Dione (moon)
|
Cassini view of Dione's leading hemisphere. The large craters on or near the terminator are (from bottom to top) Evander, Erulus, Lagus and Sagaris. The Palatine Chasmata fractures stretch across the lower right limb, and the trough Aufidus Catena extends along the bottom near the south pole. | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Giovanni Cassini |
| Discovery date | March 21, 1684 |
| Designations | |
| Saturn IV | |
| Adjectives | Dionean |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| 377396 km | |
| Eccentricity | 0.0022[1] |
| 2.736915 d[1] | |
| Inclination | 0.019° (to Saturn's equator) |
| Satellite of | Saturn |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 1128.8 × 1122.6 × 1119.2 km[2] |
Mean radius | 561.4±0.4 km[2] |
| 3964776.51 km2[3] | |
| Mass | (1.095452±0.000168)×1021 kg[4] (3.28×10−4 Earths) |
Mean density | 1.478±0.003 g/cm³[2] |
| 0.233 m/s2 | |
| 0.51 km/s | |
|
2.736915 d (synchronous) | |
| zero | |
| Albedo | 0.998±0.004 (geometric)[5] |
| Temperature | 87 K (−186°C) |
| 10.4 [6] | |
|
| |
Dione (/daɪˈoʊni/;[7] Greek: Διώνη) is a moon of Saturn discovered by Italian astronomer Giovanni Domenico Cassini in 1684.[8] It is named after the Titaness Dione of Greek mythology. It is also designated Saturn IV.
Name
Cassini named the four moons he discovered (Tethys, Dione, Rhea and Iapetus) Sidera Lodoicea ("the stars of Louis") to honor king Louis XIV. Cassini found Dione using a large aerial telescope he set up on the grounds of the Paris Observatory.[9] The satellites of Saturn were not named until 1847, when William Herschel's son John Herschel published Results of Astronomical Observations made at the Cape of Good Hope, suggesting that the names of the Titans (sisters and brothers of Cronus) be used.[10]
Orbit
Dione orbits Saturn with a semimajor axis about 2% less than that of the Moon. However, reflecting Saturn's greater mass, Dione's orbital period is one tenth that of the Moon. Dione is currently in a 1:2 mean-motion orbital resonance with moon Enceladus, completing one orbit of Saturn for every two orbits completed by Enceladus. This resonance maintains Enceladus's orbital eccentricity (0.0047), providing a source of heat for Enceladus's extensive geological activity, which shows up most dramatically in its cryovolcanic geyser-like jets.[11]
Dione has two co-orbital, or Trojan, moons, Helene and Polydeuces. They are located within Dione's Lagrangian points L4 and L5, 60 degrees ahead of and behind Dione respectively.
Physical characteristics
At 1122 km in diameter, Dione is the 15th largest moon in the Solar System, and is more massive than all known moons smaller than itself combined.[12] It is composed primarily of water ice, but as the third densest of Saturn's moons (after Enceladus and Titan, whose density is increased by gravitational compression) it must have a considerable fraction (~46%) of denser material like silicate rock in its interior.
Though somewhat smaller and denser, Dione is otherwise very similar to Rhea. They both have similar albedo features and varied terrain, and both have dissimilar leading and trailing hemispheres. Dione's leading hemisphere is heavily cratered and is uniformly bright. Its trailing hemisphere, meanwhile, contains an unusual and distinctive surface feature: a network of bright ice cliffs.
Scientists recognise Dionean geological features of the following types:
- Chasmata (chasms; long, deep, steep-sided depressions)
- Dorsa (ridges)
- Fossae (long narrow depressions)
- Craters
- Catenae (crater chains)


north and south hemispheres

trailing and leading hemispheres
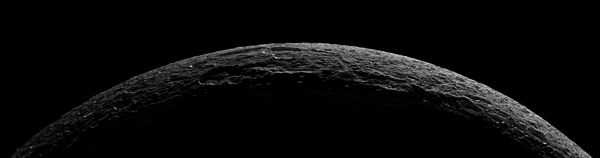
The ice cliffs (formerly 'wispy terrain')

When the Voyager space probe photographed Dione in 1980, it showed what appeared to be wispy features covering its trailing hemisphere. The origin of these features was mysterious, as all that was known was that the material has a high albedo and is thin enough that it does not obscure the surface features underneath. One hypothesis was that shortly after its formation Dione was geologically active, and some process such as ice volcanism resurfaced much of its surface, with the streaks forming from eruptions along cracks in Dione's surface that fell back to the surface as snow or ash. Later, after the internal activity and resurfacing ceased, cratering continued primarily on the leading hemisphere and wiped out the streak patterns there.
This theory was proven wrong by the Cassini probe flyby of December 13, 2004, which produced close-up images. These revealed that the 'wisps' were in fact not ice deposits at all, but rather bright ice cliffs created by tectonic fractures (chasmata); Dione has been revealed as a world riven by enormous fractures on its trailing hemisphere.
The Cassini orbiter performed a closer flyby of Dione at 500 km (310 mi) on October 11, 2005, and captured oblique images of the cliffs, showing that some of them are several hundred metres high.
Craters

