N normalization of the inverse DHT.)
Fast algorithms
Just as for the DFT, evaluating the DHT definition directly would require O(N2) arithmetical operations (see Big O notation). There are fast algorithms similar to the FFT, however, that compute the same result in only O(N log N) operations. Nearly every FFT algorithm, from Cooley-Tukey to Prime-Factor to Winograd (Sorensen et al., 1985) to Bruun's (Bini & Bozzo, 1993), has a direct analogue for the discrete Hartley transform. (However, a few of the more exotic FFT algorithms, such as the QFT, have not yet been investigated in the context of the DHT.)
In particular, the DHT analogue of the Cooley-Tukey algorithm is commonly known as the fast Hartley transform (FHT) algorithm, and was first described by Bracewell in 1984. This FHT algorithm, at least when applied to power-of-two sizes N, is the subject of the United States patent number 4,646,256, issued in 1987 to Stanford University. Stanford placed this patent in the public domain in 1994 (Bracewell, 1995).
As mentioned above, DHT algorithms are typically slightly less efficient (in terms of the number of floating-point operations) than the corresponding DFT algorithm (FFT) specialized for real inputs (or outputs). This was first argued by Sorensen et al. (1987) and Duhamel & Vetterli (1987). The latter authors obtained what appears to be the lowest published operation count for the DHT of power-of-two sizes, employing a split-radix algorithm (similar to the split-radix FFT) that breaks a DHT of length N into a DHT of length N/2 and two real-input DFTs (not DHTs) of length N/4. In this way, they argued that a DHT of power-of-two length can be computed with, at best, 2 more additions than the corresponding number of arithmetic operations for the real-input DFT.
On present-day computers, performance is determined more by cache and CPU pipeline considerations than by strict operation counts, and a slight difference in arithmetic cost is unlikely to be significant. Since FHT and real-input FFT algorithms have similar computational structures, neither appears to have a substantial a priori speed advantage (Popovic and Sevic, 1994). As a practical matter, highly optimized real-input FFT libraries are available from many sources (e.g. from CPU vendors such as Intel), whereas highly optimized DHT libraries are less common.
On the other hand, the redundant computations in FFTs due to real inputs are more difficult to eliminate for large prime N, despite the existence of O(N log N) complex-data algorithms for such cases, because the redundancies are hidden behind intricate permutations and/or phase rotations in those algorithms. In contrast, a standard prime-size FFT algorithm, Rader's algorithm, can be directly applied to the DHT of real data for roughly a factor of two less computation than that of the equivalent complex FFT (Frigo and Johnson, 2005). On the other hand, a non-DHT-based adaptation of Rader's algorithm for real-input DFTs is also possible (Chu & Burrus, 1982).
References
- R. N. Bracewell, "Discrete Hartley transform," J. Opt. Soc. Am. 73 (12), 1832–1835 (1983).
- R. N. Bracewell, "The fast Hartley transform," Proc. IEEE 72 (8), 1010–1018 (1984).
- R. N. Bracewell, The Hartley Transform (Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 1986).
- R. N. Bracewell, "Computing with the Hartley Transform," Computers in Physics 9 (4), 373–379 (1995).
- R. V. L. Hartley, "A more symmetrical Fourier analysis applied to transmission problems," Proc. IRE 30, 144–150 (1942).
- H. V. Sorensen, D. L. Jones, C. S. Burrus, and M. T. Heideman, "On computing the discrete Hartley transform," IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Sig. Processing ASSP-33 (4), 1231–1238 (1985).
- H. V. Sorensen, D. L. Jones, M. T. Heideman, and C. S. Burrus, "Real-valued fast Fourier transform algorithms," IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Sig. Processing ASSP-35 (6), 849–863 (1987).
- Pierre Duhamel and Martin Vetterli, "Improved Fourier and Hartley transform algorithms: application to cyclic convolution of real data," IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Sig. Processing ASSP-35, 818–824 (1987).
- Mark A. O'Neill, "Faster than Fast Fourier", Byte 13(4):293-300, (1988).
- J. Hong and M. Vetterli and P. Duhamel, "Basefield transforms with the convolution property," Proc. IEEE 82 (3), 400-412 (1994).
- D. A. Bini and E. Bozzo, "Fast discrete transform by means of eigenpolynomials," Computers & Mathematics (with Applications) 26 (9), 35–52 (1993).
- Miodrag Popović and Dragutin Šević, "A new look at the comparison of the fast Hartley and Fourier transforms," IEEE Trans. Signal Processing 42 (8), 2178-2182 (1994).
- Matteo Frigo and Steven G. Johnson, "The Design and Implementation of FFTW3," Proc. IEEE 93 (2), 216–231 (2005).
- S. Chu and C. Burrus, "A prime factor FTT [sic] algorithm using distributed arithmetic," IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing 30 (2), 217–227 (1982).
![\begin{matrix}
Z_k & = & \left[ X_k \left( Y_k + Y_{N-k} \right)
+ X_{N-k} \left( Y_k - Y_{N-k} \right) \right] / 2
\\
Z_{N-k} & = & \left[ X_{N-k} \left( Y_k + Y_{N-k} \right)
- X_k \left( Y_k - Y_{N-k} \right) \right] / 2
\end{matrix}](../I/m/8567c9a91c5bf39516d85c16f398bf07.png)