Dione's icy surface includes heavily cratered terrain, moderately cratered plains, lightly cratered plains, and areas of tectonic fractures. The heavily cratered terrain has numerous craters greater than 100 kilometres (62 mi) in diameter. The plains areas tend to have craters less than 30 kilometres (19 mi) in diameter. Some of the plains are more heavily cratered than others. Much of the heavily cratered terrain is located on the trailing hemisphere, with the less cratered plains areas present on the leading hemisphere. This is the opposite of what some scientists expected; Shoemaker and Wolfe[13] proposed a cratering model for a tidally locked satellite with the highest cratering rates on the leading hemisphere and the lowest on the trailing hemisphere. This suggests that during the period of heavy bombardment, Dione was tidally locked to Saturn in the opposite orientation. Because Dione is relatively small, an impact causing a 35 kilometer crater could have spun the satellite. Since there are many craters larger than 35 kilometres (22 mi), Dione could have been repeatedly spun during its early heavy bombardment. The pattern of cratering since then and the bright albedo of the leading side suggests that Dione has remained in its current orientation for several billion years.
Like Callisto, Dione's craters lack the high-relief features seen on the Moon and Mercury; this is probably due to slumping of the weak icy crust over geologic time.
Atmosphere
On April 7, 2010, instruments on board the unmanned Cassini probe, which flew by Dione, detected a thin layer of molecular oxygen ions (O+
2) around Dione, so thin that scientists prefer to call it an "exosphere" rather than a tenuous atmosphere.[14][15] The density of molecular oxygen ions determined from the Cassini plasma spectrometer data ranges from 0.01 to 0.09 per cm3.[15][16]
The Cassini probe instruments were unable to directly detect water from the exosphere due to high background levels,[15] but it seems that highly charged particles from the planets' powerful radiation belts could split the water in the ice into hydrogen and oxygen.[14]
Exploration

Dione was first imaged by the Voyager space probes. It has also been probed three times from closer distances by the Cassini orbiter. There was one close targeted fly-by, at a distance of 500 km, on October 11, 2005; another similarly close fly-by was performed on April 7, 2010. A third fly-by was performed on December 12, 2011, at an altitude of 99 km.
In May 2013, NASA’s spacecraft Cassini provided scientists with new evidence that the Saturian moon Dione could be more active than previously predicted. It is thought that Dione could be a fossil of the activity that Cassini previously discovered spraying from Enceladus, another one of Saturn’s moons. Other bodies in the Solar System that are thought to have a subsurface ocean, like Enceladus, Titan and Jupiter’s moon Europa; are some of the most geologically active worlds in our Solar System and have been targets for geologists and scientists looking for the building blocks of extraterrestrial life. This means that if there is a subsurface ocean on Dione, it would boost the habitability potential of this moon. While Cassini has been exploring Dione since 2004, recently a magnetometer on the spacecraft detected a faint particle stream coming from the moon. Some images show evidence for a possible liquid or slushy layer of rock under the ice crust surface. Other images have shown ancient, inactive cracks in Dione that are similar to the ones seen on Enceladus, further proving the idea that a subsurface ocean would exist on Dione as it does on Enceladus. Other evidence that Dione might have a subsurface ocean comes from an observation of the mountain Janiculum Dorsa, located on Dione. The journal Icarus published a paper that examined the mountain in March 2013. This mountain ranges in height from about 1 to 2 km (0.6 to 1.2 miles). The moon’s crust seems to pucker 0.5 km (0.3 miles) under the mountain, suggesting the icy crust was warm. Dione also gets warmed by tidal heating as it gets closer to and farther from Saturn in its orbit.[17]
Gallery
-

Dione as seen by Voyager 1; the craters prominent at upper and lower left are Dido and Aeneas; to the latter's right are the troughs Latium and Larissa chasmata.
-

South polar features include huge, shallow impact basin Evander, the Palatine Chasmata by the terminator and Aufidus Catena between. The curving Padua Chasmata are at top.
-

Panorama with fractures (the Palatine Chasmata) near limb, bisecting craters Euryalus (right) and Nisus just left of center. Crater Silvius is at lower left, with Himella Fossa to its upper right.
-

Wispy terrain on Dione's trailing hemisphere. The Eurotas (top) and Palatine Chasmata run from upper right to lower left; the Padua Chasmata are near vertical at right, and the Carthage Fossae horizontal at left. The crater Cassandra and its ray system are at lower right.
-

Differently sized and oriented fractures within 60-km crater Amastrus (central peak at lower right). Larger arcuate fractures running from lower left to upper right are the Padua Chasmata, while smaller more parallel fractures from lower right to upper left may be related to the Aurunca Chasmata.
-
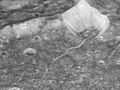
Crop of preceding image. The bowl-shaped crater at upper right has bright streaks its walls, and dark material on its floor. To its lower left can be seen an arcuate fracture postdated (covered) by a small crater's ejecta, which in turn is postdated (incised) by parallel fractures.
-
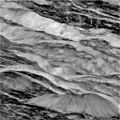
Oblique close-up of fractures
-

South polar impact basin Evander, 350 km in diameter, is by far the largest crater on Dione. The deep crater to its upper left is Sabinus.
See also
- Dione in fiction
- Former classification of planets
- The moon Helene, orbiting in Dione's leading Lagrangian point, L4
- The moon Polydeuces, orbiting in Dione's trailing Lagrangian point, L5
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://exp.arc.nasa.gov/downloads/celestia/data/solarsys.ssc Exp.arc.nasa.gov Retrieved on 05-21-07
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Roatsch, T.; Jaumann, R.; Stephan, K.; Thomas, P. C. (2009). "Cartographic Mapping of the Icy Satellites Using ISS and VIMS Data". Saturn from Cassini-Huygens. pp. 763–781. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9217-6_24. ISBN 978-1-4020-9216-9.
- ↑ Phil Davis? (April 1, 2011). "Solar System Exploration: Planets: Saturn: Moons: Dione: Facts & Figures". NASA. Retrieved March 24, 2013.
- ↑ Jacobson, R. A.; Antreasian, P. G.; Bordi, J. J.; Criddle, K. E.; Ionasescu, R.; Jones, J. B.; Mackenzie, R. A.; Meek, M. C.; Parcher, D.; Pelletier, F. J.; Owen, Jr., W. M.; Roth, D. C.; Roundhill, I. M.; Stauch, J. R. (December 2006). "The Gravity Field of the Saturnian System from Satellite Observations and Spacecraft Tracking Data". The Astronomical Journal 132 (6): 2520–2526. Bibcode:2006AJ....132.2520J. doi:10.1086/508812.
- ↑ Verbiscer, A.; French, R.; Showalter, M.; Helfenstein, P. (9 February 2007). "Enceladus: Cosmic Graffiti Artist Caught in the Act". Science 315 (5813): 815. Bibcode:2007Sci...315..815V. doi:10.1126/science.1134681. PMID 17289992. Retrieved 20 December 2011. (supporting online material, table S1)
- ↑ Observatorio ARVAL (April 15, 2007). "Classic Satellites of the Solar System". Observatorio ARVAL. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
- ↑ In USA dictionary transcription, US dict: dī·ō′·nē.
- ↑ Cassini, G. D. (1686–1692). "An Extract of the Journal Des Scavans. Of April 22 st. N. 1686. Giving an Account of Two New Satellites of Saturn, Discovered Lately by Mr. Cassini at the Royal Observatory at Paris". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London 16 (179–191): 79–85. doi:10.1098/rstl.1686.0013. JSTOR 101844.
- ↑ Fred William Price – The planet observer's handbook – page 279
- ↑ As reported by William Lassell, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 8, No. 3, pp. 42–43 (January 14, 1848)
- ↑ Porco, C. C.; Helfenstein, P.; Thomas, P. C.; Ingersoll, A. P.; Wisdom, J.; West, R.; Neukum, G.; Denk, T.; Wagner, R. (10 March 2006). "Cassini Observes the Active South Pole of Enceladus". Science 311 (5766): 1393–1401. Bibcode:2006Sci...311.1393P. doi:10.1126/science.1123013. PMID 16527964.
- ↑ See note g Triton (moon)#Notes
- ↑ Shoemaker, E. M.; and Wolfe, R. F.; Cratering time scales for the Galilean satellites, in Morrison, D., editor; Satellites of Jupiter, University of Arizona Press, Tucson (AZ) (1982), pp. 277–339
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Ghosh, Pallab (2 March 2012). "Oxygen envelops Saturn's icy moon". BBC News. Retrieved 2012-03-02.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Robert L. Tokar; Robert E. Johnson; Michelle F. Thomsen; Edward C. Sittler; Andrew J Coates et al. (10 January 2012). "Detection of Exospheric O2+ at Saturn's Moon Dione". Geophysical Research Letters. Bibcode:2012GeoRL..3903105T. doi:10.1029/2011GL050452. Retrieved 2012-03-02.
- ↑ Sven Simon; Joachim Saur; itz M. Neubauer; Alexandre Wennmacher; Michele K. Dougherty (2011). "Magnetic signatures of a tenuous atmosphere at Dione". Geophysical Research Letters 38 (L15102): 5. Bibcode:2011GeoRL..3815102S. doi:10.1029/2011GL048454. Retrieved 2012-03-02.
- ↑ Jia-Rui Cook (May 29, 2013). "Cassini Finds Hints of Activity at Saturn Moon Dione". NASA. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dione (moon). |
- Dione Profile at NASA's Solar System Exploration site
- The Planetary Society: Dione
- NASA probe video of approach to Dione
- Cassini images of Dione
- Images of Dione at JPL's Planetary Photojournal
- 3D shape model of Dione (requires WebGL)
- Dione global and polar basemaps (December 2011) from Cassini images
- Dione atlas (Sept. 2011) from Cassini images
- Dione nomenclature and Dione map with feature names from the USGS planetary nomenclature page
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



